Packet Flow in Checkpoint Firewall
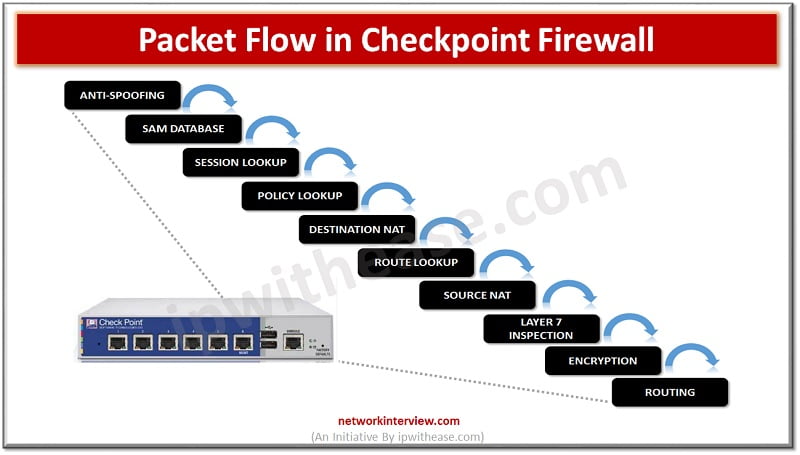
Checkpoint Firewall Packet Flow
In the above image Checkpoint Firewall packet flow is shown.
Let’s start with Anti-spoofing.
Anti-Spoofing
Anti-spoofing is a technique which can identify the packet and drop it if the packet has a FAKE/False source address.
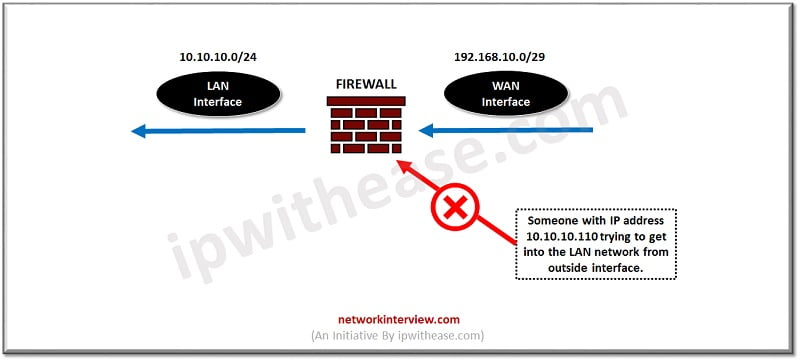
Let’s understand it with a diagram. On the WAN interface you have IP address 192.168.10.0/29 and LAN interface has 10.10.10.0/24 subnet.
When someone from the WAN interface tries to get into the LAN network by using a dummy/FAKE IP address which belongs to the LAN network, firewall blocks that traffic by its intelligence and this phenomenon is known as Anti-spoofing.
Anti-spoofing acts at interface level and Checkpoint is using this feature to protect the network from malicious invaders.
SAM Database
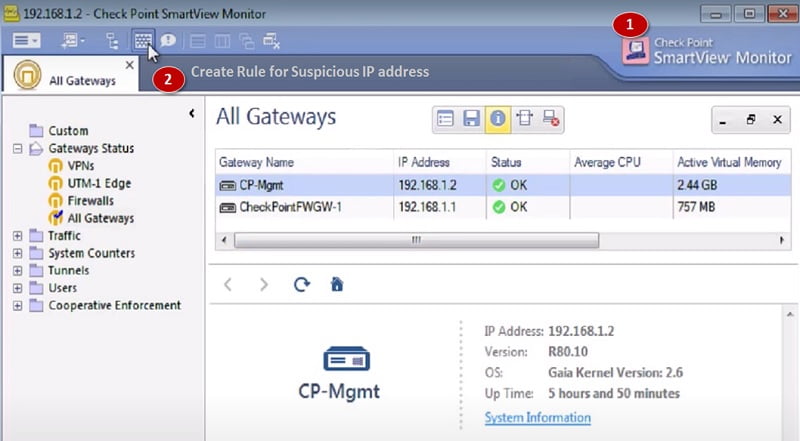
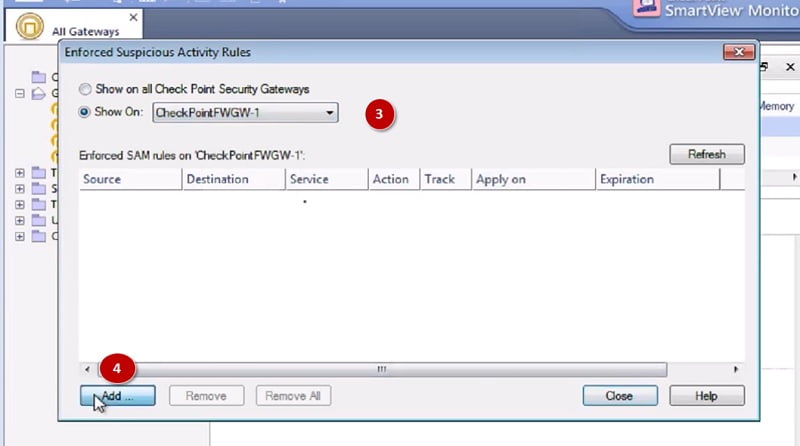
SAM means suspicious activity rule which is integrated with SmartView Monitor that is used to modify access privileges after detection of any suspicious network activity. (Example attempt to gain the unauthorised access of any server or any application in any organisation)
You can check the SAM database in SmartView Monitor and add any malicious IP address to block the traffic. Please see below images to check suspicious IP block method in the SAM database.
