CMD vs BAT The importance of the batch file can be easily understood by the power users and system administrators. But, generally most of the regular computer users are unaware of these files. This indicates that people are not utilizing …
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) is Microsoft’s technological invention intended for taking care of Windows’ varied operational environments. Microsoft has offered set of specifications in the form of WMI for strengthening applications and devices management in the network. The information regarding …
Difference between LDAP and AD The framework of IT infrastructure of most of the organizations has Active Directory as a significant part. This significance is the reason why attackers have the Active Directory at the top of their target. In …
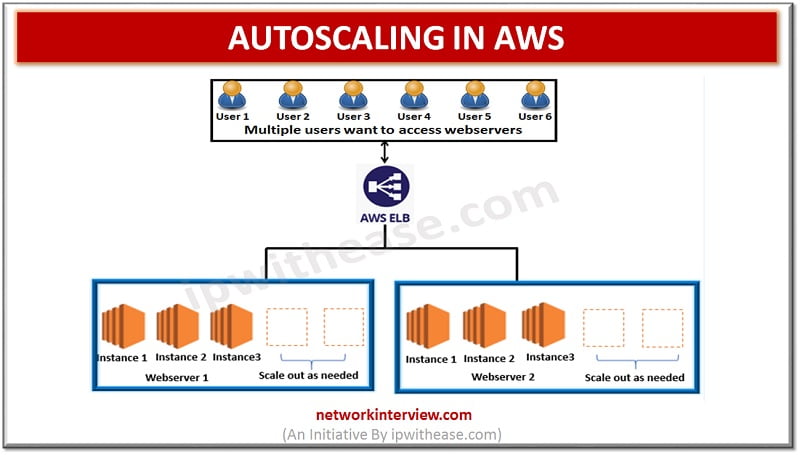
Autoscaling in AWS Better Fault tolerance/ better availability/ better cost management/ better scalability – These must be considered while hosting a website/ App on the server to allow smooth functioning of the website/ App. Website owners have a key requirement …
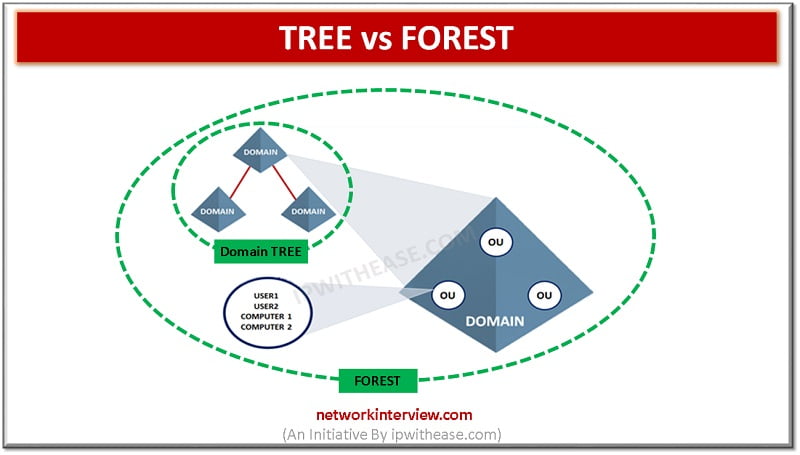
Introduction to Tree and Forest An Activity Directory is a product of Microsoft that runs on Server of Windows. It allows managing, accessing, and permissions for the network resources. The data is stored as an object in this directory and …
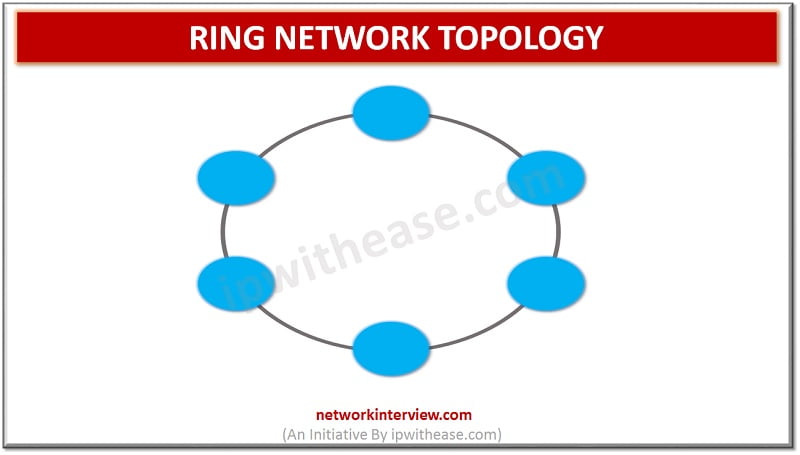
Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. Ring topology is a type of network topology in which each network device is connected to two other devices, forward and backward forming a single continuous path for signal transmission. …
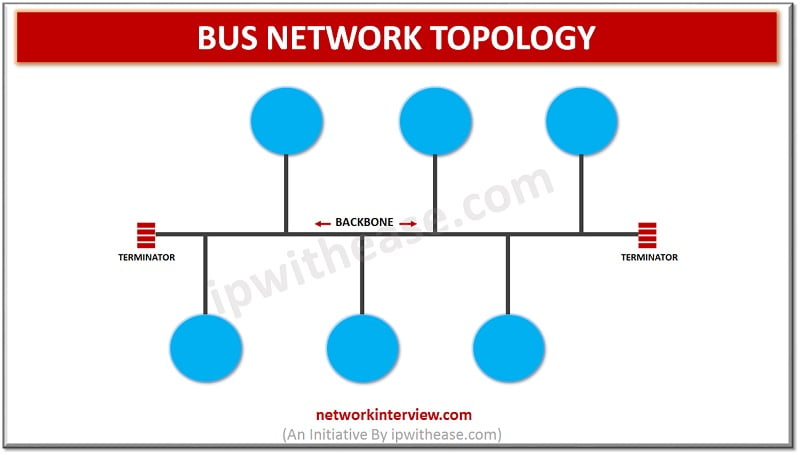
Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. BUS Network Topology Bus topology is a type of network topology where each node is connected to a single cable known as the backbone. Though there is no limit …
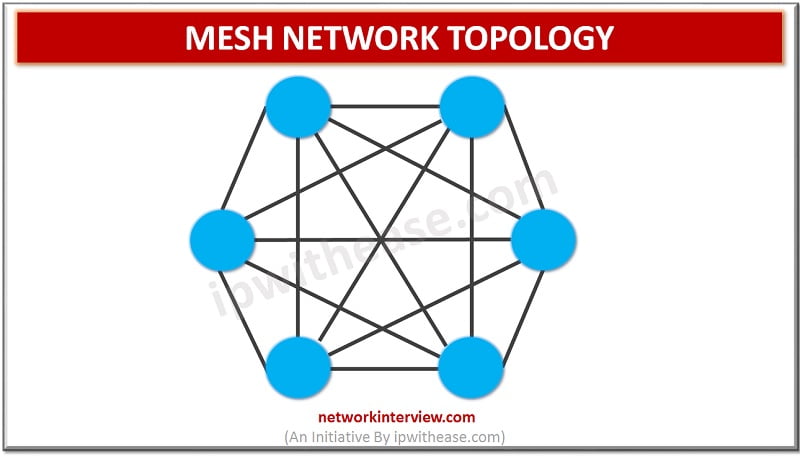
MESH NETWORK TOPOLOGY Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. Mesh network topology is a type of site-to-site WAN topology in which each network device is connected to every other device through a dedicated link …
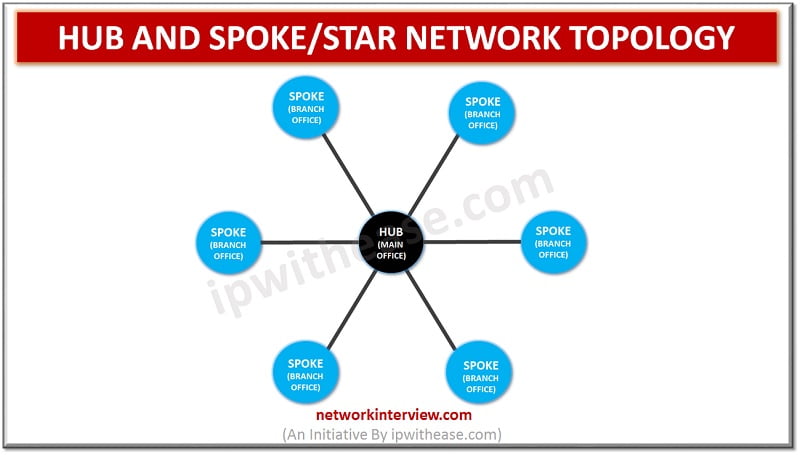
HUB AND SPOKE/ STAR NETWORK TOPOLOGY Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network. Hub and spoke or star topology is a site-to-site Wide Area Network (WAN) topology. In this type of topology, we have a central device, called …
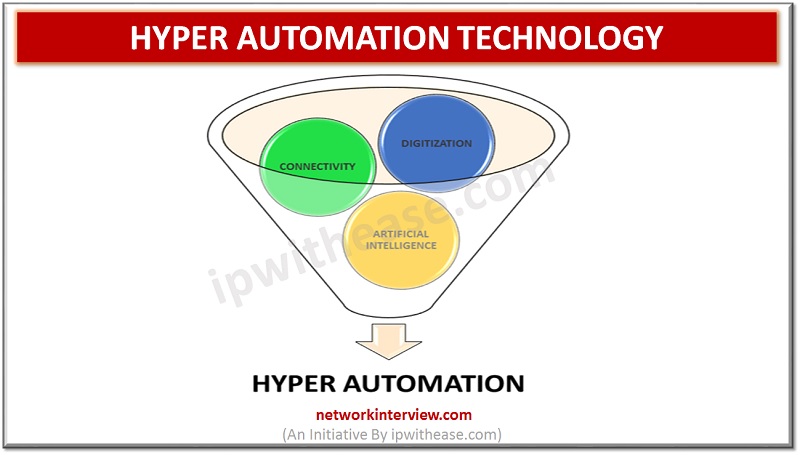
If we were speaking a decade back and one of us comes up with an idea of amalgamating machine learning and artificial intelligence to attain perfection in conventional automation industry, then most of us would have laughed at it as …
Skills required for Network Engineer In any IT setup, Network Engineer is the key and fundamental resource responsible for setup of network infrastructure on which all the services like Security, voice, wireless, messaging and Internet are made accessible. A network …
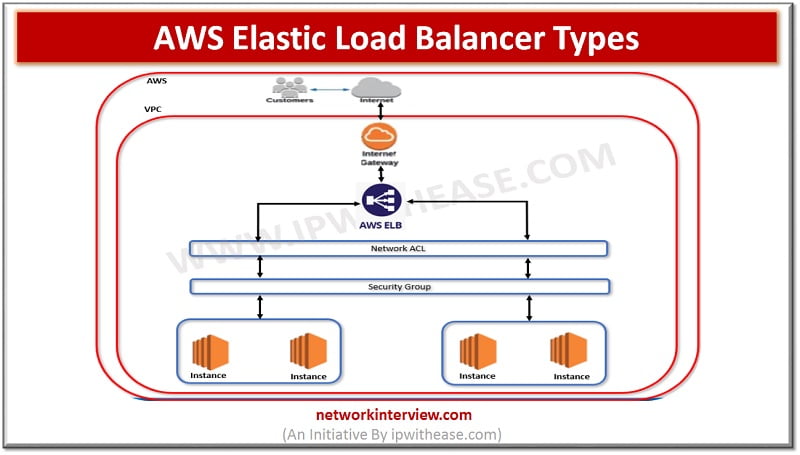
