Tree Network Topology
Introduction to Tree Network Topology
Every network is a collection of nodes and links for their interconnection. The arrangement of these nodes and links in a specific manner is known as topology. It would define how devices within will connect and how data moves from one node to another node. It can also be simply referred to as a schematic description of arrangement of network elements. There are different types of network topologies but the selection would depend on a number of factors such as performance, throughput, fault tolerance, costs etc. Network topology is defined both at physical and logical level. Logical topology defines how data will flow between network devices whereas physical topology will define physical connections within the network.
Today we look more in detail about Tree network topology, its advantages and disadvantages and use cases etc.
What is a Tree Network Topology?
Choice of topology for your network is crucial as it affects its function and performance . So, choosing the right topology for your organization is quite an important decision. By choosing the right topology for your organization, you can reduce operational costs, improve performance and achieve resource allocation optimization.
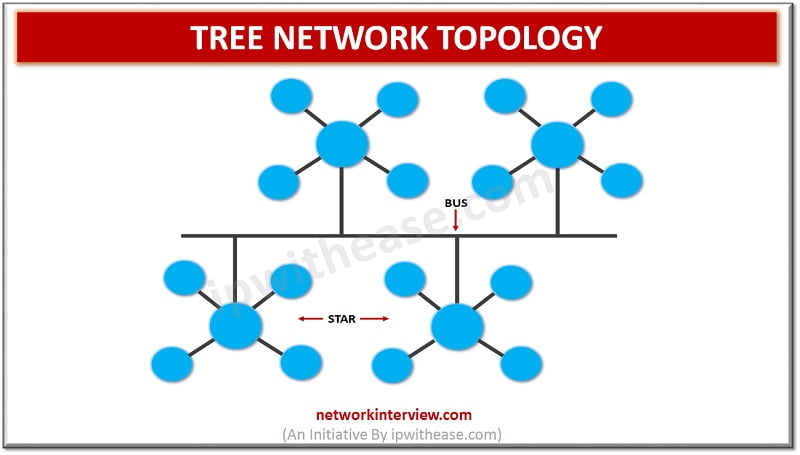
Tree network topology is a combination of the bus and the Star network. More than one-star networks can be connected together using a bus network. Different branches, that is the star network looks in tree topology which are connected on a bus at different points at a particular distance and the bus network looks like a root of a tree.
The central ‘root’ node is connected to one or more other nodes which are one level lower in the branching with a point-to-point link between each second level node and the top level ‘root’ node. Each of the second level nodes is connected to the ‘root ‘ node but also has one or more nodes connected to one level below again (third level). The ‘root’ node is top most in the hierarchy and there is no node above it, all other nodes are descendants of the ‘root’ node. There is only one path between two nodes for transmission of data. Thus, it is a parent-child hierarchy.
The central hub contains a repeater, which looks at incoming bits and regenerates them as the full blow signal for 0 or 1 as required. This allows digital signals to travel long distances. The central hub is also known as an active hub. The tree topology may have many secondary hubs, which may be active or passive in nature.
Advantages of Tree Network Topology
- For networks where neither star nor bus topology can be implemented tree topology is best alternative.
- Support for broadband transmissions – It is mainly used to provide broadband transmission as signals can be sent to long distances without being weakened.
- Ease of expansion – new devices can be added to the existing network without much hassles. Whole readymade branches can be attached to the main cable channel which is bus network which is especially designed for expansion of network
- Not just physical appearance but logically also branches of the tree network are divided functionally and each segment of branches can be managed separately.
- Ease of management – the whole network is divided into segments known as Star networks which are easy to manage and maintain
- Error detection – error detection is quick and error correction is also easy as roles are divided, responsibilities and functions are segregated
- Limited failures – the breakdown of one station in the hierarchy don’t impact availability of the entire network. Each of the branches are connected with base cable channel with a separate point to point wiring so damage to one branch will not affect function of another branch
- Point to point wiring – Individual segments are point to point connected
Disadvantages of Tree Network Topology
- Difficult to identify fault and troubleshoot – Its fault occurs in the node; it becomes tough to troubleshoot the issue as defective node detection is tedious task
- Higher costs – devices required for deployment of broadband transmission are expensive
- Failures – even though one branch cannot cause impact to other , but its main dependency is on the bus cable and failure in main bus cable could lead to downfall of entire network
- Complexity in reconfiguration – addition of new device requires expertise in configuration
- Maintenance costs are more with number of nodes or branches and wiring extensions
Continue Reading:
Tag:routing



