SLA vs SLO vs SLI : SRE Fundamentals
Introduction to SRE
SRE (Site reliability engineering) is the fastest growing role and rising trend which is sharing software teams. Organizations adopting best practises for incident management, automation, runbooks, and many more. One of the most fundamental principles of SRE are SLA, SLI and SLOs (Service level objectives), as they provide a paradigm shift to truly measure and enforce reliability. There are three major benefits or key pillars of SRE –
- keeping customers happy,
- keeping teams aligned and
- balancing reliability and innovation velocity.
When it comes to building and delivery of modern software and applications both enterprises and cloud native organizations are faced with unprecedented systems complexity.
Today we look more in detail about SLOs, SLIs and SLAs, its benefits, limitations and use cases.
About SLA (Service level agreement)
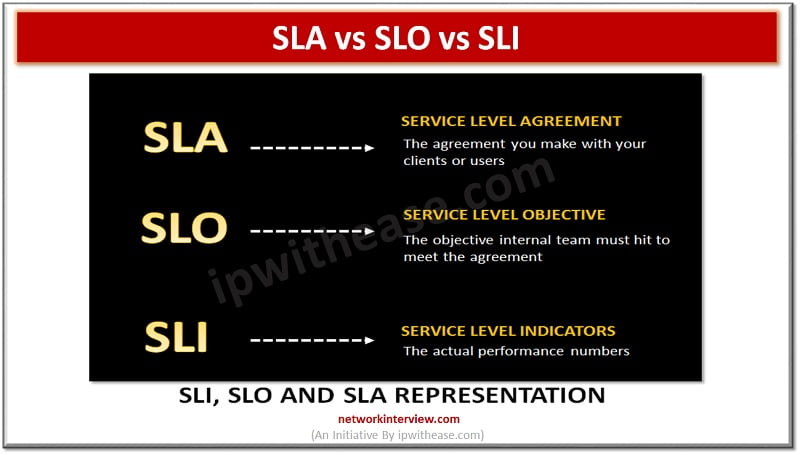
‘SLA’ is an explicit or implicit contract with your users which includes consequences of meeting (or missing) the SLOs they contain.
Service level agreements are set by business rather than engineers, SREs, or Operations. When anything happens to an SLO, SLA will kick in, they are actions which are taken when your SLO fails and often result in contractual or financial consequences.
SLAs are usually drawn up by company new business and legal teams and they represent the commitment you are making to customers and the consequences if you fail to live up to those commitments. One of the limitations of SLAs are they are difficult to measure, report and meet.
About SLO (Service level objective)
An SLO (Service level objective) is an agreement within an SLA about a specific metric like uptime or response time. If SLA is a formal agreement between you and your customer, SLOs are the individual commitments we make to customers. SLOs are what set customer expectations and inform IT and DevOps teams what goals they need to hit and measure against that.
SLOs can be useful for both paid and unpaid accounts, as well as internal and external customers. Internal systems such as CRM, client data repositories, and intranet are equally important and have SLA for those internal systems to enable internal teams to meet their own customer facing goals.
About SLI (Service level indicator)
An SLI (Service level indicator) measures compliance with an SLO (Service level objective) for example if SLA specifies that systems will be available 99.95% of the time, SLO is likely 99.95% uptime and your SLI is an actual measurement of uptime. To stay in compliance within SLA, the SLI will need to meet or exceed the commitment made in the document.
Comparison Table: SLA vs SLO vs SLI
Below table summarizes the difference between them:
FUNCTIONS | SLA | SLO | SLI |
| Definition | SLA is an agreement between provider and client which outlines measurable metrics such as uptime, responsibilities, and responsiveness as a measure to manage client service level expectations | SLO is an agreement clause with an SLA. SLOs involve certain metrics such as uptime, or response time and are used to set customer expectations as well as let IT and DevOps teams know the standards required to be met. | SLIs are parameters which indicate the successful transactions, requests served by the service over the predefined intervals of time. SLI is used to measure the compliance level within an SLO. |
| Measurements/ Penalties | Partial refund of service subscription fee Additional subscription time added for free SLAs are numbers of monitoring metrics applying to the SLOs | Durability of disks should be 99.9 % Availability of services should be 99.95% Service should be successfully serve 99.999% requests/transactions | Availability / uptime of service Number of successful transactions/requests Consistency and durability of data |
| Key differentiator | SLAs are the numbers of the monitoring metrics applying to the SLOs | SLOs are alerting rules | SLIs are metrics in the monitoring system |
| Features | SLA is looser objective than SLA SLA only specifies a subset of SLO metrics SLAs are signed with business customers SLA is a legal agreement between service provider and customer | SLOs are set for internal teams SLOs are derived from SLAs SLO has no legal binding attached as it is internal | SLI is an indicator to define and measure the SLO |
| Who sets it? | Business development and legal team, IT and DevOps teams | Product owner, SRE, OPs team, developers and customers | SRE (Service reliability engineers) |
Download the comparison table: SLA vs SLO vs SLI
Continue Reading:
What is Site Reliability Engineering?
DevOps vs SRE (Site Reliability Engineer)
Tag:comparison, services



