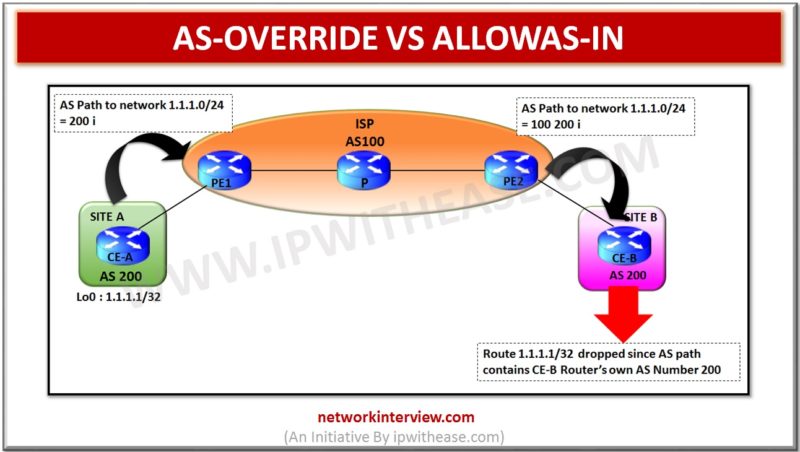
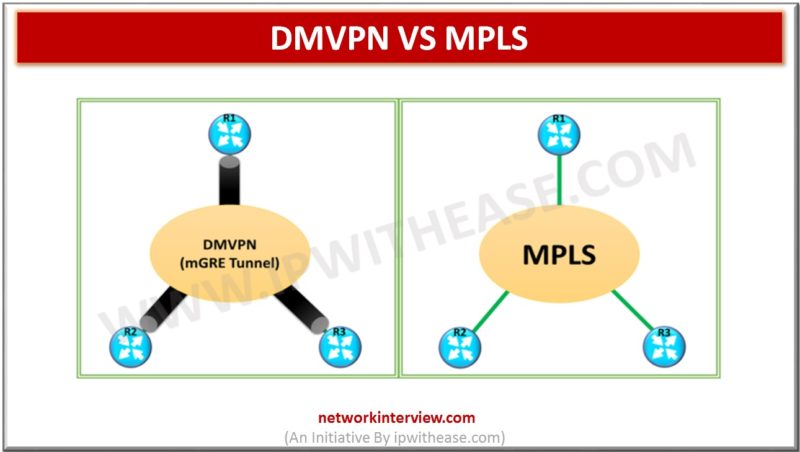
Below table describes the difference between AS-OVERRIDE and ALLOWAS-IN; PARAMETER AS-OVERRIDE ALLOWAS-IN Overview Used by PE to modify the AS Path so that prefix is not dropped based on BGP default behaviour to disallow its own AS number in the …
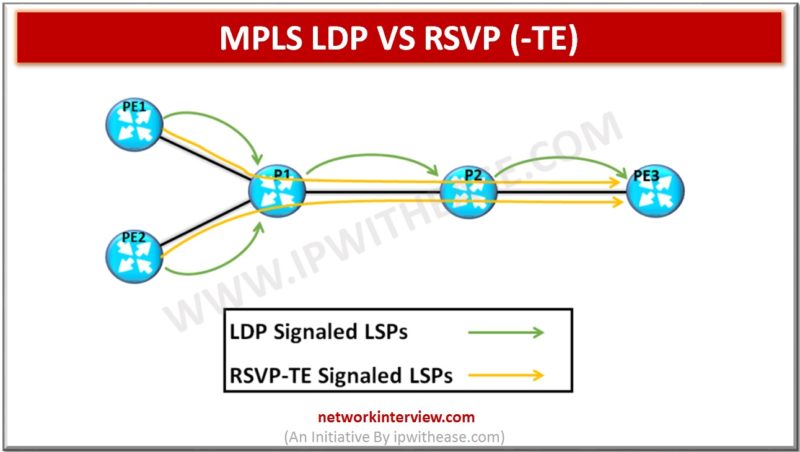
Comparison Table : LDP vs RSVP Below table describes the difference between LDP and RSVP: PARAMETERS LDP RSVP Abbreviation for Label Distribution protocol Resource Reservation Protocol Provisioning Easy to configure. We just need to enable on interfaces. Label bindings automatically …
Comparison Table : RD vs RT in MPLS Below table describes the difference between RD vs RT in MPLS: PARAMETER RD RT Abbreviation for Route Distinguisher Route Target Definition 64-bit identifier prepended to IPv4 route used to identify VPN the …
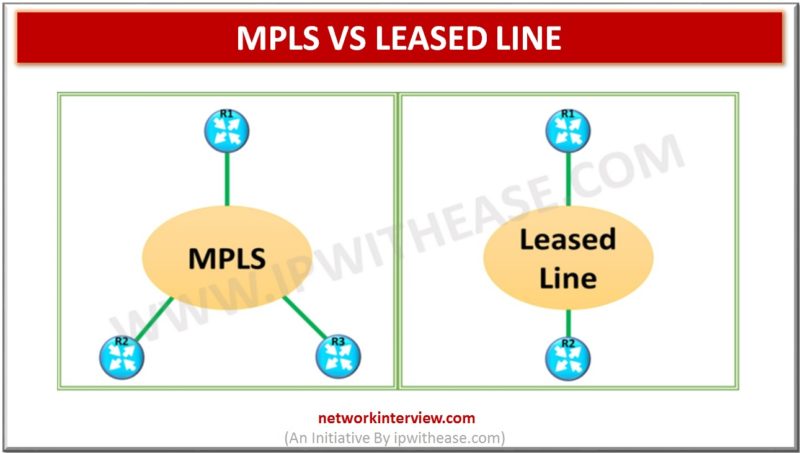