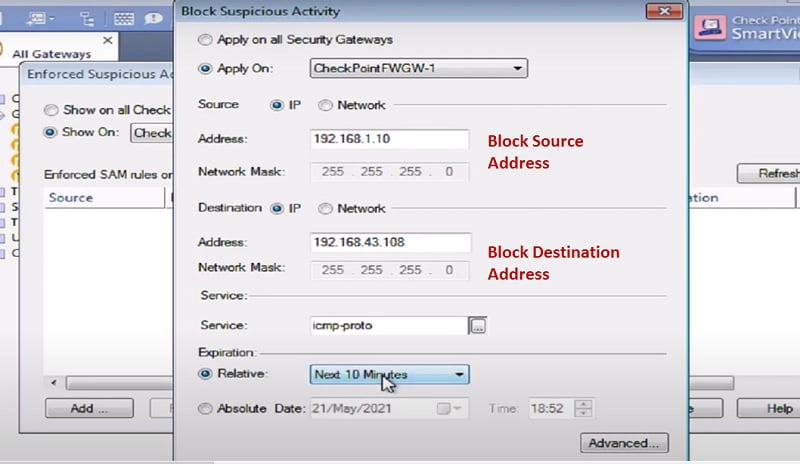
Session Lookup
Session lookup means the firewall checks if a session is there in the firewall session table OR if it’s a new packet. Next step is to match the traffic with firewall policy.
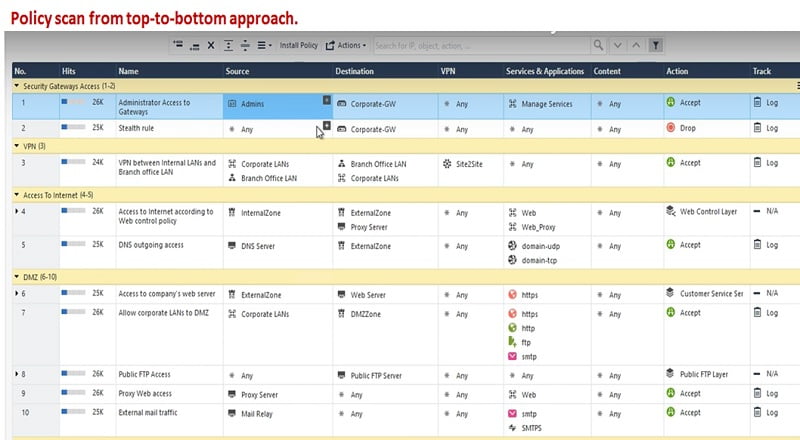
Policy lookup is performed by firewall from top-to-bottom approach once session lookup completed by Checkpoint firewall.
Policy Lookup
Checkpoint Firewall checks 5 tuples in a packet to match with the security policy of Firewall rules. These 5 tuples are source address, source port, destination address, destination port and protocol (TCP/UDP).
If policy exists for the current packet, traffic will be allowed by the firewall else dropped silently at policy level.
When a firewall searches any packet against the Security policy rule, it checks Policy name, Source address, destination address, if the packet has any VPN configuration, services and Applications, action (drop/accept/block) and takes decision according to the policy match.
Firewall discards the packet if no policy match is found in the security rule. Means by-default traffic is dropped by firewall.
Firewall has two types of policies
- Explicit Policy: Administrator defined policies are known as explicit policy.
- Implicit Policy: System generated policies are known as Implicit policy. We neither modify them nor disable/enable them.
