How to make a career in Cybersecurity or Ethical hacking? 2025
Career in Cybersecurity
In this digital world, data is everywhere. This ensures that there are ample opportunities for people who have a passion for ethical hacking, known as “ethical hackers” to find jobs with companies that need their services. A Cybersecurity job requires technical skills and the ability to think strategically. It’s not just about figuring out how to hack into a system; it involves finding ways to protect sensitive data and make sure that systems can’t be hacked. This article will explore what it takes to make a career in Cybersecurity, look at different types of Cybersecurity job opportunities, explain educational requirements and give advice on how to become one.
What is a Cybersecurity Expert?
A Cybersecurity expert is someone who has mastered the art of hacking and uses their expertise to protect a company’s systems. He/She is an individual who has the skills and expertise to protect a company’s computer networks and sensitive data by finding and fixing vulnerabilities. As more companies move their data to the cloud, the need to protect remote data has increased.
Cybersecurity associate uses its hacking skills ethically to test systems for vulnerabilities. They use the same hacking tools malicious hackers use to find security holes and then fix them. Cybersecurity associates are also responsible for keeping company employees safe from online threats by training them about cybersecurity best practices.
Cybersecurity is a growing field with a projected 22% increase in jobs from 2016 to 2026, which is much faster than average. There is currently a shortage of skilled workers in this field, so the demand for qualified candidates will be high.
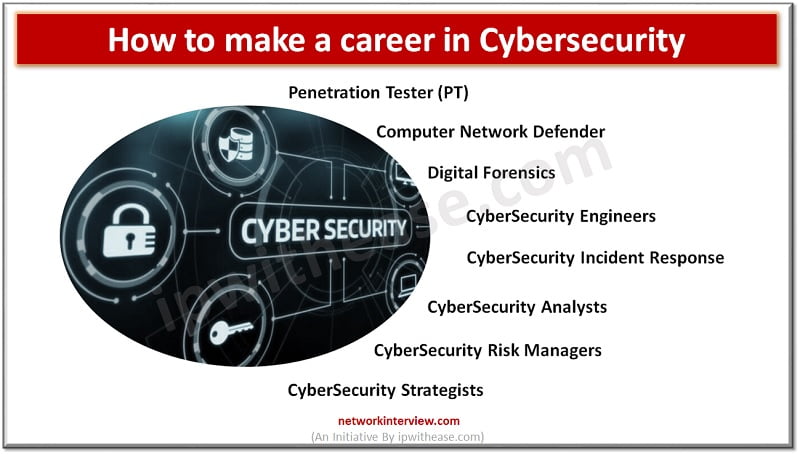
Career in Cybersecurity: Jobs
There are many different types of jobs in the Cybersecurity field, and each has its own specific set of skills and duties. The type of job you choose will likely reflect the type of education you have.
- Penetration Tester (PT): Penetration testers hack into computer systems to see how easy it is to gain unauthorized access. They often do this with network security monitoring software and by creating false logins. As part of their job, they might also investigate data breaches or other cyber attacks. Penetration testing is a common task of ethical hackers.
- Computer Network Defense: Computer network defenders try to stop attackers from gaining access to computer systems. They might design security systems and policies or perform incident response. Computer network defenders often work in the government or military.
- Digital Forensics: Digital forensics experts investigate data breaches or other cyber attacks. They collect evidence for law enforcement and might testify in court about what happened.
- CyberSecurity Engineers – CyberSecurity Engineers design systems that protect computer networks. They will often be involved in the installation of new systems and may also be responsible for making sure that the systems are operating correctly.
- CyberSecurity Analysts – CyberSecurity Analysts investigate cybersecurity incidents and breaches. They will often be involved in the forensics part of investigations and may be required to testify in court cases.
- CyberSecurity Incident Response Teams – CyberSecurity Incident Response Teams are responsible for responding to cybersecurity incidents. These incidents can range from small data breaches to large-scale cyber warfare.
- CyberSecurity Risk Managers – CyberSecurity Risk Managers assess risk to a company’s computer systems. They will make recommendations to senior management on how to improve security and which systems need more attention.
- CyberSecurity Strategists – CyberSecurity Strategists design the overall cybersecurity strategy for a company. They will develop plans to protect computer networks and identify areas of risk.
CyberSecurity Engineers, Analysts and Incident Response Teams are often employed by organizations such as defense contractors and government agencies that deal with sensitive information. Risk Managers and Strategists typically work for companies that manage sensitive data, such as financial institutions, healthcare providers and retail companies.
Educational Requirements
There is no degree specifically for Cybersecurity, but there are many degree programs that will prepare you for a career in Cybersecurity, such as –
- Information or Computer Science: These programs will teach you fundamentals such as programming and computer systems. You also might study cryptography, machine learning, artificial intelligence or other topics relevant to cybersecurity.
- Information Systems: An information systems degree program will combine computer science with business courses. You’ll learn about systems design and management, including how to protect computer systems.
- Computer Engineering: Computer engineers need to know about computer systems, programming and networks. You’ll learn about how computers work and how to design systems that run efficiently.
- Computer Forensics: A computer forensics degree will teach you about collecting evidence from computers. You might learn about network security, digital evidence, cryptography and computer crime laws.
How to Become a Cybersecurity Expert
- Start with a Boot Camp: Boot camps are intensive courses that usually last three months. They often focus on cybersecurity, coding and data analytics. Boot camps are great ways to jump into a cybersecurity career quickly. You may be able to earn a certificate or degree after the program.
- Get a Bachelor’s Degree: You may want to earn a bachelor’s degree to get a job or advance in your career. Most employers prefer job candidates with a bachelor’s degree, and this degree may help you earn more.
- Find an Internship: You may want to get experience before you start applying for jobs in Cybersecurity. This can be helpful if you don’t have the right education or don’t have the time to go back to school. Look for cybersecurity organizations that offer internships.
- Get Experience: Many employers hire people with experience in a field. You can build your experience by creating your cybersecurity project. You might want to work on your own or as part of a team.
Cybersecurity Certifications
Many different certifications can help you. You can earn many of these by taking online courses or by studying at a college or university. The SANS Institute is one of the most well-known organizations for cybersecurity training. It offers a variety of courses, including Introduction to Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking.
These courses are designed for beginners and are a great way to get started in the field. Another well-known organization is (ISC)2. It offers many different cybersecurity certifications, including
- Certified Cybersecurity Risk Engineer (CCRE),
- Certified Cybersecurity Risk Management (CCRM) and
- Certified in Cybersecurity Defense (CCD).
CyberOps Associate certification
The Cisco Certified CyberOps Associate accreditation is designed to affirm the everyday, tactical knowledge and abilities that Security Operations Center staffs require to identify and answer cyber security risks. The CyberOps Associate exam and education are connected to understanding and capabilities associated with security principles, protection tracking, host-based assessment, network intrusion analysis, and security protocols and guidelines.
Bottom Line
Cybersecurity is a growing field with a projected 22% increase in jobs from 2016 to 2026, which is much faster than average. There is currently a shortage of skilled workers in this field, so the demand for qualified candidates will be high.
With the rise of online learning and the many free courses available, it has become much easier for people to explore new careers and try out new fields. Cybersecurity is a great field to explore if you have a passion for technology and enjoy problem-solving.
Continue Reading:
Career in Cyber Security or Cloud Computing: Which is better?
Top 10 Cybersecurity trends for 2023



