Hypervisor in Cloud Computing
Hypervisor in Cloud Computing:
For long, Applications were assigned dedicated physical servers and resources like CPU, memory and storage. Growth and demand in the ever changing IT environment stipulated for a cost effective and energy saving solution. Virtualization technology gained acceptance in the IT world and henceforth Hypervisors gained global preference. Hypervisor technology is not as young, infact it was introduced by IBM in the 1960s for the purpose of its mainframe computers. Till date, hypervisor technology has developed considerably such that a single mainframe can handle hundreds and thousands of VMs.
Hypervisor is the key ingredient of virtualization which is responsible for sharing of physical hardware resources for different application and minimizing dependencies of application on physical machine. In its simpler form, the hypervisor is specialized firmware or software, or both, installed on single hardware that would allow you to host several virtual machines. It permit physical hardware to be shared across several VMs. A computer on which hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine. The VM is known as a guest machine. The hypervisor allows the physical host machine to run various guest machines. Hypervisor computes resources such as memory, storage, network bandwidth, and CPU cycles. Infact, these resources are considered by hypervisor as a pool which can be reallocated between existing guests or to new VMs.
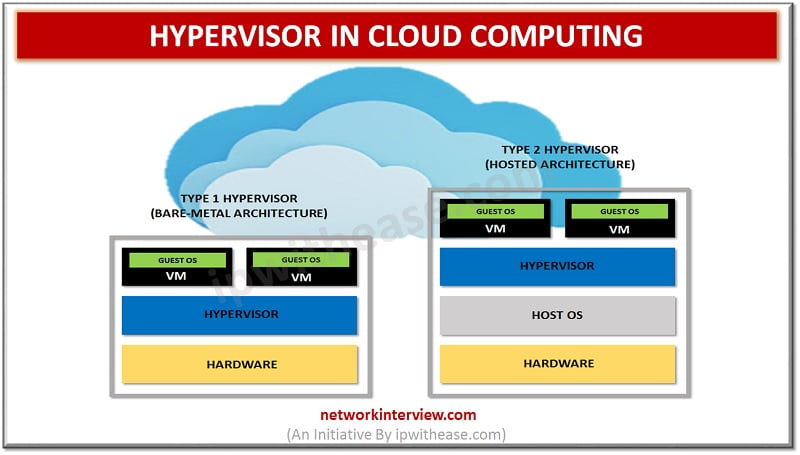
Types of Hypervisor in Cloud Computing
- Type I Hypervisor
- Type II Hypervisor
Related – Type-1 vs Type-2 Hypervisors
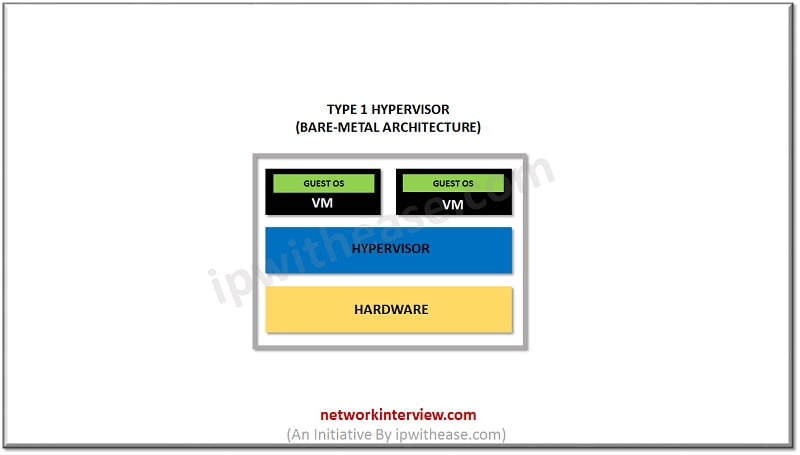
Type I Hypervisor in Cloud Computing
Type I is the bare-metal hypervisor that is deployed directly over the host’s system hardware without any underlying OS or software. Usually, they don’t require the installation of software ahead of time. It can be install onto the hardware. This type of hypervisor tends to be powerful and requires a great deal of expertise to function it well. Type I hypervisors are more complex. It has certain hardware requirements to run adequately. Due to this, it is mostly chosen by IT operations and data center computing. Type 1 hypervisors vendors are
- Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor
- Oracle VM
- VMware ESXi
- Citrix XenServer.
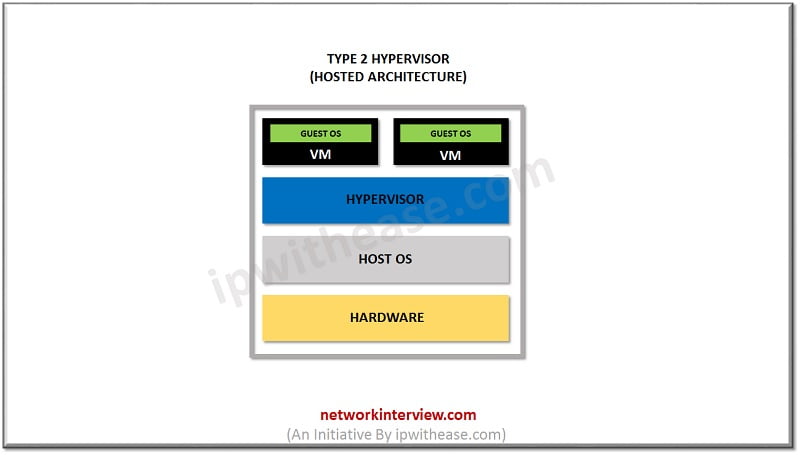
Type II Hypervisor in Cloud Computing
Type II is a hosted hypervisor that runs as a software layer within a physical operating system. The hypervisor runs as a separate second layer over the hardware while the OS runs as a third layer. Type two is not much efficient to handle complex virtual tasks. It can be used for basic development testing and emulation purpose. If there is any security flaw found inside the host OS, it can potentially compromise all of virtual machines running. That is why type II hypervisors cannot be used for Data Center computing. They are designed for end-user systems where security is less of a concern. For instance, developers could use type II Hypervisor to launch virtual machines in order to test software product before their release. Type II hypervisor vendors are –
- Parallels Desktop
- Windows Virtual PC
- VMware Workstation Pro/VMware Fusion
- Oracle VM
- Virtual Box
- VMware Player.
Advantages of Hypervisor in Cloud Computing
- Though virtual machines operate on the same physical hardware, they are separated from each other. This also depicts that if one virtual machine undergoes a crash, error, or a malware attack, it doesn’t affect the other virtual machines.
- Another benefit is that virtual machines are mobile and portable as they don’t depend on the underlying hardware. Since they are not linked to physical hardware, switching between local or remote virtualized servers gets a lot easier as compared to traditional applications.
Summary
When you achieve virtualization, it brings a merger of multiple resources. This tends to reduce costs and improves manageability. In addition to it, a hypervisor can manage increased workloads. In a situation when a specific hardware node gets overheated, you can easily switch those virtual machines onto some other physical nodes. Virtualization also delivers other benefits of security, debugging and support. A Hypervisor is a natural target for hackers because its design controls all the resources of the hardware while managing all the virtual machines residing on it.
Related – Top 5 Type-1 Hypervisors in Market
Watch Related Video
Tag:virtualization



