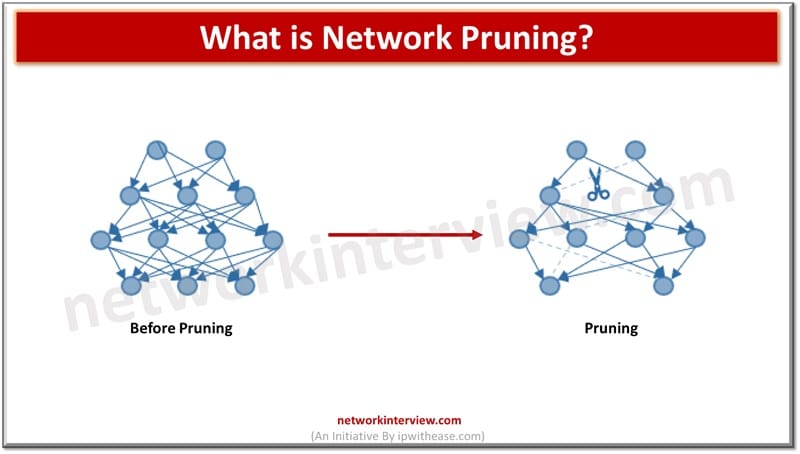
Network pruning is a process of optimizing or simplifying a network by removing unnecessary or redundant elements to improve performance, efficiency, and manageability. Here are some common network pruning techniques: Network Pruning Techniques 1. VTP Pruning VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol) …
It is not possible to 100% prevent the router attacks. However, there are possibilities of few things that could be done for preventing the occurrence of most common attacks of routers on the network and the system. Widespread attacks are …
As the world becomes increasingly digital, the need for efficient, reliable, and cost-effective networking solutions is more critical than ever. One such solution that has gained popularity in recent years is the Virtual Router. In this article, we will learn …
Objectives Routing in Fortinet FortiGate Configuration Steps of Static Routing Configuration Steps of Dynamic Routing (BGP) Policy Base Routing Routing Monitor GUI Troubleshooting Commands for Routing in FortiGate Routing in Fortinet FortiGate Firewall Routing means how a packet can …
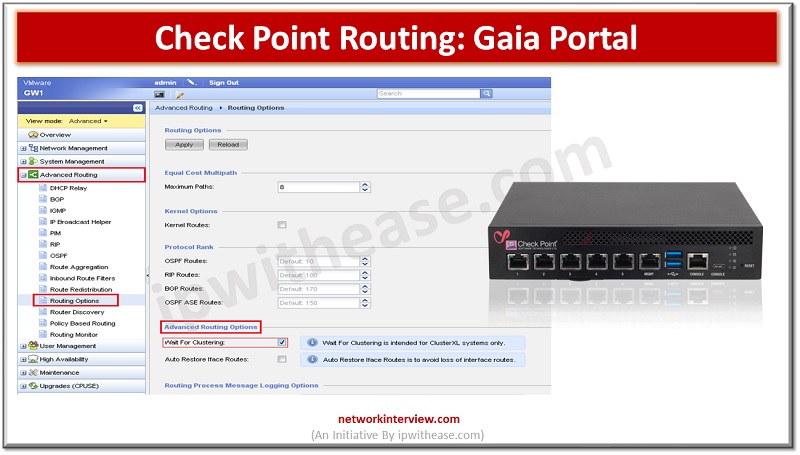
Gaia is the latest operating system for security applications developed by Check Point. It is named after Gaia, the mother of all in Greek mythology, symbolizing a well-integrated system comprising various components to ensure optimal performance. Gaia OS is designed …
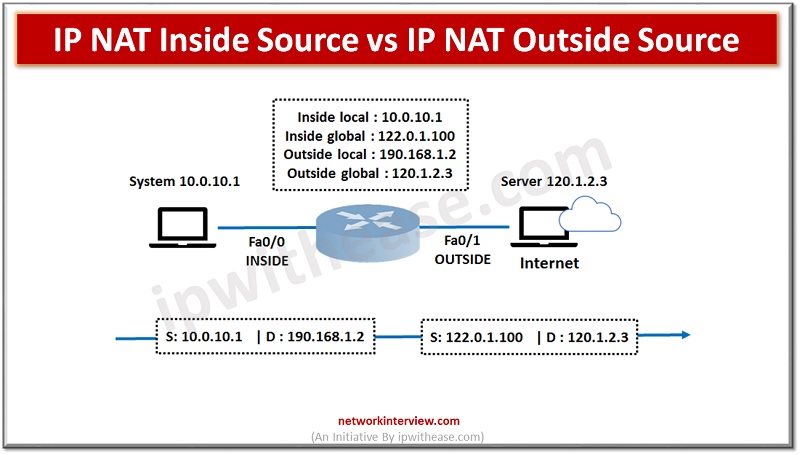
