Extended Star Network Topology
A network topology determines how systems, printers, routers , switches and other devices will be connected over the network. It describes the layout of wires, devices, and routes. Which topology to choose for your organization depends on a set of factors such as usage requirements, costs, installation and management , performance , scalability , fault tolerance etc.
Today we look more in detail about extended Star network topology , its need, advantages and disadvantages and use cases etc.
About Extended Star Network Topology
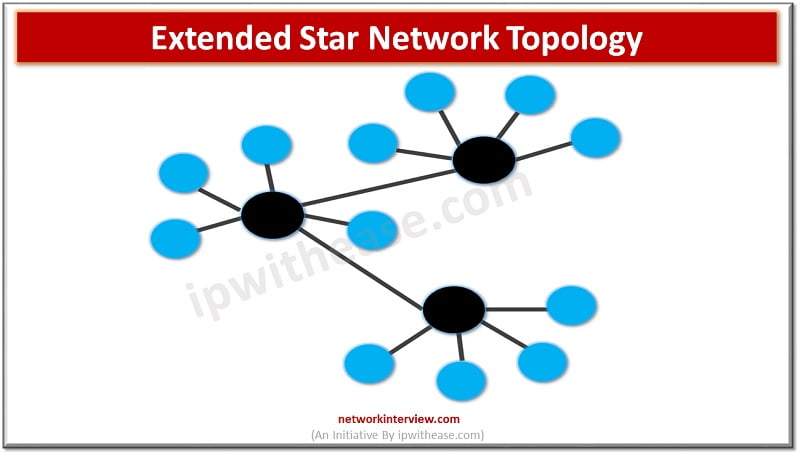
An extended star network topology includes an additional networking device that is directly connected to the central networking device. It seems like a mesh of switches which are interconnected to the network and once central networking device which controls the network. Star topology is the most widely used network topology at homes and offices.
It has different nodes that are known as hosts and the central node of communication called a hub or the server. The central hub is also called peripheral host and nodes are called leaves of the peripheral host. The central hub is the central point of communication and if any node needs to transfer a message to another node the first step is to send a message to the central hub and then the central hub will transfer the message to the recipient node.
This sort of network setup is known as star topology or extended star topology and it is good for short distance communication which can be used in offices, homes, computer labs, and small buildings where the LAN is established. All the nodes can be managed from a one-point central hub. The central hub has content addressable memory (cam) table which is used to store the address of all nodes so that all information of connect nodes can be managed by the central hub in the proper manner.
In extended star topology instead of connecting all devices to the central unit, we have sub central devices added to allow more functionality for organization and subnetting.
Advantages of Extended Star Topology
- The performance is better in extended star topology compared to bus topology. As there is no unnecessary transmission of messages in the network. The message is transferred only between source node , a central hub and destination node
- Ease of adding devices as network expansion happens
- One node failure do not bring down entire network
- The new equipment can be added to the network and connected to the central hub. The nodes can be easily removed from the network
- It is easy to find device and cable issues
- It can be upgraded to faster speed
- This topology helps to control multiple nodes at the same time
- The data transmission can be done across the network and there is very less chance of network failure as compared to its counterparts like bus topology
- Mostly widely used so support is easily available
Disadvantages of Extended Star Topology
- As all nodes are connected to central hub it requires more wire at each node to connect to central hub which increases its setup cost hence it requires more cable than a bus or ring network
- As all nodes are connected to the central hub and if central hub goes down it will lead to whole network failure and bring down entire network
- Increase in number of connected nodes will decrease the performance of central hub or switch and will cause network congestion
- Comparatively higher costs than bus networks (Installation and equipment)
Uses of Extended Star Topology
- The extended star topology is majorly used where we need to connect multiple nodes to one central node and control of all nodes is from the central node.
- It can be used to establish the LAN (Local Area network) connection. The LAN connection helps to connect systems to one central point. The LAN connections are meant for shorted distances
- It helps to transmit the data and information to any other node on the network. One node can send message to any other node provided all nodes are connected to central hub or switch
- It is used in homes and offices. The failure probability of the network can be reduced using extended star topology. As the nodes connected to one central hub there is a little chance that network will fail as the nodes are independent of each other and connected to central hub or switch
Continue Reading:
Hub and Spoke/Star Network Topology
What is LAN? Detailed explanation
Tag:routing