Comparison Table: MPS vs LEASED LINE Below table describes the difference between MPLS and Leased Line: PARAMETER MPLS LEASED LINE Segregation of customer traffic Logical separation of customer traffic. Physical separation of customer traffic Connectivity Type Multipoint or point-to-Point Point-to-Point …
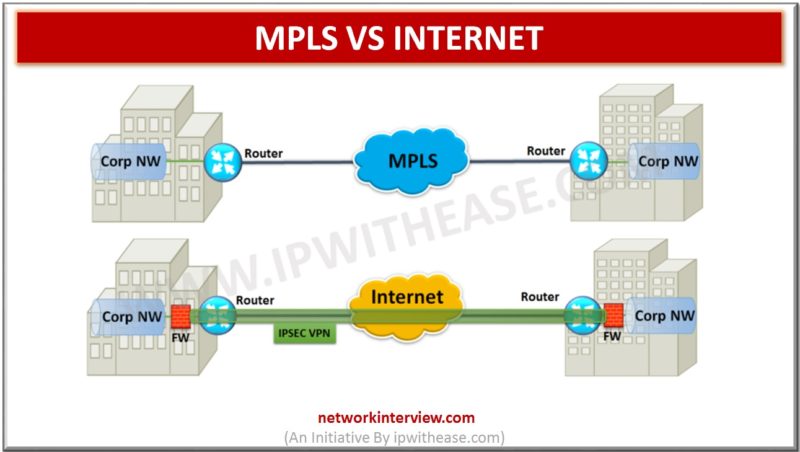
Comparison Table : MPLS vs INTERNET Below table describes the difference between MPLS and Internet: PARAMETERS MPLS INTERNET Carriers Single carrier provides MPLS connectivity for all the locations Not limited to single carrier. Different locations can be connected through various …
Comparison Table: MPLS vs VPN Below table describes the difference between MPLS and VPN: PARAMETER MPLS VPN Scope of Operation Operates on carrier provided Network (Logically segregated to support multiple customers) that will further connect to all customer sites. Operates …