In order to access the Internet, we need one public IP address; however, we can use Private IP address in private networks. The Network address translation (NAT) allows multiple devices to access the Internet with a single public IP address. …
Low power wide area network (LPWAN) technologies offer a cost and power efficient wireless solution options for leveraging existing networks, global reach and strong built in security. They empowered and strengthened business case for IoT solutions as they help network …
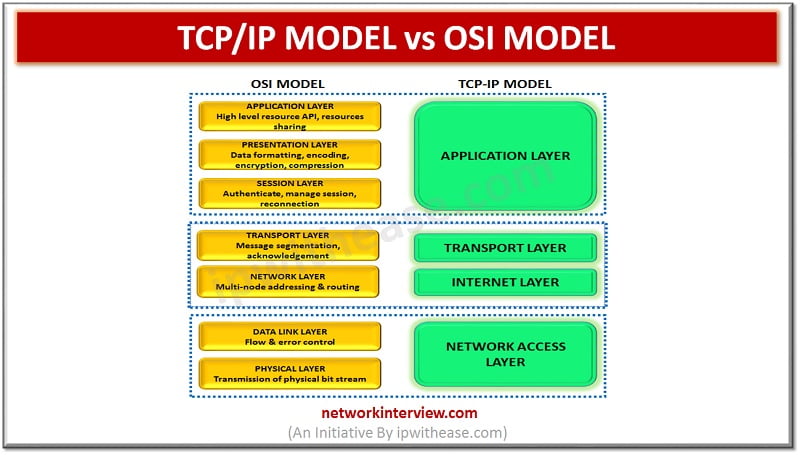
Whenever networks are implemented and different devices try to communicate over the network. Some of the other reference models are being referred to which is a standard specification or framework to provide standardization on how implementation, connectivity, communication will happen. …
Introduction The Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is a network communication protocol that interconnects the network devices into the internet. It provides a communication between the source and the destination. It specifies how data packets should be broken, addressed, routed, …
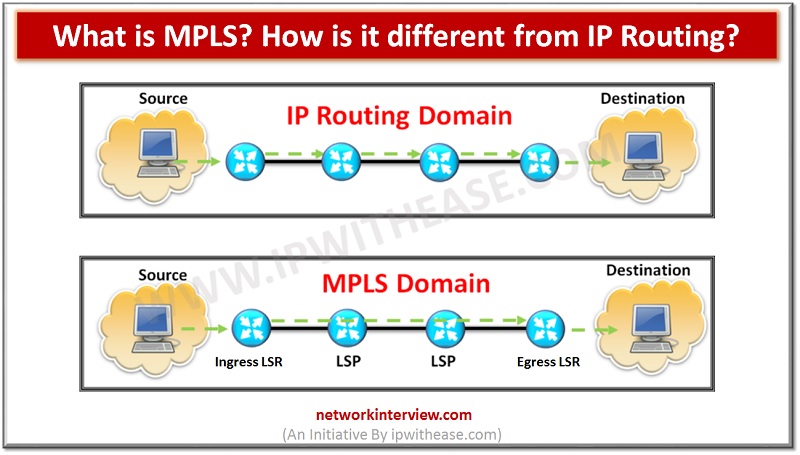
Introduction to MPLS MPLS i.e. Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS). It is a technique that is used for the routing of network packets. It is called a Multiprotocol as it supports multiple protocols like Internet Protocol (IP), Asynchronous Transport Mode …
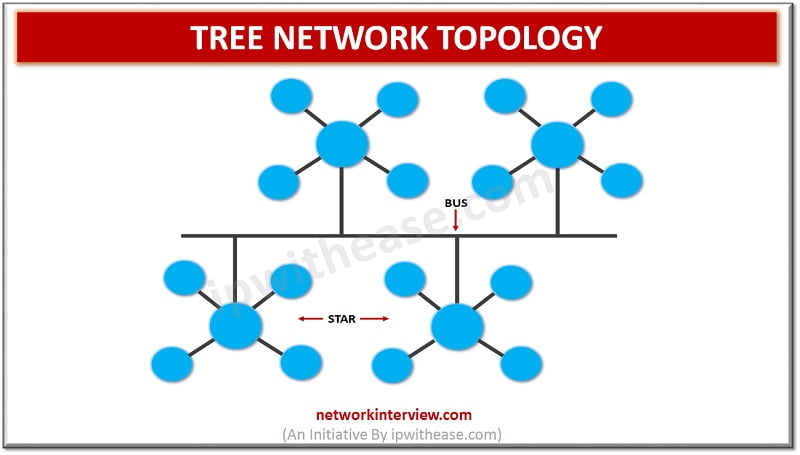