Elastic Load balancer types in AWS Application availability, continuity of service, greater performance of the application – These are the things we would always require from a platform owner while designing the network and answer to this in AWS is …
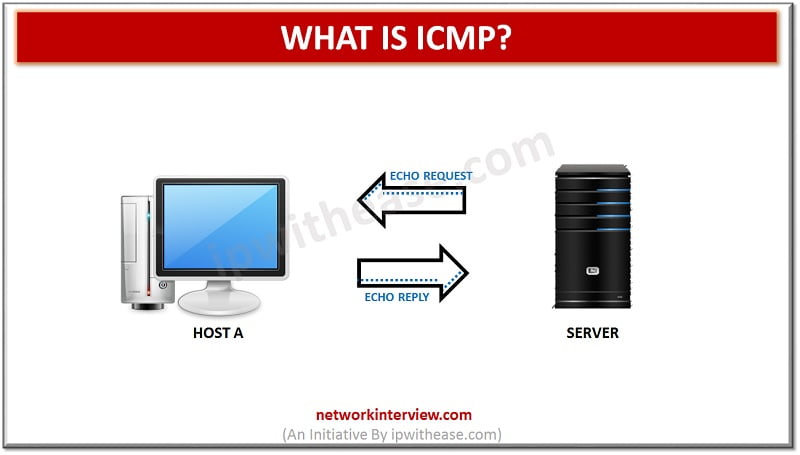
ICMP stands for the Internet Control Message Protocol. It is a primary protocol in the Internet Protocol Suite. It is used by network devices to relay an error message and management queries. It helps to reroute the message to its …
Cloud Migration Cloud computing is a technology that involves delivering different hosting services over the Internet using various hardware and software. Cloud computing allows we can access any files from anywhere in the world. It creates files remotely accessible. It …
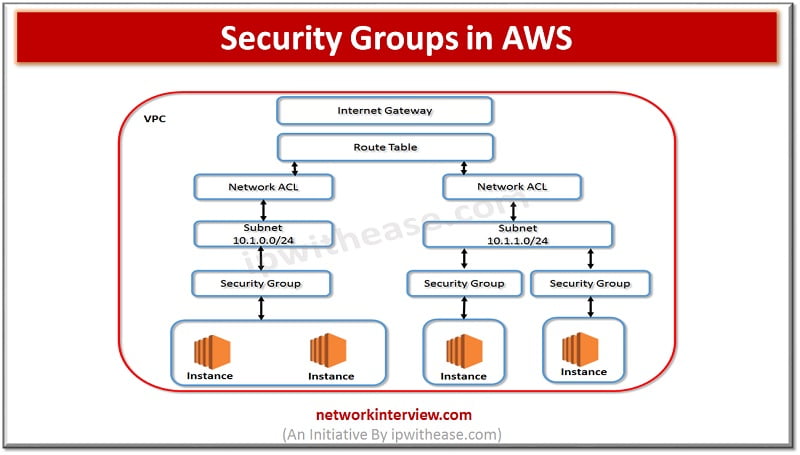
Security Groups in AWS I am sure that while working on Security groups, we do ponder about Firewalls and Rules i.e. allowing or denying traffic based on hardware or software firewalls. In case of AWS security groups are very similar …
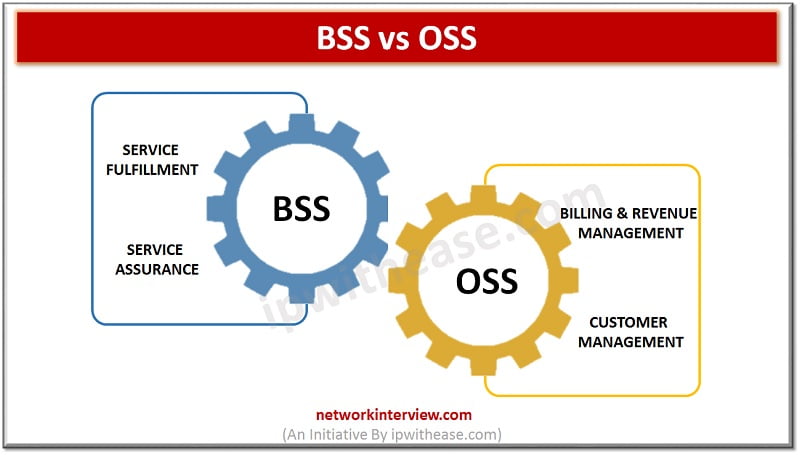
BSS vs OSS Two terms which in limelight especially in Telecom Operation world are BSS and OSS. BSS stands for Business Support Systems while OSS refers to Operations Support Systems. By their names, both the terms may seem complementary, however …
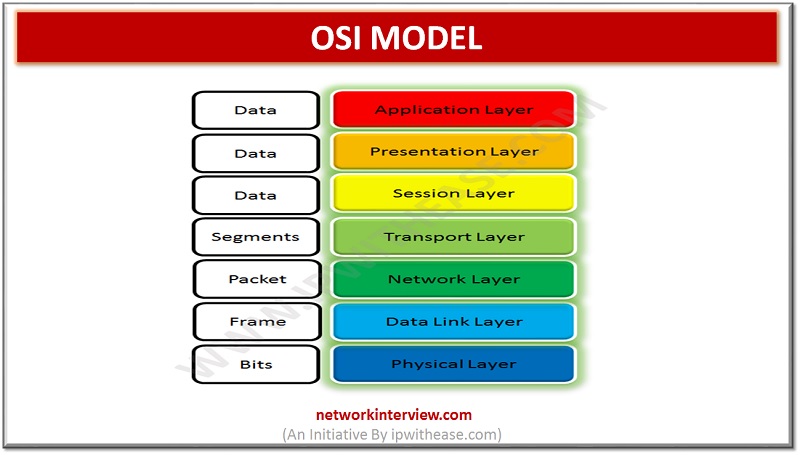