Comparison Table: MPLS vs SD-WAN Below table describes the difference between MPLS and SD-WAN: PARAMETER MPLS SD-WAN Abbreviation for Multiprotocol Label Switching Software Defined – Wide Area Network Provisioning time High Very low Configuration Manual Configuration “Zero Touch provisioning” allows …
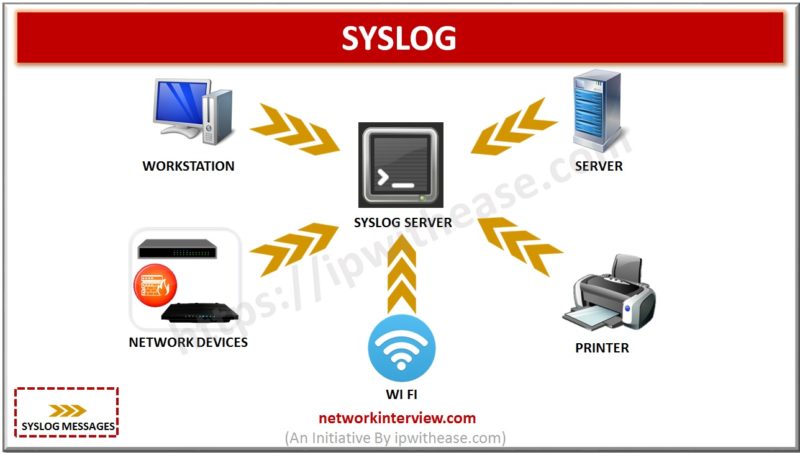
Syslog is a method to collect messages from devices to a server running a syslog daemon. Logging to a central syslog server helps in aggregation of logs and alerts. Cisco devices can send their log messages to a Unix-style SYSLOG …
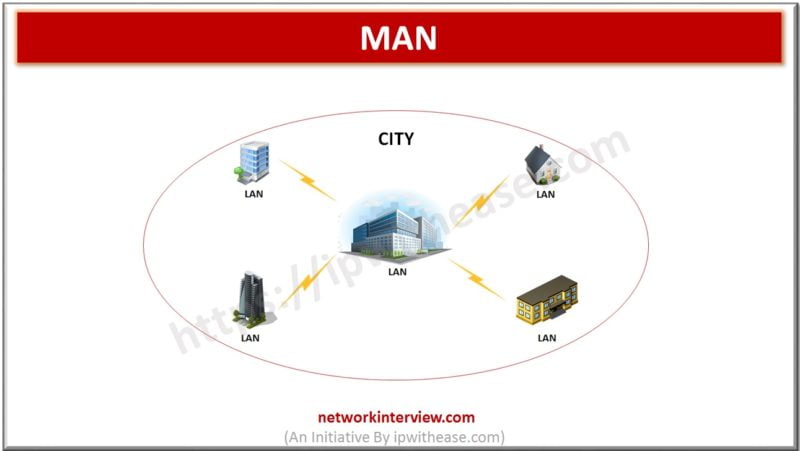
Introduction Computer Networks can be divided into various types depending upon their size and usability. The size of a network can be assessed by its geographical distribution. It can be as small as a room with a few devices/computers or …
Introduction Computer Networks can be divided into various types depending upon their size and usability. The size of a network can be assessed by its geographical distribution. It can be as small as a room with a few devices/computers or …