Introduction to Tree Network Topology Every network is a collection of nodes and links for their interconnection. The arrangement of these nodes and links in a specific manner is known as topology. It would define how devices within will connect …
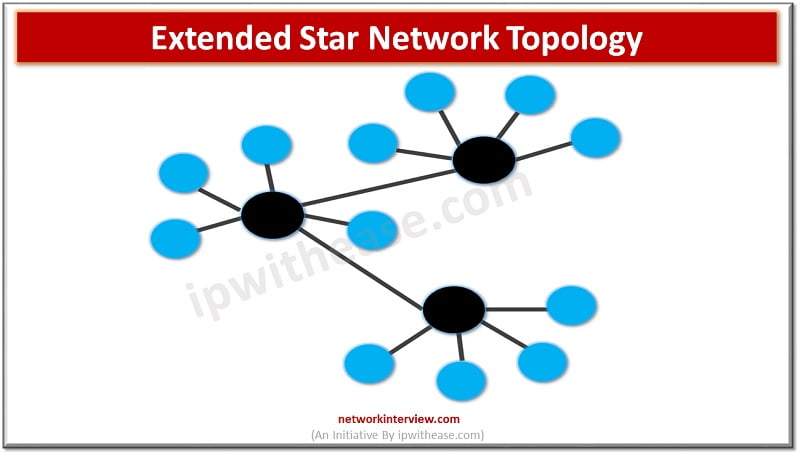
A network topology determines how systems, printers, routers , switches and other devices will be connected over the network. It describes the layout of wires, devices, and routes. Which topology to choose for your organization depends on a set of …
Networks are the backbone of any IT infrastructure. Networks can be set up in different topologies; its choice depends on performance requirements, number of systems, location, cost factors etc. sometimes a mix of topologies is deployed to attain flexibility, fault …
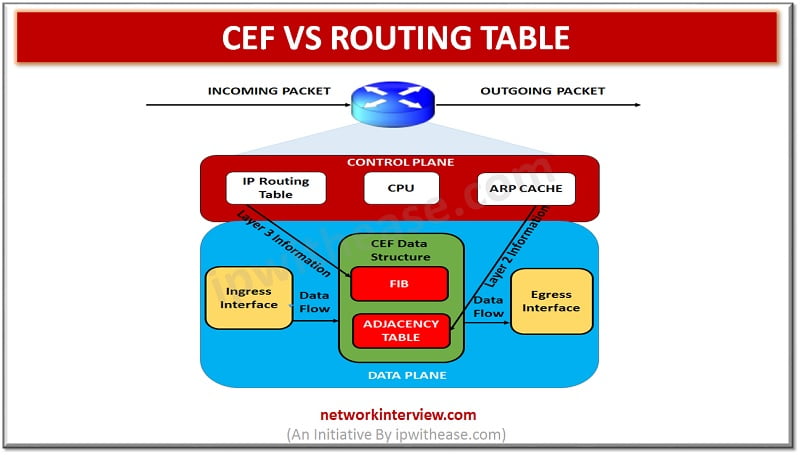
CEF vs Routing Table RIB (or routing table) and CEF (Cisco Express Forwarding) are two different tables which are used in routing across IP networking platform. Both have common information but perform two distinctly different purposes. CEF technology is new in …
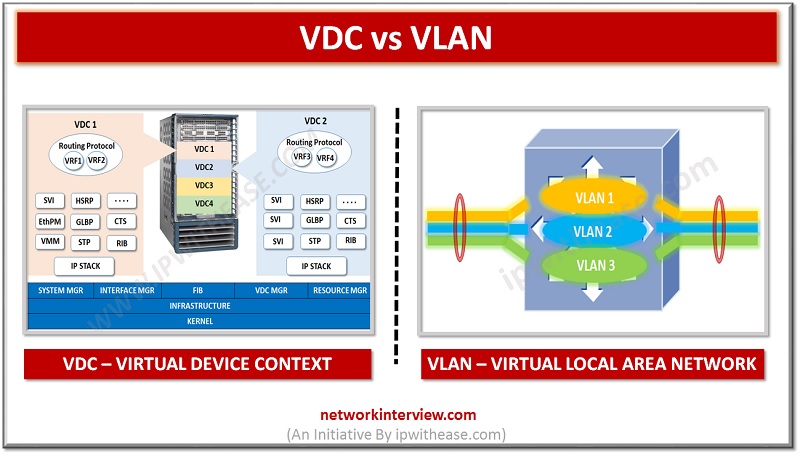
Introduction : VDC vs VLAN Virtualization in IT systems has helped Network estate immensely. 2 technologies which have helped networking across various segments are VLAN and VDC. While VLAN is short for Virtual Local Area Network, VDC means Virtual device …
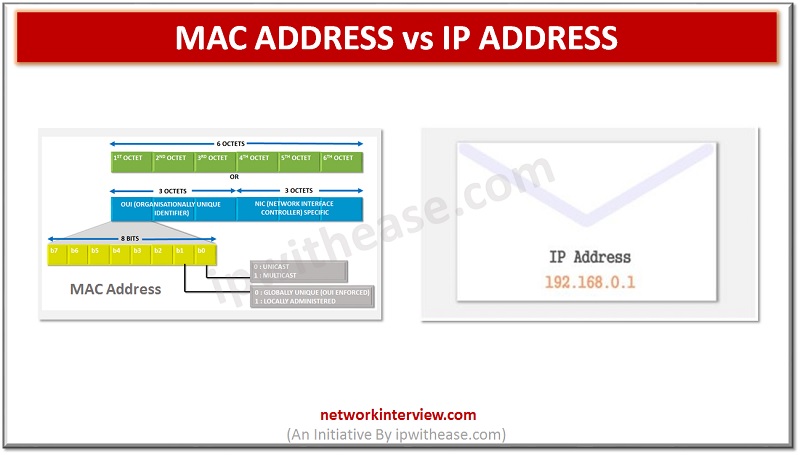
