Cisco FTD Deployment Modes
(FTD Deployment Modes: Routed, Transparent, Inline, Inline with tap, Passive SPAN, Passive ERSPAN)
Cisco FTD design and deployment implementation involves setting up firewall, SSL inspection, NAT, IPS and active/standby HA. Deployment model determines placement of FirePower into the network as Firewall/IPS device or as an IPS only device. In Firewall/IPS mode you have the option to choose between routed and transparent mode and in IPS only devices you can choose between inline and passive mode.
In today’s blog we will cover in detail about FTD deployment modes, differences between each of the modes, and use cases.
Cisco FTD Deployment
Cisco FTD interface could be deployed in
- Regular firewall mode and
- IPS only mode
We can include both firewall and IPS only interfaces on the same device.
FTD Deployment Modes: Regular Firewall Mode
Regular firewall mode interface subject traffic to firewall functions such as maintain flows, track flow states at IP and TCP layer, IP defragmentation, TCP normalization. IPS functions can be configured optionally for traffic according to security policy. The type of firewall interfaces one can configure based on firewall mode set for the device: routed or transparent mode.
FTD Routed Mode Deployment
Routed mode interfaces routed firewall mode only, each interface that you want to route between is on a different subnet.

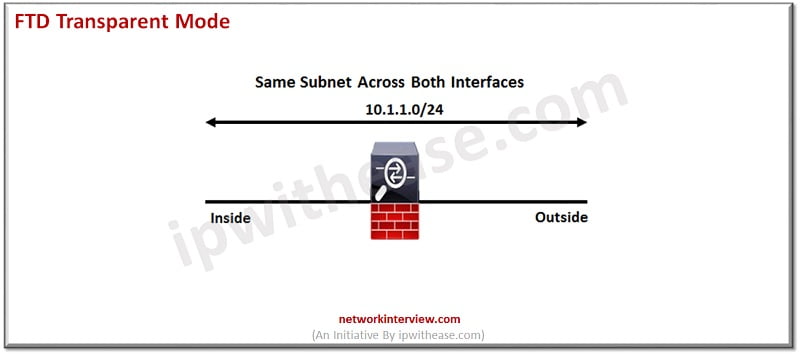
FTD Transparent Mode Deployment
In transparent mode the firewall is configured as a switch and no IP address is assigned to any interface except to the firewall itself.
Limitations of FTD transparent mode (Firewalls)
- No unicast/ multicast routing
- No DHCP relay
- No VPN termination
- LAN cannot be used as an enterprise gateway
However, NAT feature can be enabled in transparent mode
To configure a transparent firewall, we have to configure the bridge group and add interfaces to that bridge group. In transparent mode each bridge group is separate and not communicate with each other. FirePower threat defence (FTD) system use bridging technique to pass traffic between interfaces. Each bridge group includes Bridge virtual interface (BVI) to which IP address is assigned on network. In routed mode FTD routes between BVI and regular routed interfaces.
Access rules in transparent firewall mode
- ARP is allowed by default and can be controlled with ARP inspection
- IPv6 neighbour discovery is not allowed by default
- Multicast and broadcast (RIP/OSPF/EIGRP) traffic not allowed by default
- STP BPDU is allowed by default to prevent loop
FTD Deployment Modes: IPS Only Mode
IPS only mode can be deployed in three ways. Let us understand each one of them more in detail.
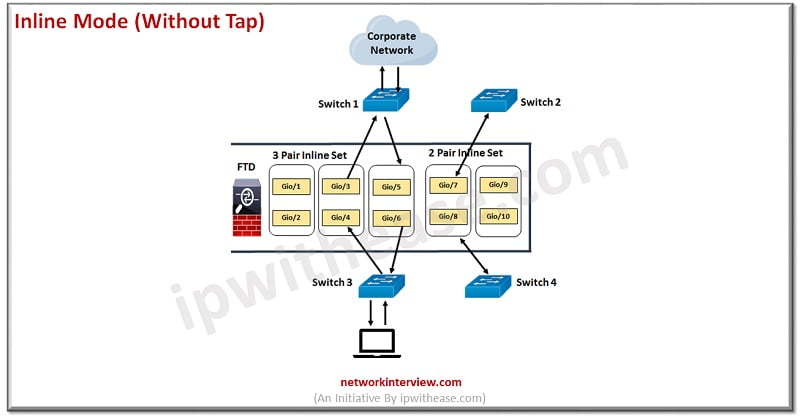
Inline Mode
Inline Mode (without tap) – When it comes to inline mode, only two interfaces can be connected for each pair. Whatever is received on either of the interfaces will be checked and then transmitted to the other interface without any MAC switching or IP routing. It functions similarly to a wire with an inspection module in the middle.
