SDP vs VPN: Understand the difference
Traditional model of working from the office is quickly diminishing and becoming a thing of the past. As we transition to a hybrid model of working, network security becomes more and more complex. At the same time organizations resources are moving rapidly over cloud which workers need to access. This combination of remote working and cloud storage poses a high-risk scenario. Data leaks are the primary threat with malware attacks just behind. Software defined perimeter security is seen as a popular alternative to VPNs systems.
Today we look more in detail about Software defined perimeter security framework and virtual private networks (VPNs), how they differ from each other i.e. SDP vs VPN, their advantages and use cases etc.
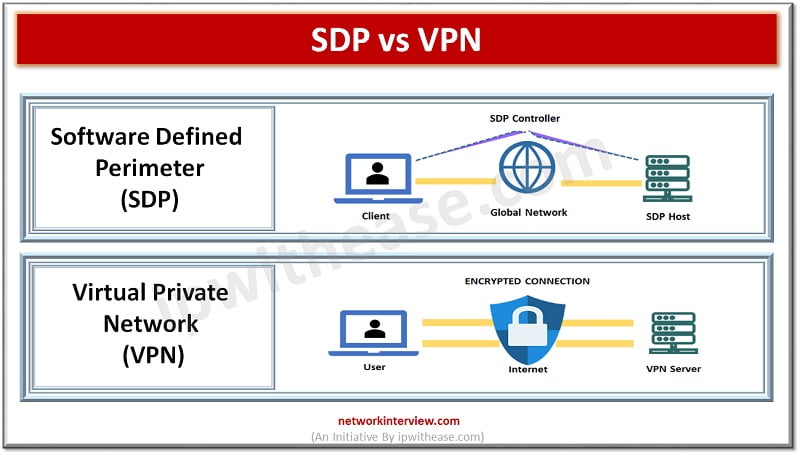
What is SDP?
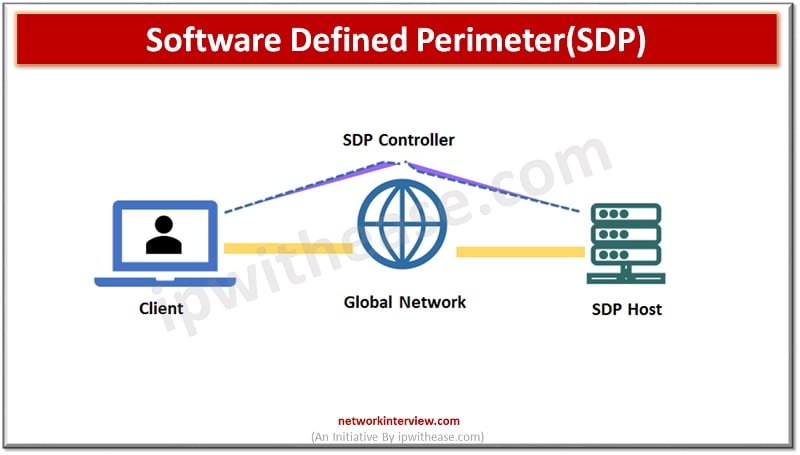
SDP uses software to secure networks. The software works as a perimeter to secure assets such as client databases, accounting tools, communication applications and much more which is internal to the organization. SDP comprises controllers which govern the access setup of the system and act as intermediaries between SDP hosts seeking access, authentication providers.
- Gateways – are generally central data centres, servers or cloud resources which require protection from unauthorized access from illegitimate users. The resources are micro segmented in SDP implementations to ensure clients have only access to data on ‘need to know’ basis.
- Clients – request access to remote access to network gateways. Access requests are made by clients by offering authentication information to controllers, setting up secure connection via VPN style tunnels to gain access to gateways.
- Authentication Providers – user authentication information provided by them when Multi factor authentication is used. They liaison with the SDP controller and decide whether users have access permissions to the gateway. All communication within system is encrypted.
What is VPN?
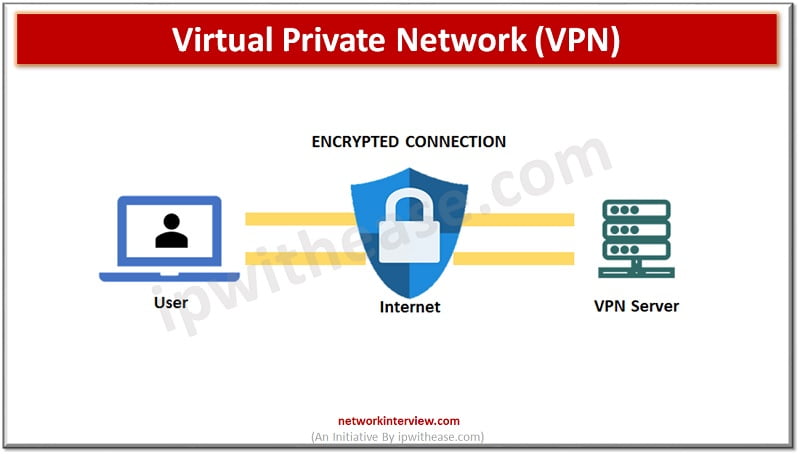
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are software tools which create encrypted barriers around the data passing across the network. The ‘virtual’ refers to the fact that no physical networking infrastructure is there. ‘Private’ refers to the application of encryption and anonymity. The ‘Network’ element explains use of VPNs in connecting devices to external and internal networks.
Users typically connect to VPNs servers via their routers. The VPN server provides an anonymous IP address and creates an encrypted tunnel. Data from the user passes through this tunnel to its destination. It obscures user identity, conceal location information and device type and makes the data passing through tunnel unreadable to external parties.
Comparison Table: SDP vs VPN
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
Function | SDP | VPN |
| Network access | SDP uses an ‘Armed guard’ approach around the castle where guards stop them going around any area of the castle where they should not. SDP operates on principle of Zero trust. | Uses ‘Moat and castle’ approach towards security by creating a strong perimeter around the network, applying encryption and anonymization across network traffic. VPN operates on the principle of Trust based network design. |
| Security | SDP follows a simpler approach to security. The system will authenticate each user via their VPN style connection and system will scan connecting devices to ensure credential theft is not happening. | VPNs makes things complex as a company may need VPN for different departments – accounting, customer management, human resources etc. to ensure total protection |
| Remote working | SDP access is defined with policies and access is granted on a temporary basis and for a limited time. Credential theft risk is minimized in SDP as compared to VPN access. | VPNs create encrypted tunnels between remote devices and organization resources. If tunnels are compromised then intrusion is inevitable. Users need to be trusted to use latest Virtual private network tools every time while connecting and to guard against theft of VPN credentials |
| Access Authorization | It offers granular user and resource access with continuous assessment | It offers network access authorization which is more than what is required |
| Features | ●Access is granted after authentication ●Identity based access ●Granular access to organization resources ●Applications and services are invisible to internet ●Continuous risk assessment ●Ability to enforce least privilege access via IAM | ●Access is granted before authentication ●IP centric access ●Network level access to organization resources ●Application and services are exposed to Internet ●No risk assessment of devices is performed ●Difficult to apply least privilege access |
Download the comparison table: SDP vs VPN
Continue Reading:
ISP vs VPN: Know the difference
Tag:comparison, Security