Introduction: MAC Address vs IP Address All devices part of a network can connect and communicate with each other. However, when we try to put logic around the communication between these devices, the key query that always arises in our …
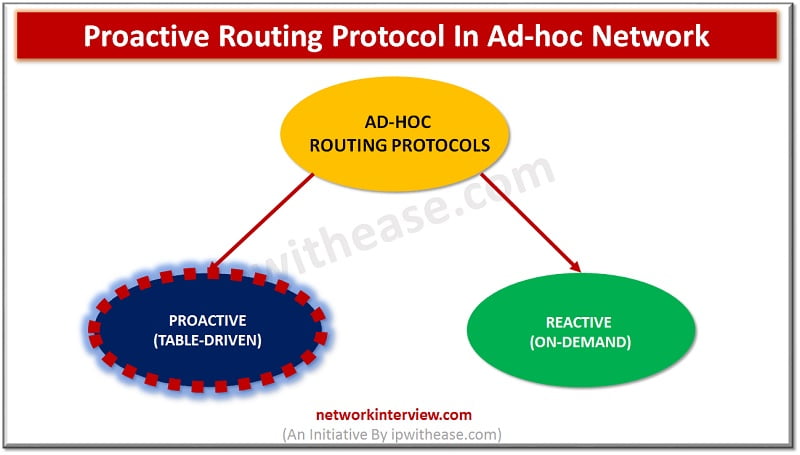
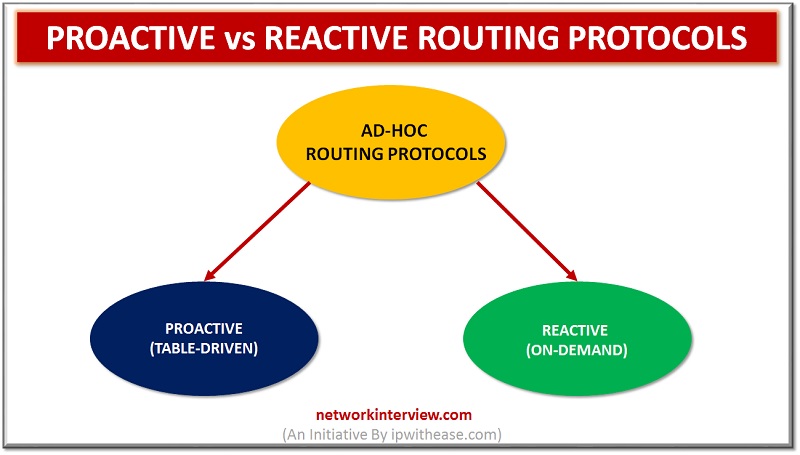
Proactive Routing Protocol Introduction Ad-hoc network is a collection of mobile nodes forming an instant network without a fixed topology. In such a network each node acts as both router and host simultaneously and can join or move out in …
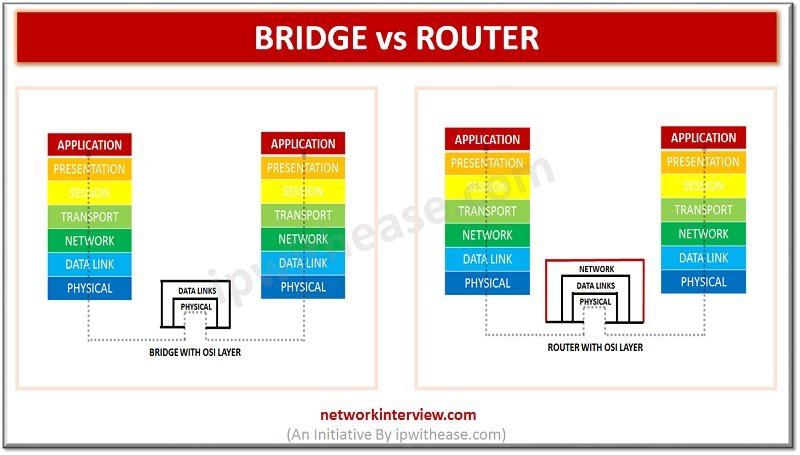
Network Bridge and Router are 2 key networking devices used in connecting segments or networks. While Bridge has been taken by switch, Router still remains the cornerstone of any WAN Network and has been expanding its role with introduction of …
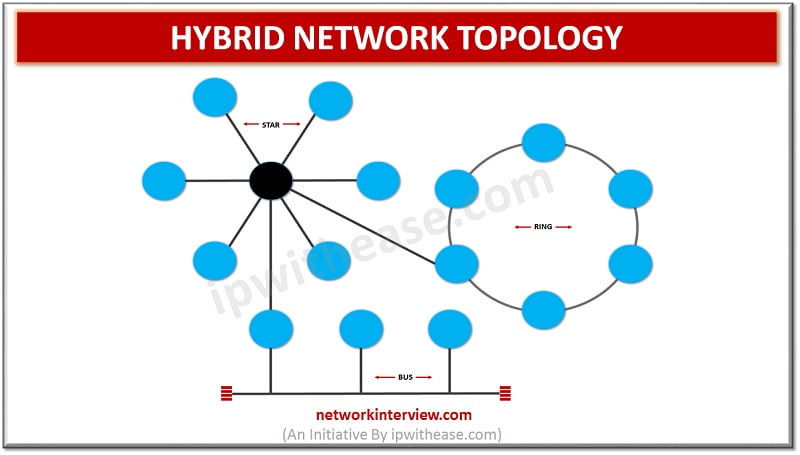
Different types of network topologies exist and based on multiple factors organizations can choose the best topology to suit them. Performance, Fault tolerance , redundancy, ease of error detection and correction, installation and configuration , scalability requirements, management and costs …
Proactive vs Reactive Routing Protocols Routing protocols are the routes that help to learn dynamic routes. These protocols are organized on routers in regards with exchanging the information related with routing. Using the routing protocols in your network has many …
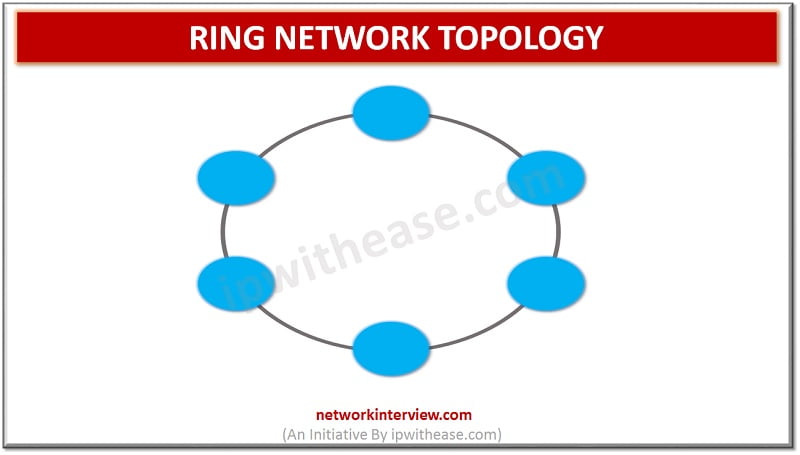
Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. Ring topology is a type of network topology in which each network device is connected to two other devices, forward and backward forming a single continuous path for signal transmission. …
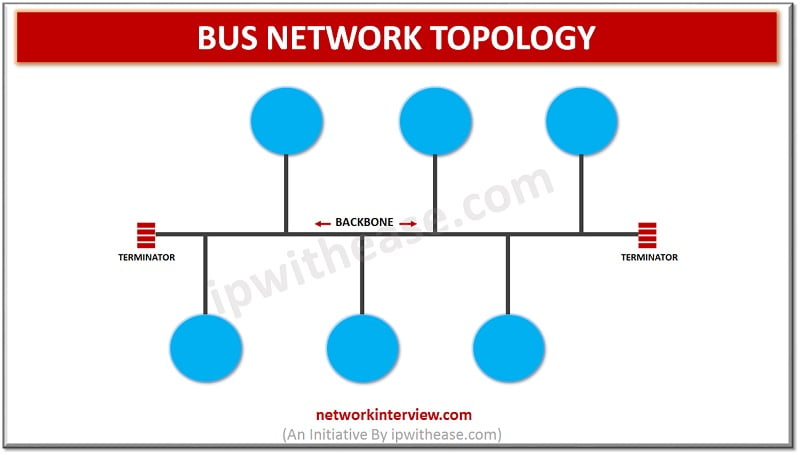
Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. BUS Network Topology Bus topology is a type of network topology where each node is connected to a single cable known as the backbone. Though there is no limit …
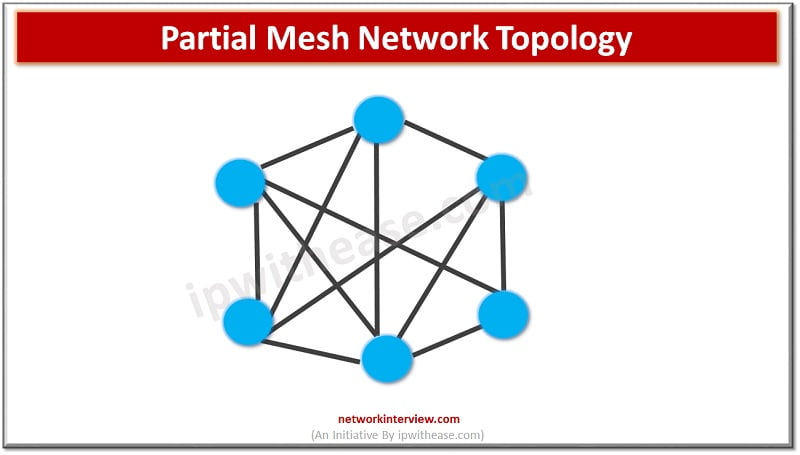
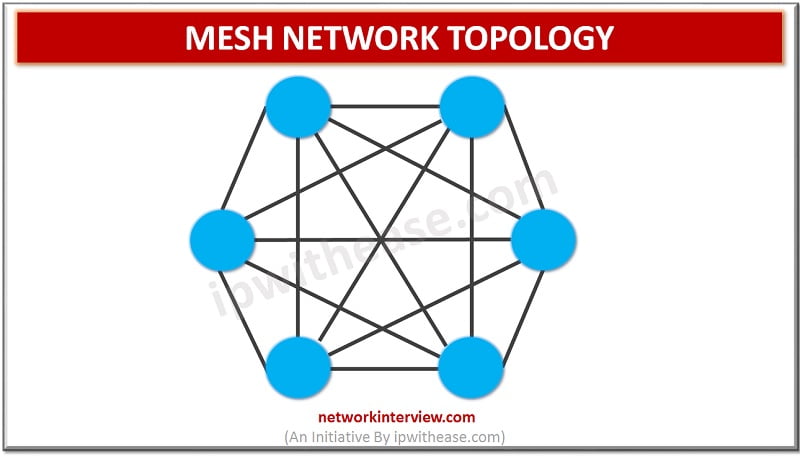
MESH NETWORK TOPOLOGY Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. Mesh network topology is a type of site-to-site WAN topology in which each network device is connected to every other device through a dedicated link …
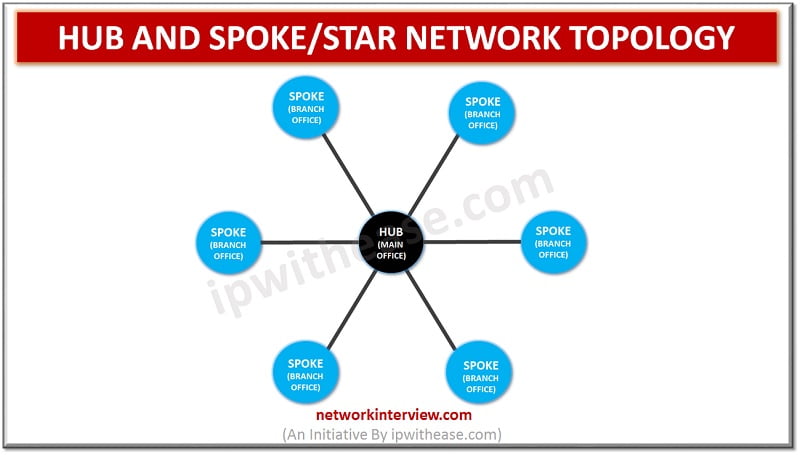
HUB AND SPOKE/ STAR NETWORK TOPOLOGY Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. Hub and spoke or star topology is a site-to-site Wide Area Network (WAN) topology. In this type of topology, we have a central device, called …
Skills required for Network Engineer In any IT setup, Network Engineer is the key and fundamental resource responsible for setup of network infrastructure on which all the services like Security, voice, wireless, messaging and Internet are made accessible. A network …
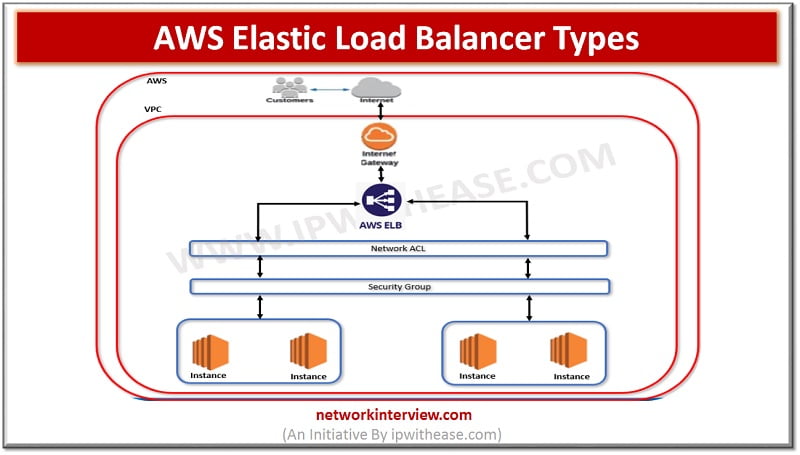
Elastic Load balancer types in AWS Application availability, continuity of service, greater performance of the application – These are the things we would always require from a platform owner while designing the network and answer to this in AWS is …