When compared to transparent mode, inline mode has a different function as multiple interfaces may be incorporated into each bridge group, making each bridge group behave like a separate switch.
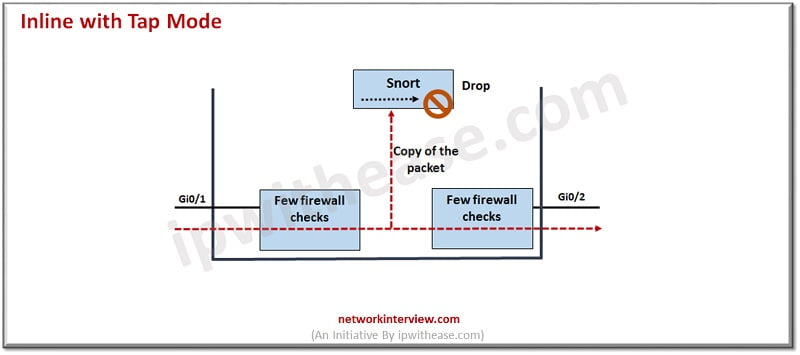
Inline with Tap Mode
In tap mode however, traffic itself is not inspected but its copy is inspected. So, it is not possible to drop intrusions in this mode but only alerts can be received. FTD will make a copy of each packet so it can analyse it. This is ideal where you want to fine tune your intrusion policy and add drop rules which best protect your network without hampering its efficiency. Once you are ready to deploy FTD online you can disable tap mode.
Passive Mode
In this mode FTD will not sit physically inserted into the path. Copy of traffic will be sent to IPS with the help of SPAN/RSPAN/ERSPAN technology.
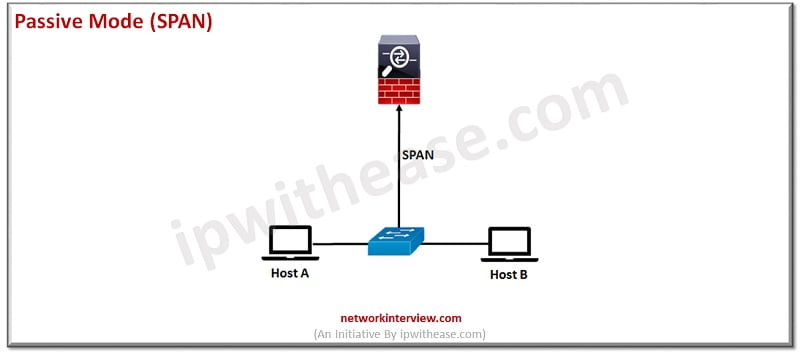
Passive Span Mode
Passive interface monitors traffic flow across the network using a switch SPAN or mirror port. The SPAN or mirror port allows for traffic to be copied from other ports on switch. FTD cannot take actions such as blocking or shaping traffic in passive mode.
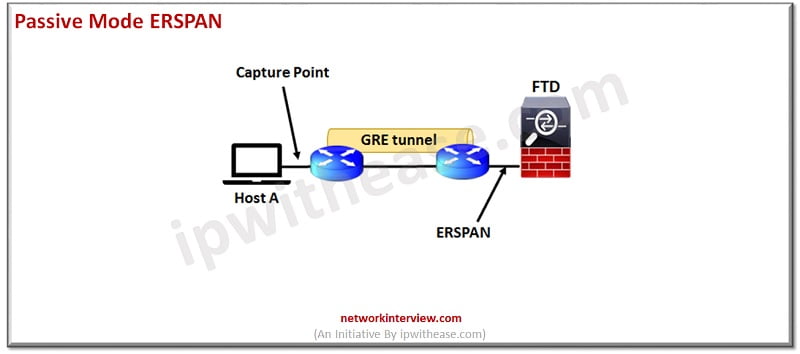
Passive ERSPAN Mode
Encapsulated remote switched port analyzer (ERSPAN) interfaces allow monitoring traffic from source ports and uses GRE to encapsulate traffic. In routed firewall mode only ERSPAN interfaces are allowed.
Continue Reading:
Palo Alto Interface Types & Deployment Modes Explained
Understanding Checkpoint 3-Tier Architecture: Components & Deployment