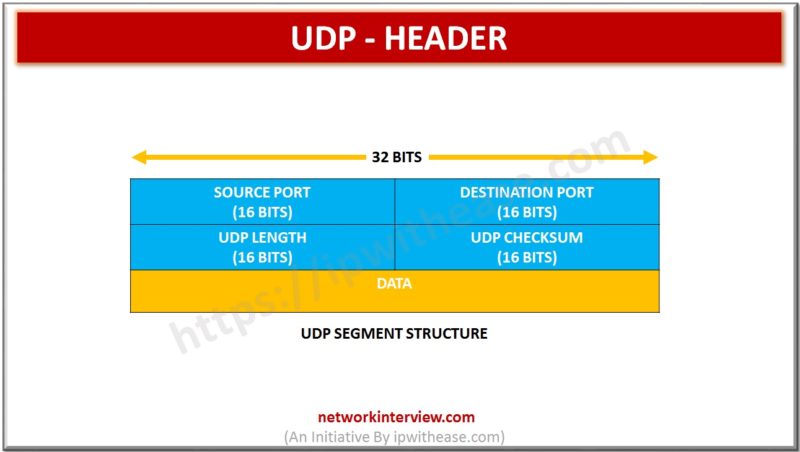
UDP HEADER It consists of four fields each of 2 bytes in length – Source Port(16 bits) – This field identifies the sender’s port. Cleared to zero if not used. Destination Port(16 bits) – This field identifies the receiver’s port. …
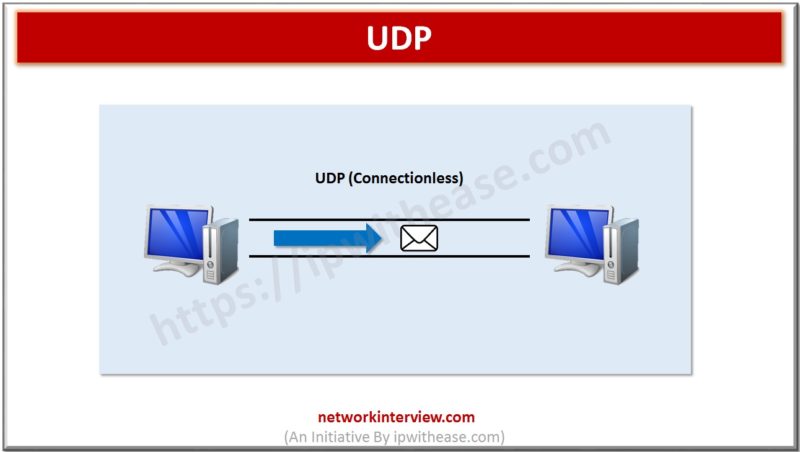
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a transport layer protocol used primarily for low-latency and loss tolerating connections. Outlined by RFC 768 it provides a best-effort datagram service to an end host.In distinction to TCP, UDP just sends the packets with no packet acknowledgements that ends up into much lower bandwidth overhead and latency. However …
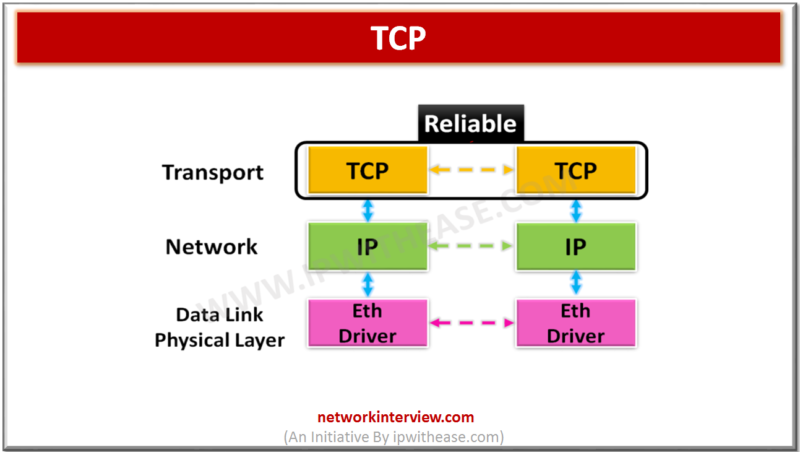
TCP i.e.Transmission Control Protocol is one of main Transport Layer protocol which provides reliable, connection-oriented communication over IP networks between two end stations. When data is provided to the IP protocol, it encapsulates them in IP datagrams. TCP is defined by the …
