What are the types of Wireless Networks
Network is a collection of systems, software, and hardware which all are connected to provide services to its users and work together. A network comprises systems connected via cables or wireless connectivity. Specialized software, and devices to manage data traffic. A network enables users to share files and resources, such as printers, scanners as well as send electronic messages (Email) services. Wireless networks had gained a lot of popularity in recent years due to businesses’ demand for availability and expectation of ubiquitous Connectivity.
In this article we will learn more about different types of wireless networks, their advantages and how they are used in different places – home or offices or public places etc.
About Wireless Networks
Wireless network refers to any network not connected by cables , which is what enables desired mobility and convenience for the end user. Dozens of wireless technologies exist to meet the needs each with its unique performance characteristics and optimization for specialized tasks and context be it WiFi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, NFC, WiMax, LTE, HSPA, EV-DO , earlier 3G standards, satellite services and many more.
In the case of wireless networks, radio communication is the usual medium of choice. But within the radio powered subset dozens of different technologies designed to use at different scales, topologies and for varied use cases.
The first professional wireless network was developed under the brand ALOHAnet in 1969 at the University of Hawaii and became operational in June 1971.
Types of Wireless Networks
Let’s look at four different types of wireless networks and understand their characteristics :
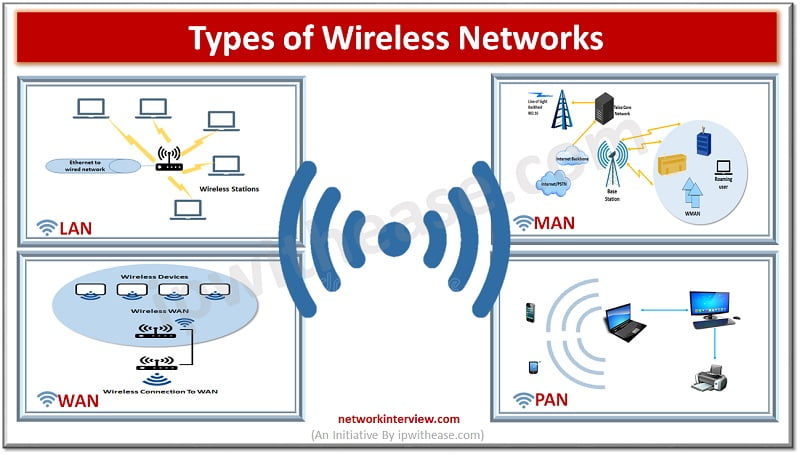
- Wireless Local Area Networks (LAN)
- Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks (MAN)
- Wireless Personal Area Networks (PAN)
- Wireless Wide Area Networks (WAN)
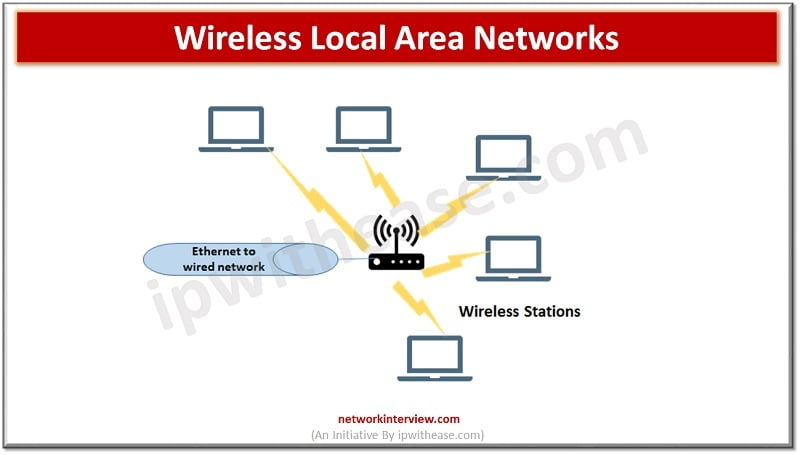
Wireless Local Area Networks –
Provides internet access within a building floor, or a limited external area. It is mostly used in offices and homes and nowadays used in stores and restaurants also. The use of home networks has increased greatly during Covid-19 pandemic where people were forced to work from homes or students required to study from homes. Most home network wireless networks are simple in design, usually a modem connecting to cable or fiber from a local service provider.