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model It refers to a logical and conceptual network model that defines the network communication protocol that is used by open systems to communicates and connect with other network systems. This network model has seven subcomponents. …
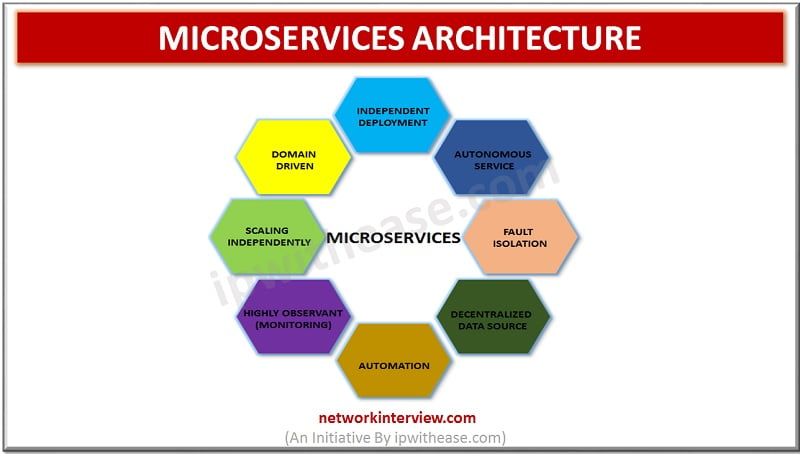
Microservices is the current hot topic being discussed in the software development circles. People are using microservices architecture for their businesses instead of using monolithic approach. The traditional methods of building enterprise application i.e. monolithic approach creates many problems when …
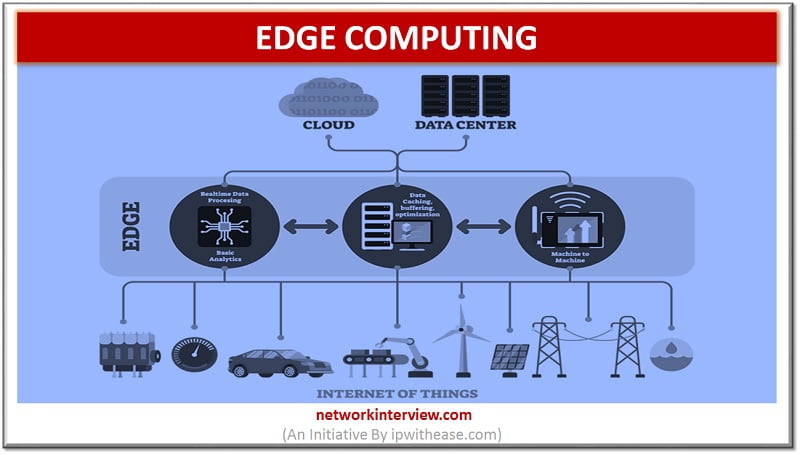
What is Edge computing? The networking philosophy known as Edge computing is aimed at taking computing close to data source so as to reduce the bandwidth and latency use. In other words, running fewer procedures in cloud is termed as …
High Level Language vs Low Level Language Computer programming languages are broadly categorized into 2 types namely – High Level Language and Low Level Language. Abbreviation for High Level Language is HLL and Low Level Language is LLL. The former …
Linux vs Windows Windows has been quite a popular choice for home and office users. It’s been the widely used Operating system used in desktops, laptops and personal computers. Linux is an open-source operating system which is based on UNIX …
The DVD technology was emerged in 1997. It revolutionized the movie industry and brought digital sound and video into homes all over the world. The Blu-ray Discs (BD) were introduced in 2006. With their high storage capacity, these discs can hold and …