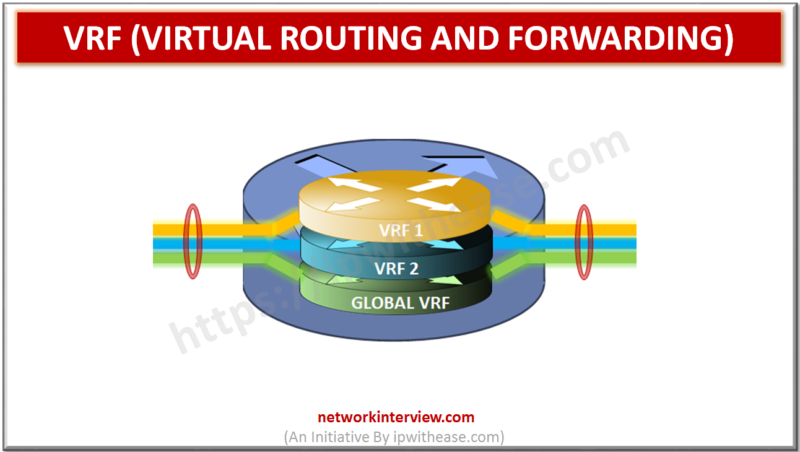
VRF (Virtual routing and forwarding) is a technology that allows multiple instances of a routing table to co-exist within the same router at the same time. Overlapping IP addresses can be used without conflicting with each other as the routing …
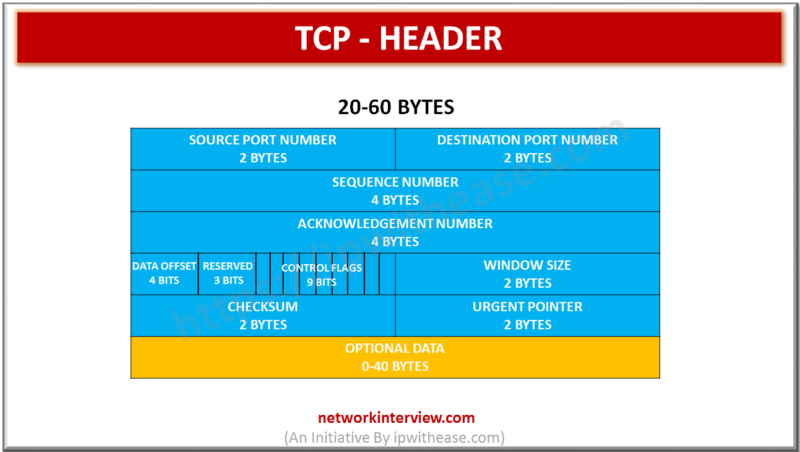
TCP HEADER (Transmission Control Protocol ) Source port (16 bits): Port related to the application in progress on the source machine Destination port (16 bits): Port related to the application in progress on the destination machine Sequence number (32 bits): When the …
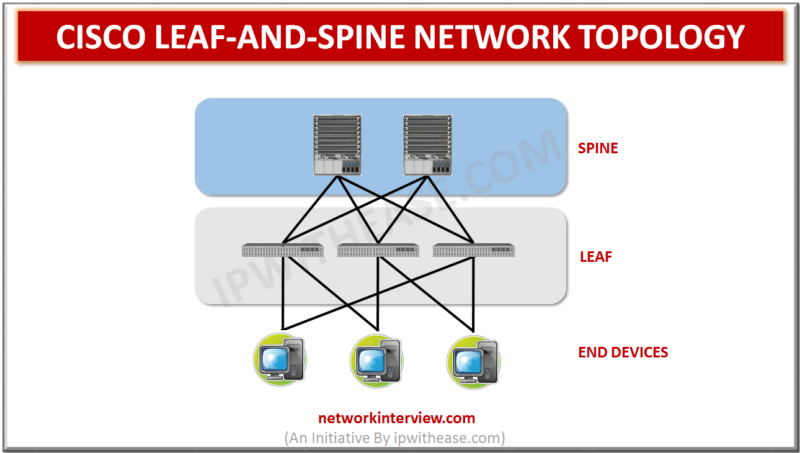
Network Topology Leaf-and-spine is a two-layer network topology composed of leaf switches and spine switches. We are all aware of the Cisco’s 3-tier network topology with the following 3 layers – 1)Access Layer 2)Aggregation/Distribution Layer 3)Core layer The Access Layer …