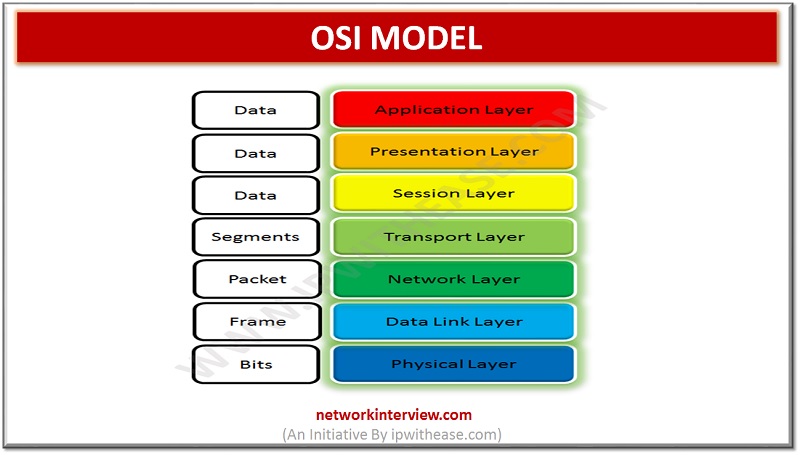
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model It refers to a logical and conceptual network model that defines the network communication protocol that is used by open systems to communicates and connect with other network systems. This network model has seven subcomponents. …
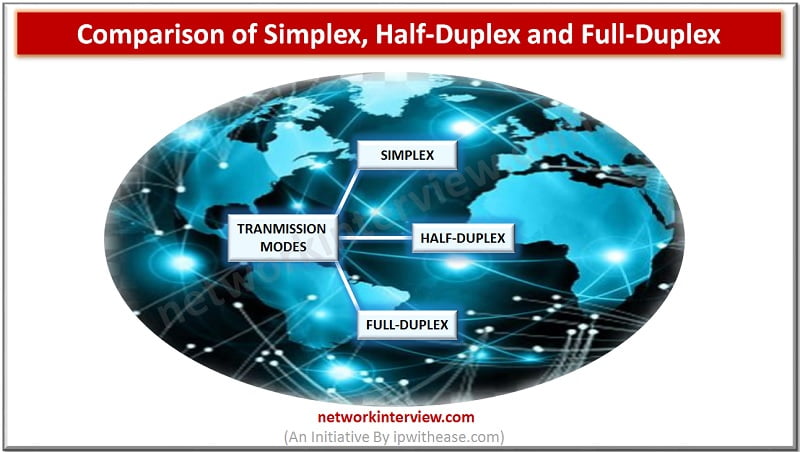
The transferring of data between two devices is known as Transmission Mode or Communication Mode in Computer Networks. So the Transmission mode basically defines the direction of flow of signal between the connected devices. TYPES OF TRANSMISSION MODES The different …
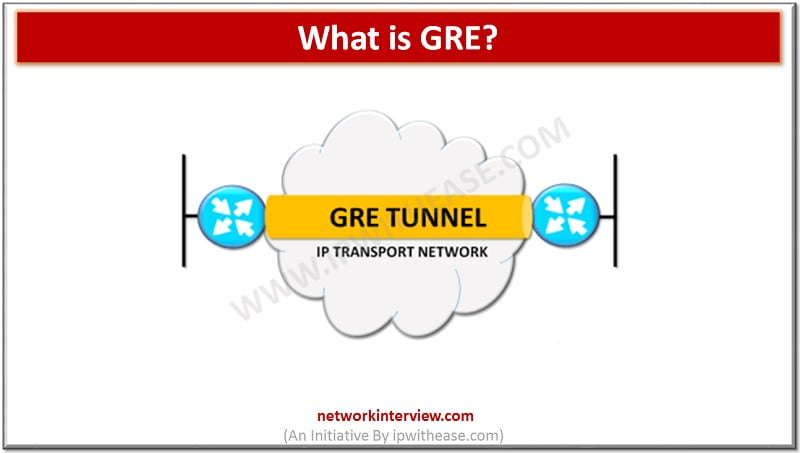
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is the IP encapsulation protocol that is used to transport IP packets over the network. Generic routing encapsulation was initially developed by Cisco, but later become industry standard (RFC 1701, RFC 2784, RFC 2890). GRE can …
Address mask is also known as Subnet mask. IP address has the 2 main components among which the one is “Network Address” and other one is “Host address”. The subnet mask or the address mask separate network address with the …
NIC or Network Interface Card is a circuit board or expansion card or a chip, that enables a computer to connect to a network, be it a home network, or the Internet using an Ethernet cable. Initially, network controllers were implemented as expansion …