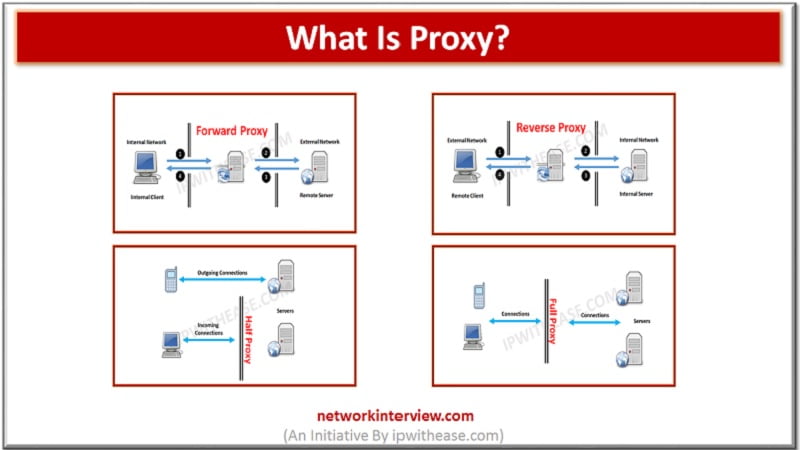
Proxies (often called intermediaries in the SOA world) are hardware or software solutions that sit between the client and the server and do something to requests and sometimes responses. The most often heard use of the term proxy is in …
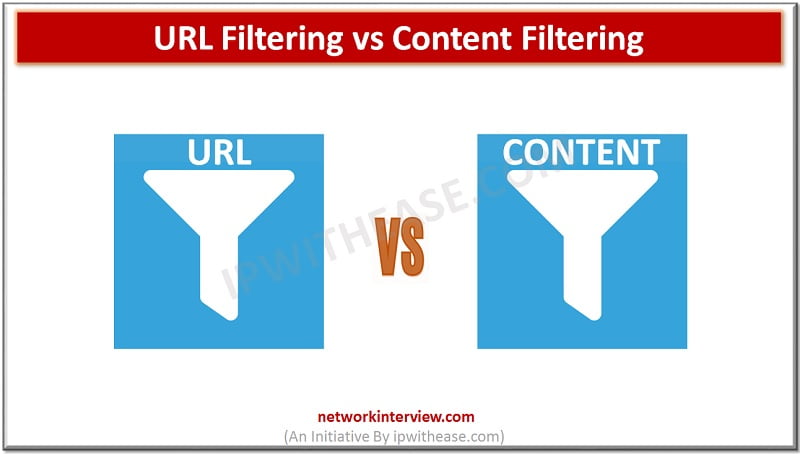
Introduction to URL Filtering Make sure that you type the name of your favorite social networking site in the web browser and it displays a message “The policy of your organization does not allow navigation to this website” and does …
Botnet(BOT) Users began to know this malicious program from the year 2000 when a teenager from Canada launched a series of denial of service attacks against very popular websites. The young man, whose nickname was Mafiaboy, attacked Yahoo, ETrade, Dell, …
For some years now, the word cyber security has become a standard among companies. Information Technology is already a common tool in business and to keep systems safe, security measures are lacking to help us avoid being exposed to large …
SSH PROTOCOL SSH (or Secure Shell) is a protocol that facilitates secure communications between two systems using a client/server architecture and allows users to connect to a host remotely. Unlike other remote communication protocols such as FTP or Telnet, SSH …
Equifax, Avanti or Down Jones, are sadly famous companies in 2017 for having suffered significant leaks of sensitive information. Thus, those who committed to ensuring the confidentiality of their customers, are faced with the obvious failure of wrong Data Loss …