Introduction to WAN Computer Networks can be divided into various types depending upon their size and usability. The size of a network can be assessed by its geographical distribution. It can be as small as a room with a few …
Introduction to LAN Computer Networks can be divided into various types depending upon their size and usability. The size of a network can be assessed by its geographical distribution. It can be as small as a room with a few …
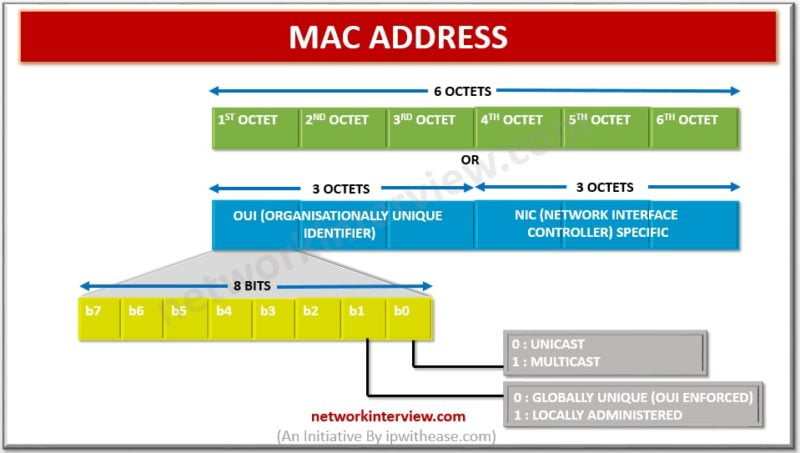
MAC (Media Access Control) Address The MAC address is used by the Media Access Control sublayer of the Data-Link Layer (DLC) of telecommunication protocols. Every NIC (also called LAN card) has a hardware address that’s known as a MAC, for Media Access Control. …
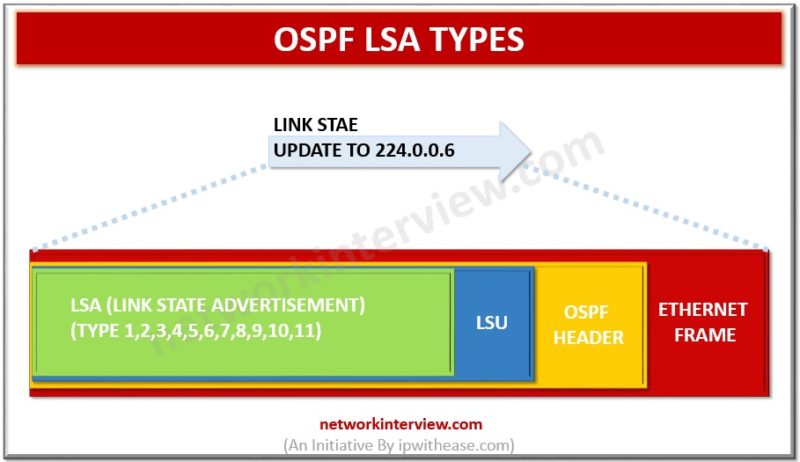
OSPF uses LSAs or Link state Advertisements to share information of each network and populate the LSDB (Link State Database). The main LSA types are : LSA Type 1 (Router LSA):generated by each router for each area it is located. …