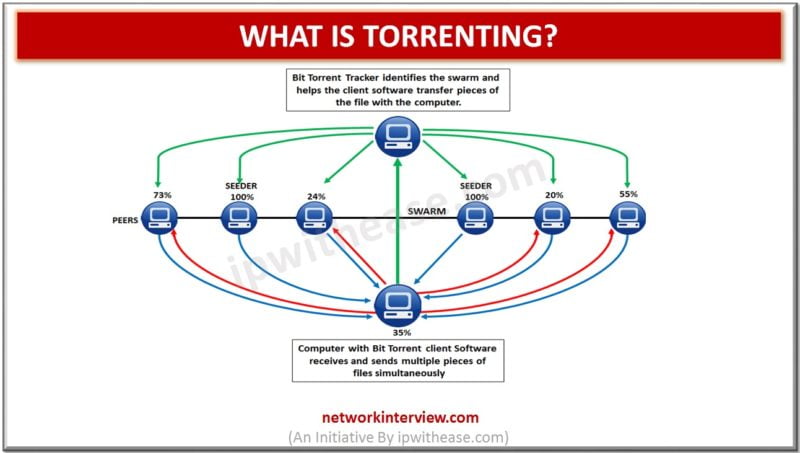
Introduction to Torrenting Torrenting is a P2P (peer-to-peer) file sharing technology used to share files efficiently. This technology relies on a community of decentralized users for file sharing rather than being dependent on traditional single website or source for downloading. …
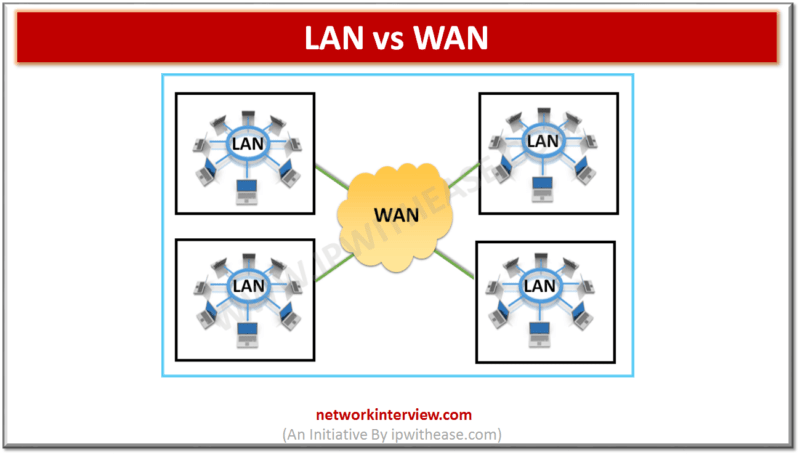
Before understanding LAN vs WAN, let’s know the two terms. LAN is abbreviation for Local Area Network. LAN is a network covering a small geographic area and connecting various end devices like computers and printers. LAN may be limited to a home, office, …
In today’s world, a stable internet connection is essential for work, entertainment, and staying connected. But when setting up your home network, you might wonder: What’s the difference between a modem and a router? Many people confuse these two devices, …
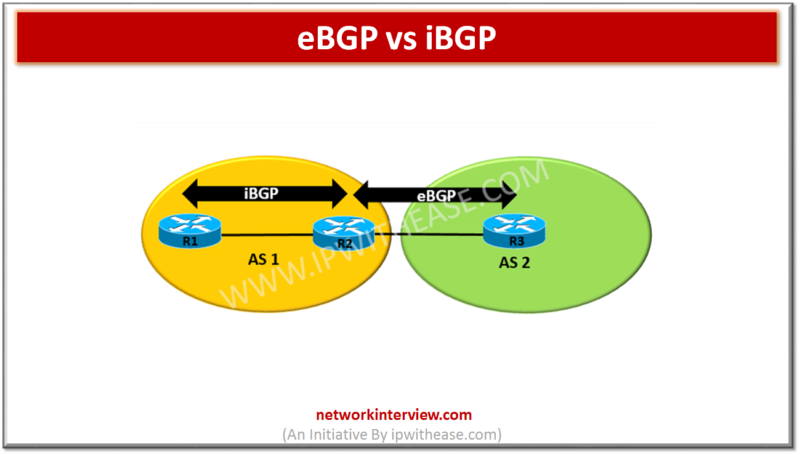
Before discussing eBGP vs iBGP, let’s understand the two protocols briefly. What is eBGP It is abbreviation for External Border Gateway Protocol and is one of the flavors of BGP protocol. eBGP Routing protocol is used between BGP speaking neighbors …
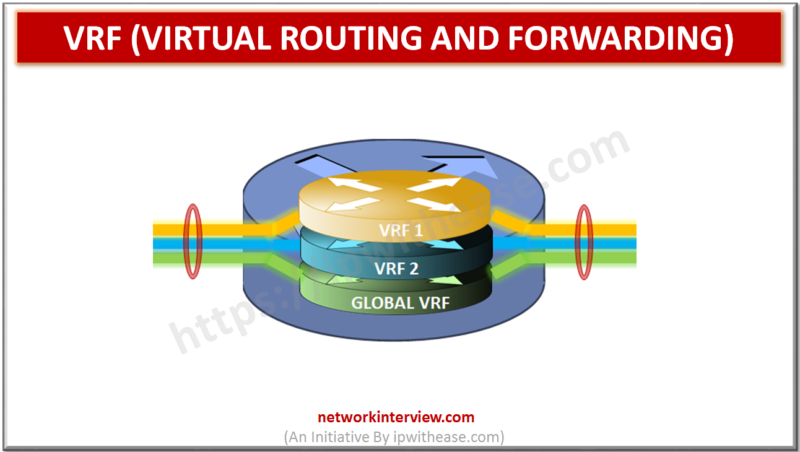
VRF (Virtual routing and forwarding) is a technology that allows multiple instances of a routing table to co-exist within the same router at the same time. Overlapping IP addresses can be used without conflicting with each other as the routing …