NAT (NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION) In computer networking, Network Address Translation (NAT) is the process of modifying IP address information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device. Network Address Translation (NAT) allows security administrators to overcome …
In this post, we shall discuss about comparison of URL filtering and Content filtering. Both the terms are interrelated, however differ in flavor of how they protect and assets they protect. SO, lets understand them in more detail – URL …
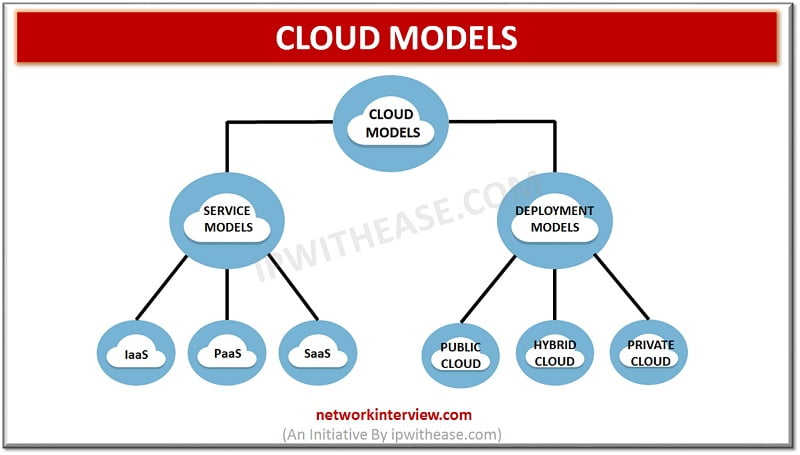
Cloud computing and related services have been one of the most talked about keyword in the IT world. In this article, we will discuss around cloud computing models. Primarily, Cloud Models are of 2 types – Service Model’s Deployment models. …
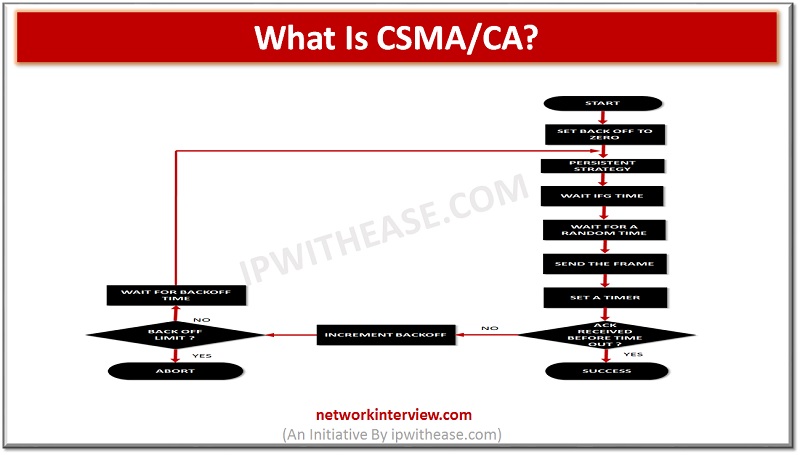
CSMA/CA stands for Carrier Multiple Access/Collision avoidance. It is a technique using which the chances of collision are decreased. In most of the cases, the collision is avoided. It is used to transmit data using 802.11 standards. The similar technique …
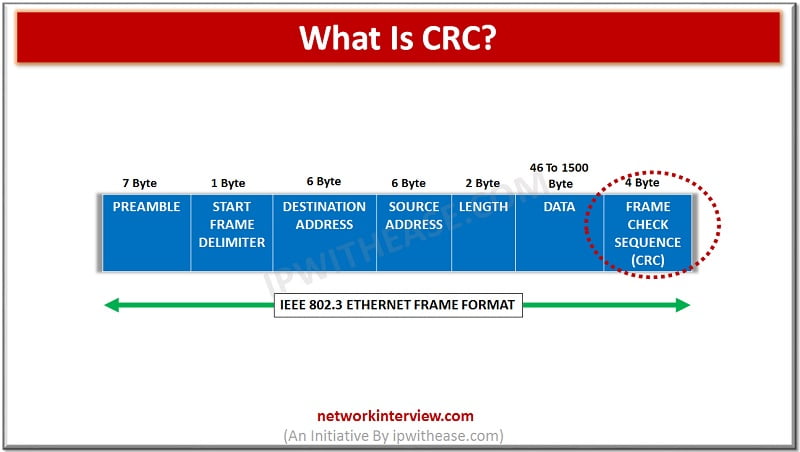
To detect the error in any type of digital data, CRC is used. CRC stands for Cyclic Redundancy check. It is a type of has function that will automatically detect even the minor changes in the raw data of the …
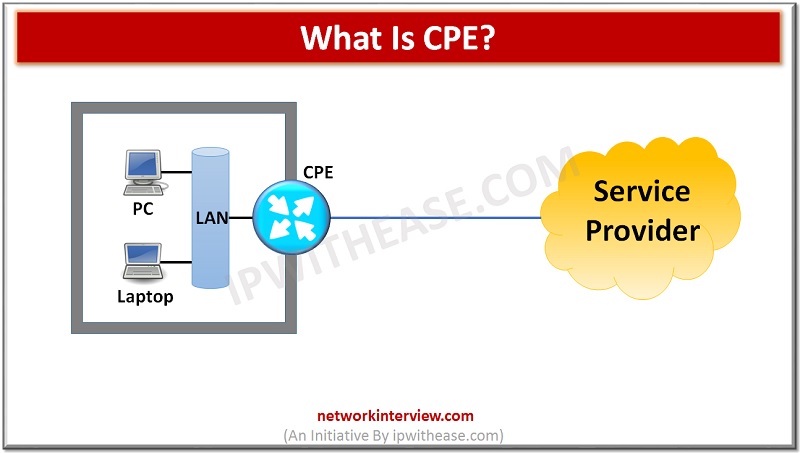