A Wireless router connected to the modem receives the signal which is broadcasted using wireless protocol such as 802.11 standard. In offices access points are mounted on the ceiling , each broadcasting wireless signal to the surrounding area. Multiple access points are required in bigger offices connected to the office backbone network via a wired connection to switch.
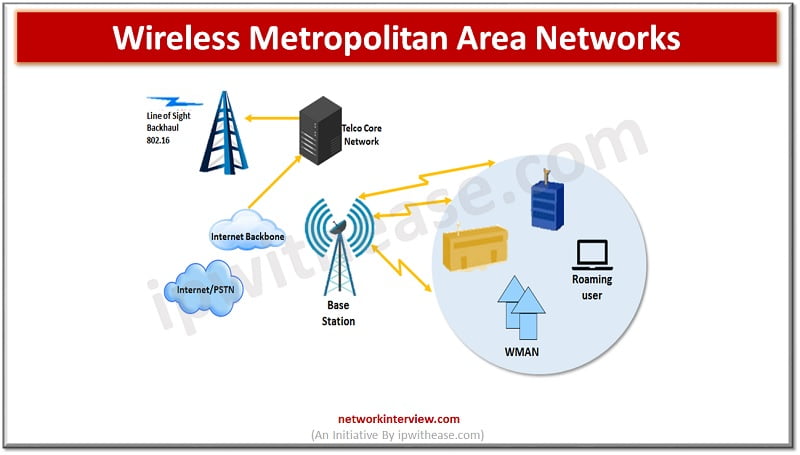
Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks –
Are installed in cities worldwide to offer access to people outside home and offices. Their networks cover wide areas rather than office or home networks. Access points are located on sides of buildings or on telephone poles across the coverage area. Access points are connected to the internet via wired network and broadcast a wireless signal throughout the area. Users connect to their desired destination via the nearest access point which forwards the connection through its internet connection.
Wireless Personal Area Networks –
They cover a very limited area usually 100 meters for most applications using Bluetooth and ZigBee protocols. Bluetooth enables hands free phone calls, connecting phones to earpieces and transmitting signals between smart devices. (Bluetooth enabled) ZigBee connects stations along an IoT networks , Infrared technology is limited to line of sight such as TV remotes.

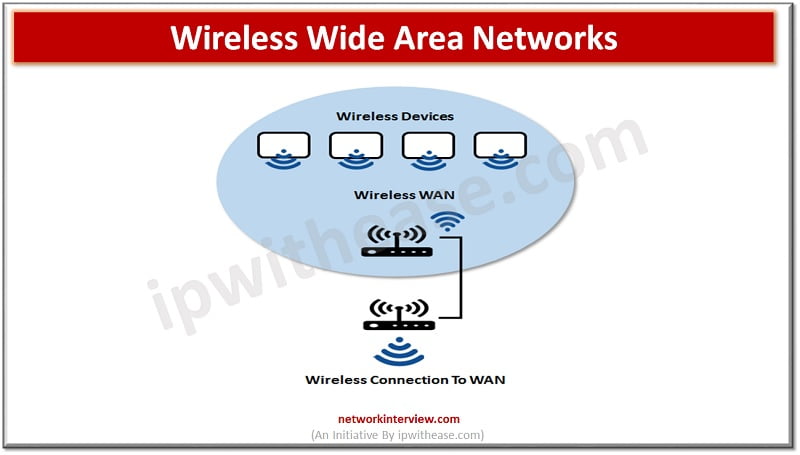
Wireless Wide Area Networks –
Use cellular technology to provide access outside the range of a wireless LAN or wireless MAN. These networks enable users to make phone calls to other users connecting via wireless WAN or wired telephone systems. Cell towers are located in vicinity and user connection is routed to the nearest cell tower which is connected to a wired internet or another tower connected to a wired network.
Difference between Wireless Networks
TYPE | RANGE | APPLICATIONS | STANDARDS |
| Wireless local area networks | Within a floor, building or campus | Wireless extension of LAN | IEEE 802.11 (WiFi) |
| Wireless metropolitan area networks | Within a city | Wireless inter-network connectivity | IEEE 802.15 (WiMAX) |
| Wireless personal area networks | Within reach of a person | Peripherals cable replacement | Bluetooth, ZigBee, NFC |
| Wireless wide area networks | World wide | Wireless network access cellular phones etc. | Cellular (UMTS, LTE etc.) |
Continue Reading:
Rivet Networks and Intel Killer Wireless Technology
Top 10 wireless technology trends
Tag:wireless