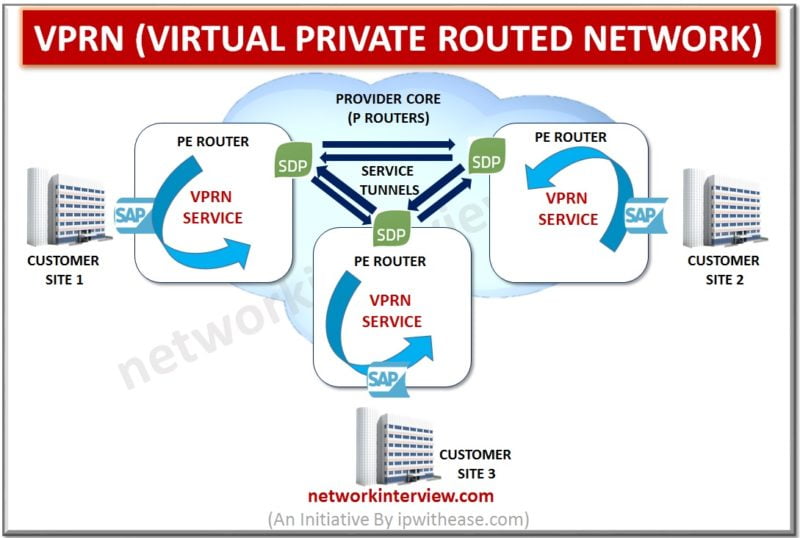
VPRN (Virtual Private Routed Network) is a Multipoint-to-Multiponit Layer 3 VPN Service that connects multiple branches in a single logical routed architecture over IP/MPLS network of a Service Provider. This is called Layer 3 VPN generally, but Alcatel-Lucent define this Layer 3 VPN as VPRN(Virtual Private Routed …
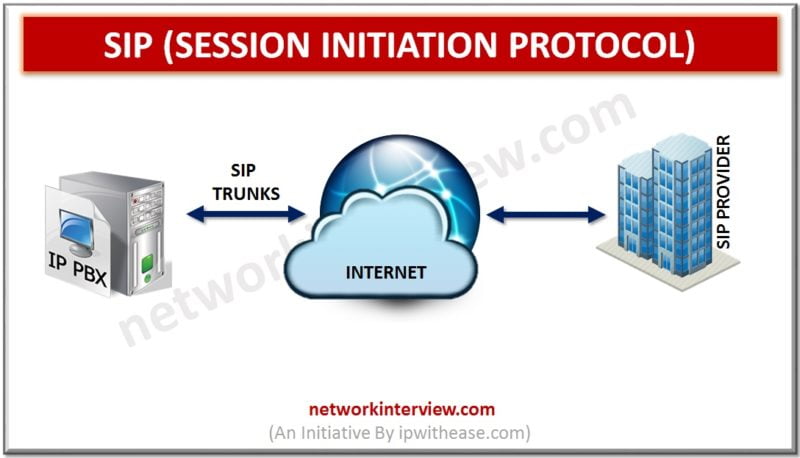
SIP i.e. Session Initiation protocol is an open source protocol. It communicates on TCP or UDP on port numbers 5060 or 5061. SIP has got a range of different messages with each having lot of additional data, thus making it …
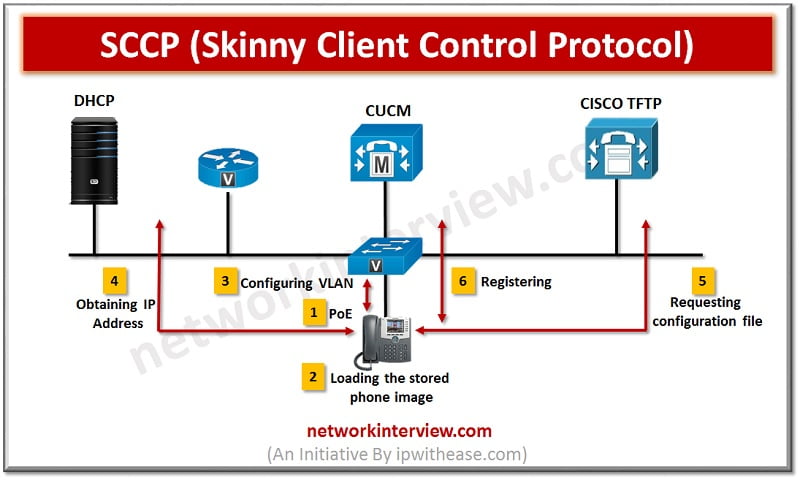
SCCP stands for Skinny Client Control Protocol . It is a lightweight , proprietary control and communication protocol originally developed by Selsius Systems and later taken over by Cisco Systems.It is a lightweight IP-Based protocol for Signalling with CUCM and CME for Cisco …