CPE stands for Customer Premises Equipment. When it comes to telecommunication terminology, any of the telecommunication equipment that is either sold or rented/leased by the official carrier to any of their customers and that equipment is installed in customer’s location …
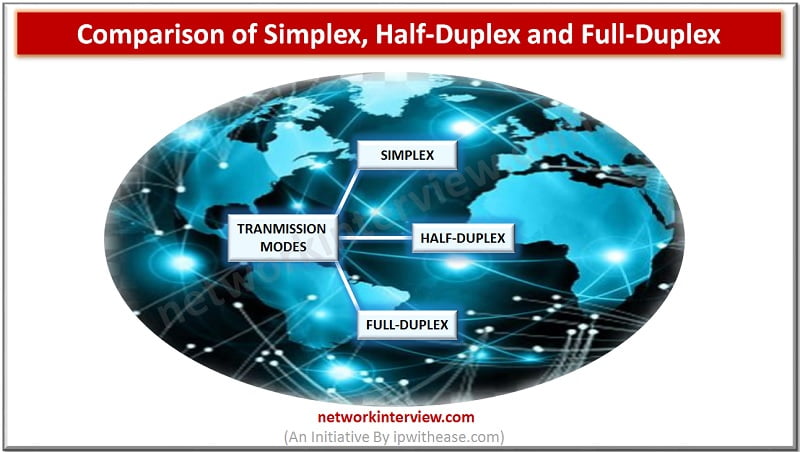
The transferring of data between two devices is known as Transmission Mode or Communication Mode in Computer Networks. So the Transmission mode basically defines the direction of flow of signal between the connected devices. TYPES OF TRANSMISSION MODES The different …
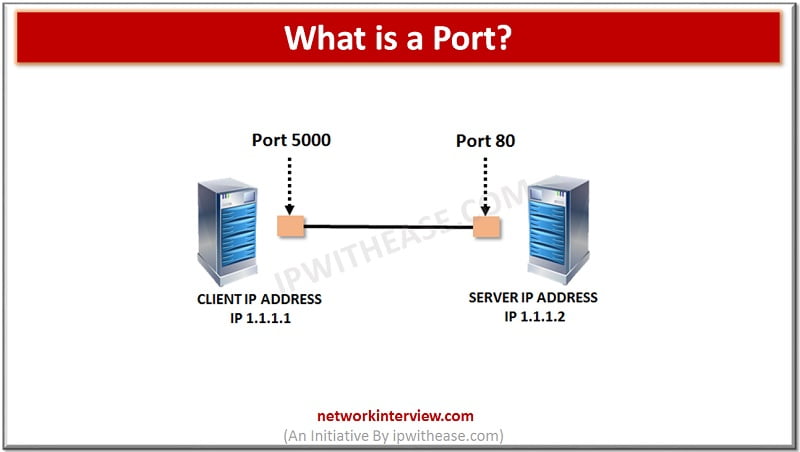
In networking, a port is defined as the endpoint of any data communication. This applies to a kind of data transfer whether they are using a wireless connection or these re physical connections. In the same way, when it comes …
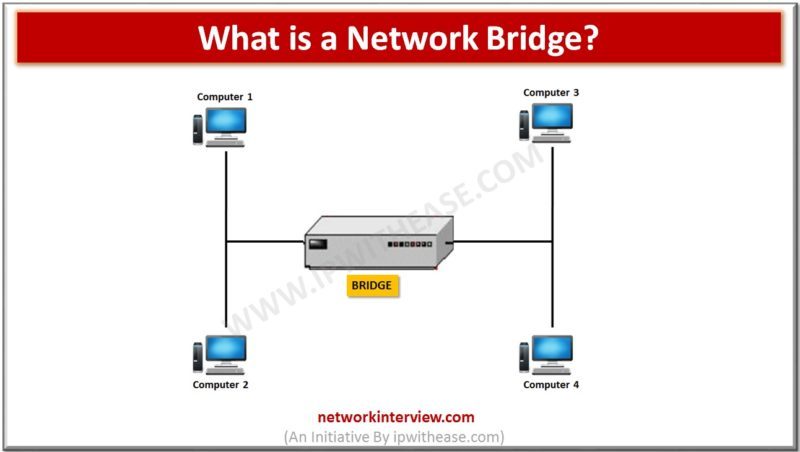
A network bridge is a device that can create a single network from different and multiple network segments. In other words, it can connect the two or more networks. The function used here is called Network Bridging. There is a …
VLAN is the abbreviation of a Virtual local area network. In the real sense, it is a category of network devices, servers, and workstations that are visible on the same Local area network (LAN) in spite of their geographical positioning. …
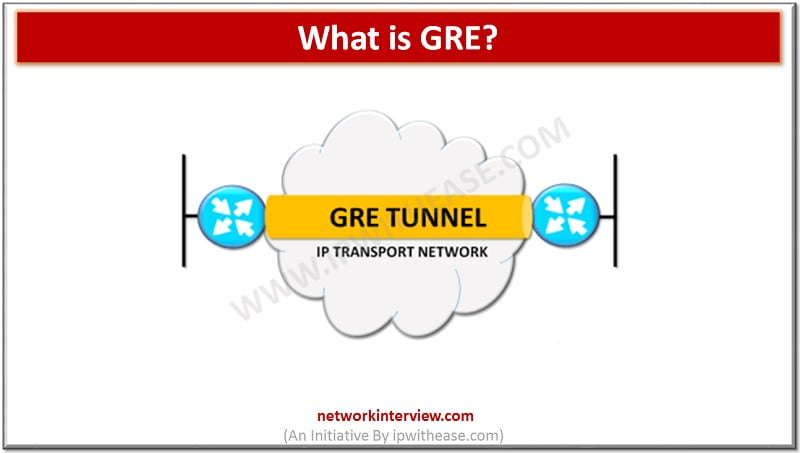
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) is the IP encapsulation protocol that is used to transport IP packets over the network. Generic routing encapsulation was initially developed by Cisco, but later become industry standard (RFC 1701, RFC 2784, RFC 2890). GRE can …