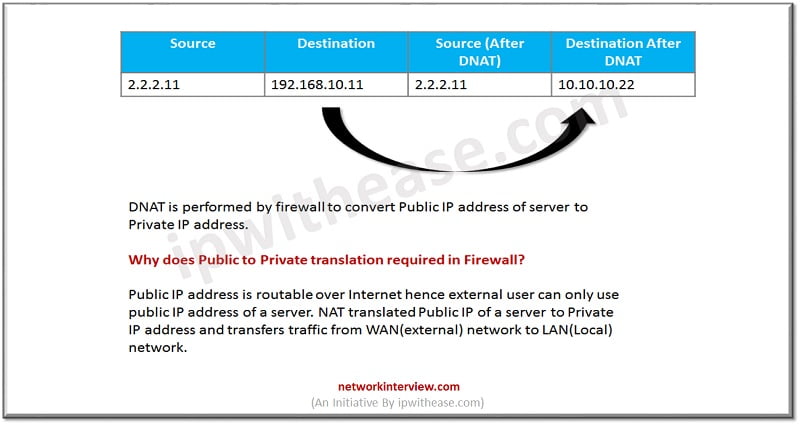
Destination NAT
Packet moves to the Destination NAT phase post policy lookup performed by Checkpoint firewall. Destination NAT is always created for the inside server which needs to be accessed from the outside world.
In Destination NAT firewall checks if the IP address in the packet comes from outside to inside to access the services.
In Destination NAT Public IP address of server will be changed to Private IP address. After that route for Private IP address will be checked by firewall to move the traffic to correct server zone (LAN/DMZ/etc.)
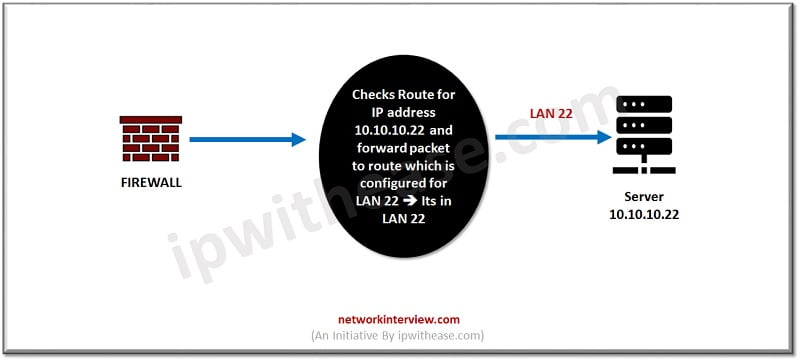
Route Lookup
Route of the source in packet will be checked in the route table. When traffic comes from outside to the inside server, e.g. DMZ server must be hosted on the Internet segment to communicate with Internet users.
Once a public IP address changed to Private IP firewall looks for the route for private IP address of server and send traffic to private IP address.
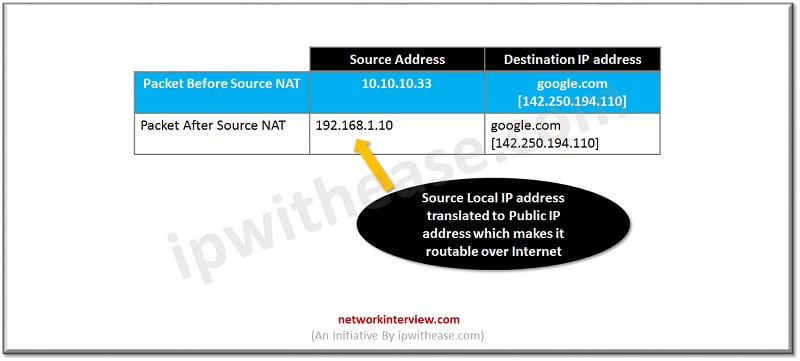
Source NAT
Source NAT will be checked when traffic goes from inside to outside. If the packet goes from inside LAN segment to outside Internet, then source NAT will be performed by Firewall. Otherwise, this step will be skipped by the firewall. Internal IP addresses are not routable over the Internet. Source NAT can be performed for single IP address or for multiple IP address.
Layer 7 Inspection
First understand what Layer 7 inspection is.
It is a technology which is used to analyse TCP/IP based traffic. Layer 7 inspection included Anti-Virus scanning, URL-Filtering, Application Control, anti-spoofing, website-categorisation, Anti-bot, Anti-spam blades.
It is a deep level packet inspection performed by Checkpoint firewall by using its security blades. Checkpoint security blades have below featured
- IPS
- Anti-Virus
- Anti-Bot
- Application Control
We can enable Application Layer & inspection by using below steps:
Encryption
Here, Checkpoint checks if the packet is encrypted or not. If the packet belongs to VPN or SSL, it is in encryption format. Encryption is performed on VPN traffic after L7 inspection and check if there is any route for tunnel Gateway from source to destination.
Route is a mandatory factor in site-to-site VPN. Packet takes IPSec route whenever traffic goes via VPN tunnel.
Routing
Final step is to redirect the firewall packet to the correct interface (Ingress or Egress) as to reach the destination hop from Checkpoint firewall. It could be an exit interface or inbound interface.
Routing will be checked by Checkpoint firewall post encryption to redirect the traffic to the correct route.
Continue Reading:
FortiGate Packet Flow: Ingress And Egress
Packet Flow in Palo Alto – Detailed Explanation
Tag:Checkpoint, Security