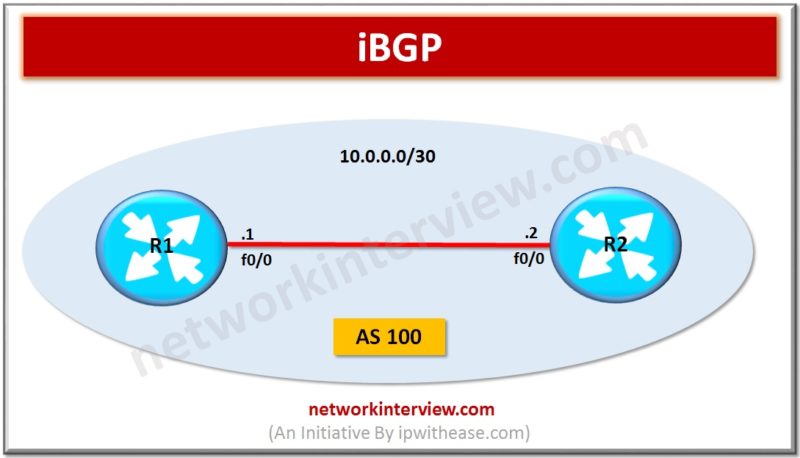
Introduction iBGP is abbreviation for Internal Border Gateway Protocol. iBGP protocol is used between the routers within the same autonomous system (AS). iBGP speaking Routers need to form full mesh to maintain full routing information. Full mesh (iBGP neighborship with all Routers …
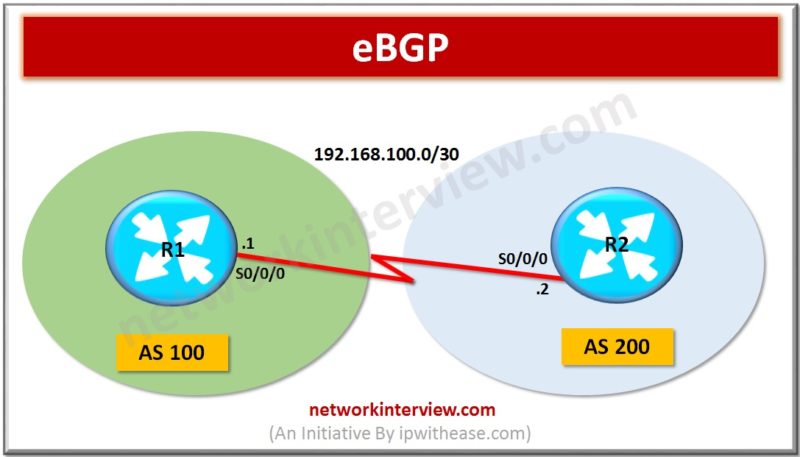
Introduction eBGP is abbreviation for External Border Gateway Protocol and is one of the flavors of BGP protocol. eBGP Routing protocol is used between BGP speaking neighbors which belong to different ASNs (Autonomous System Numbers). eBGP functions as the protocol for …
Network Switching Network Switching works at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of OSI model. Switching is a process of receiving frame from one incoming port (ingress) and then forwarding it to as desired destination (egress). Types of Network Switching Switching …