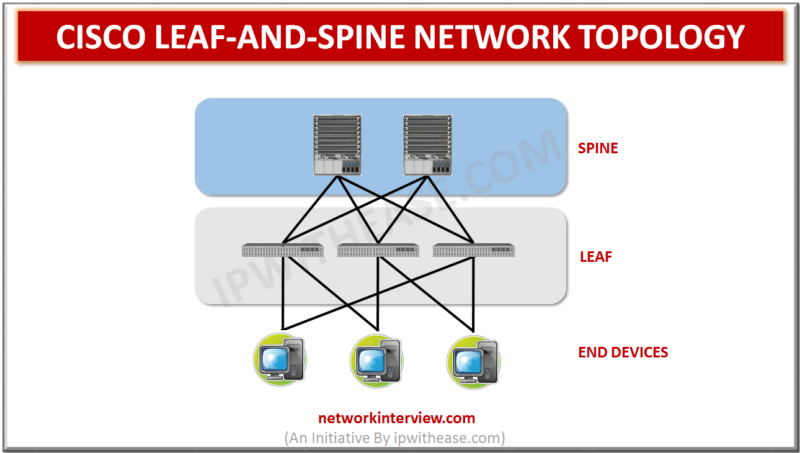
Network Topology Leaf-and-spine is a two-layer network topology composed of leaf switches and spine switches. We are all aware of the Cisco’s 3-tier network topology with the following 3 layers – 1)Access Layer 2)Aggregation/Distribution Layer 3)Core layer The Access Layer …
Introduction to LAN Computer Networks can be divided into various types depending upon their size and usability. The size of a network can be assessed by its geographical distribution. It can be as small as a room with a few …
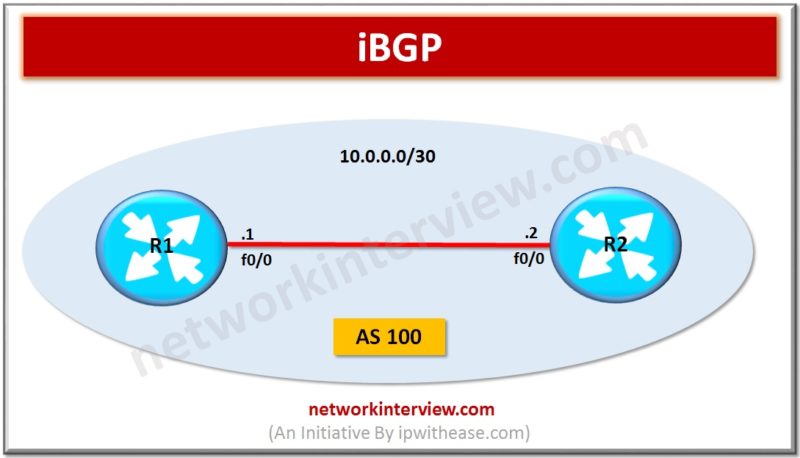
Introduction iBGP is abbreviation for Internal Border Gateway Protocol. iBGP protocol is used between the routers within the same autonomous system (AS). iBGP speaking Routers need to form full mesh to maintain full routing information. Full mesh (iBGP neighborship with all Routers …
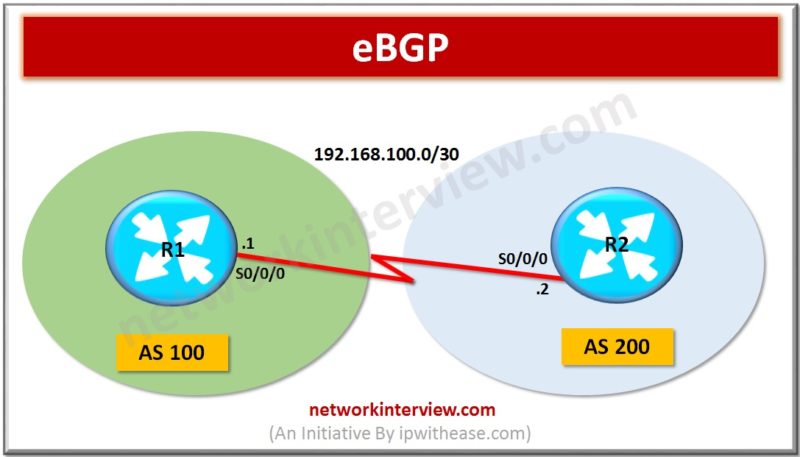
Introduction eBGP is abbreviation for External Border Gateway Protocol and is one of the flavors of BGP protocol. eBGP Routing protocol is used between BGP speaking neighbors which belong to different ASNs (Autonomous System Numbers). eBGP functions as the protocol for …
Network Switching Network Switching works at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of OSI model. Switching is a process of receiving frame from one incoming port (ingress) and then forwarding it to as desired destination (egress). Types of Network Switching Switching …