Firewalls are computer software programs that hinder illegitimate access to or from a personal network. They are used to improve security in a system of computers connected to a similar interface, including the Internet and LAN. Thus, they are a …
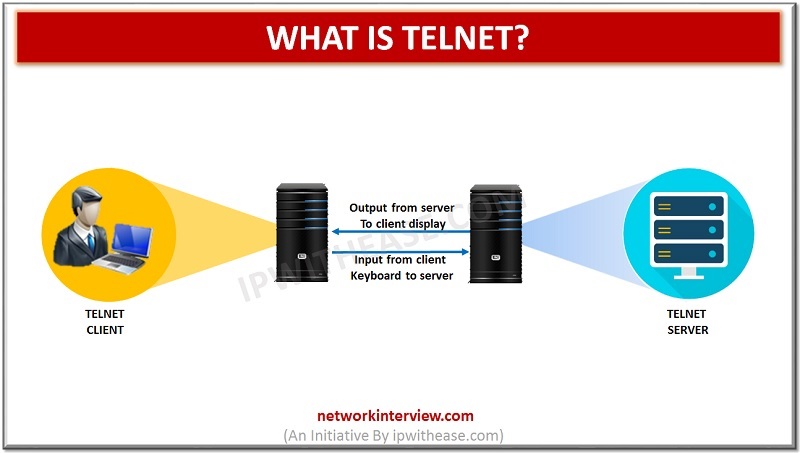
Telnet is one of the protocols that is used both on the internet and LAN (Local Area Network). In other words, Telnet is a protocol that is used in order to get access to the remote computer or the terminals. …
Address mask is also known as Subnet mask. IP address has the 2 main components among which the one is “Network Address” and other one is “Host address”. The subnet mask or the address mask separate network address with the …
URL Stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is a web address that is used to locate any of the data stored on the cloud using the internet. URL is a type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). Use Cases of URL …
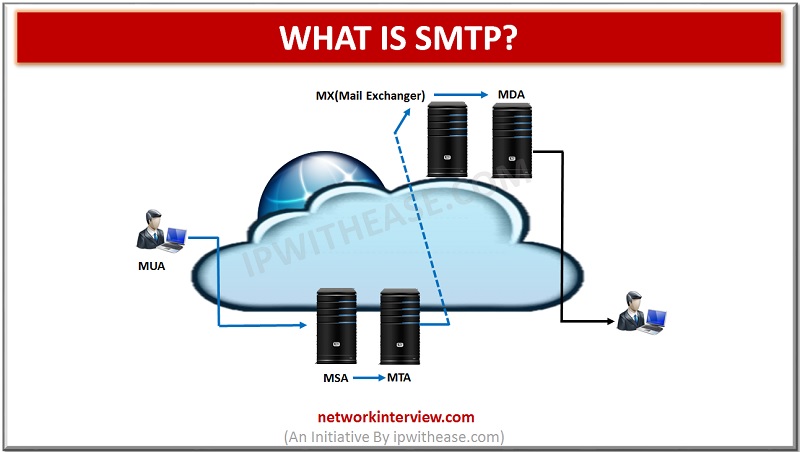
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. It is the protocol used for the email service that is used on the internet. It works on the TCP/IP protocol. Using the SMTP, we can either send or receive email messages from …
Introduction to NTP NTP is the protocol used in reference to time. NTP is responsible for synchronizing the time of the computer with the time of the network. NTP stands for Network Time Protocol. It is one of the oldest …