Partial Mesh Network Topology
Different types of network topologies exist and based on multiple factors organizations can choose the best topology to suit them. Performance, Fault tolerance , redundancy, ease of error detection and correction, installation and configuration , scalability requirements, management and costs are many factors which are key to this decision. Usage of the network is also one of the key factors in determining which topology to be used.
Today we look more in detail about Partial mesh network topology , its need, advantages and disadvantages and use cases etc.
About Partial Mesh Network Topology
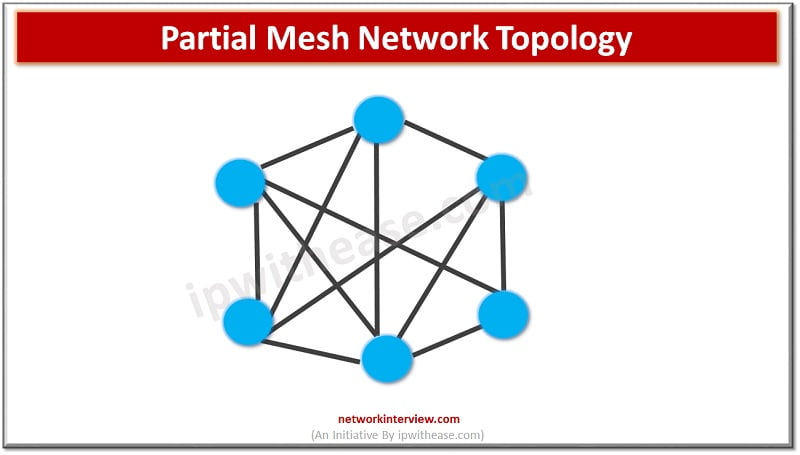
Partial mesh is a structure to map routers in such a way that they are coupled tightly among themselves but still not fully interconnected. Partial mesh is a subset of full mesh and links are arranged in a strategic manner based on frequent operating paths or signals to facilitate usage. Users of partial mesh enjoy better usability and time management but there are definitely some additional benefits using partial mesh in your organization. Only a few nodes, not all are attached with other nodes.
There is no centralized regulation in partial mesh, for any number of connections in the network no admin or controller exists. They are applicable to Wireless area networks as they are meant to cover large geographical areas. WANs as we are aware are suitable to handle large crowds and numerous devices or remote areas. It is not simply more redundant than Hub and spoke WAN topology but it lies somewhere between Mesh and Spoke in terms of costs and it is comparatively less expensive than full mesh but costlier than spoke.
Partial mesh networks are highly robust and if a user loses connection still data will not be lost as data is not hosted centrally in one location. Partial mesh topology creates datasets with better management capabilities and integrity. There is validation and tracking for any misconduct that occurs.
Principles of Mesh Network Topology
Mesh topology works on two principles as under.
- Routing – in routing mode data is communicated in a pre-arranged path containing many hopping across nodes. All intermediary nodes require to be active and connected then only data will be transmitted over the network
- Flooding – the data is transmitted to every active node. The node looks at address data and passes it to next active node if data is not supposed to be addressed
Protocols used in Partial Mesh Topology
Protocols fit in layer 3 of the OSI model and define standards for data communication between two nodes. The three kinds of protocols: Proactive, Hybrid and Reactive are used in this topology. Each protocol plays a vital role in management of the networking and impacts performance and scalability.
- Proactive protocol – provides constant self-monitoring of nodes with the help of feedback mechanisms from nodes. If any node fails, it reroutes the network path. Maximum up time is ensured and quick recovery from failure with robust performance. In a dynamic environment chances of collision are increased but in a static environment it is ideal where network paths don’t change very often.
- Hybrid protocol – offers the best combination as per environment and communication requirements and uses reactive methods and characteristics of proactive protocol . network cost optimization can be achieved using this
- Reactive protocol – is used to determine the network path at the time of request for transmission of data. It defines the optimal path and scans the entire network and best fit for a dynamic environment.
Advantages of Partial Mesh Topology
- High volume of data transmission can be handled at a very fast rate to any number of devices. Data transmission is possible from different devices simultaneously
- No effect of failure even if one hub or end of the terminal is deactivated. Things are arranged in such a manner that best optimal path is automatically directed without overloading the process
- The expansion and modification is possible in every sense and without impacting existing nodes or terminals. As each node acts like a router. There are no exclusive routers.
- It is an optimal solution for best user experience with minimum charges
- It is a very robust structure ; a connection only communicate with others only if they are allowed to do so and this eliminate chances of misconduct
- It is very easy to diagnose and identify fault
- Customization could offer better security and privacy to users as desired
- As failures do not disrupt processes , data transmission has consistency
Disadvantages of Partial Mesh Topology
- Since each node acts as router the complexity is increased
- Overall cost of this network is too high as compared to other topology options
- Setup and maintenance is tough and even administration
- All the time in this topology each node will have to remain active which led to high power consumption and load increase
Continue Reading:
Hub and Spoke/Star Network Topology
Tag:routing



