What is ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request)?
Various techniques are used at the Data link layer to control errors to simply ensure and confirm that all the data frames or packets; i.e., bit streams of data are transmitted and transferred from sender to receiver with accuracy. Using or providing error control at the Data link layer is a feature of optimization rather than a requirement.
Error control process tracks data frames that got lost or corrupted during transmission. The Data link layer follows a technique to retransmit frames to detect or identify transit errors and also take actions which are required to reduce or eliminate such errors.
In this article we will learn more about a technique used at Data link layer protocols known as Automation Repeat Request (ARQ) to make an effort to detect loss of packets during transmission, its advantages and how it is performed.
What is ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request)?
There are two ways of doing error control namely error detection and error correction. Error detection simply means detection or identification of error. These errors may cause the receiver to receive garbled or unclear or distorted messages. Error correction means correction or fixing errors. Reconstruction and rebuilding of original data which is error free.
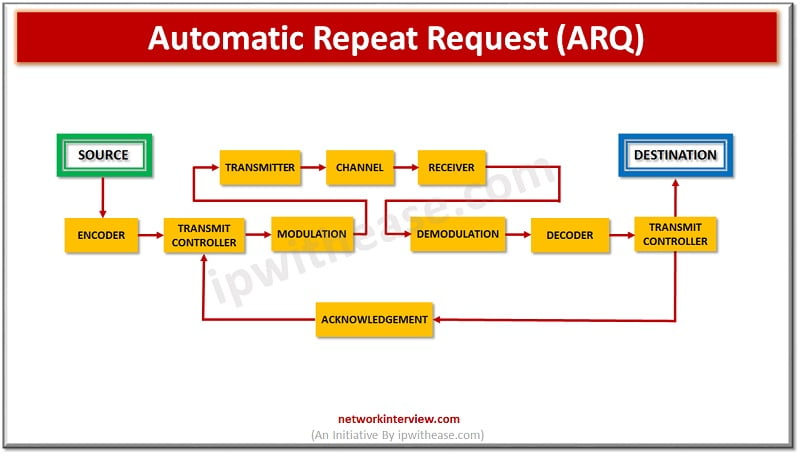
The main function of ARQ protocol is send receives an acknowledgement from the receiver end suggesting that the frame or packet is received correctly before timeout is occurred, timeout defines a specific time window within which acknowledgement has to be sent by the receiver to the sender.
If timeout happens sender will not get acknowledgement within specific time, which implies that data packet or frame is either lost or got corrupted during its transmission hence sender will re-transmit the data frame or packet and ARQ protocol will ensure that process will be repeated until the right packet transmission is completed.
Techniques of Error Control
There are various techniques of error control such as:
Stop and Wait ARQ –
It is also known as alternating bit protocol. It is the simplest flow and error control mechanism. This is usually required in telecommunications to transmit data or information between two connected devices. Receiver signals its readiness to receive data for each frame, sender sends information or data packet to receiver. Sender will stop and wait for acknowledgement from the receiver.
If acknowledgement is not received within a fixed time frame, the sender will resend the data frame and wait for acknowledgement. If the sender receives acknowledgement, it will send the next data frame and wait again. And this process will keep on repeating until send has left with no data frame or information to send to the receiver.
Sliding Window ARQ –
It is used for continuous transmission error control and it is categorized into Go Back N ARQ and Selective repeat ARQ.
Go Back N ARQ –
It sends frames within a specified window frame even without receiving acknowledgement.
Selective Repeat ARQ –
Only suspected or damaged or lost data frames are retransmitted. Sender only retransmits frames for which No acknowledgement is received. It is used however lesser because of more complexity at sender and receiver end as each packet must be acknowledged individually.
Applications of Automatic Repeat Request
ARQ protocols have a wide range of applications to ensure they provide reliable transmissions over unreliable upstream sources. These protocols operate on short wave radio so as to ensure reliable delivery of signals.
For the same function of ARQ, there are various applications:
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- Specific Service Orientation Protocol: Error-correction of message signals in ATM networks
- High-Level Data Link protocol (HLDL)
- IBM Binary synchronous Communications Protocol (IBSC)
- Xmodem : modem file transfer protocol
Pros and Cons of Automatic Repeat Request
PROS
- Quite simple error detection and error correction techniques
- Simple decoding equipment as compared to other techniques
- ARQ is adaptive, as information is retransmitted only if error occurs
- Ideal for using noisy channels
- It has both error flow and error control mechanism
- It has timer implementation
CONS
- High error rate on a medium and channel could cause too much transmission of the frames or packets of information
- High error rate in channel could lead to loss of information and lead to reduction in efficiency or productivity of the system
- System throughput is lowered by ARQ when channel error is high
Continue Reading:
What is HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) ?
What is MPLS and how is it different from IP Routing?
Tag:protocol



