TCP/IP MODEL vs OSI MODEL: Detailed Comparison
Whenever networks are implemented and different devices try to communicate over the network. Some of the other reference models are being referred to which is a standard specification or framework to provide standardization on how implementation, connectivity, communication will happen. It could be OSI or TCP/IP Model. Both are reference models which means we can take a reference or help from the specification of these two models while designing a network. All reference models follow a layered architecture approach and the same applies to OSI and TCP/IP.
Today we look more in detail about two most popular and widely used reference models – OSI and TCP/IP, their features, functions and use cases.
About TCP/IP model
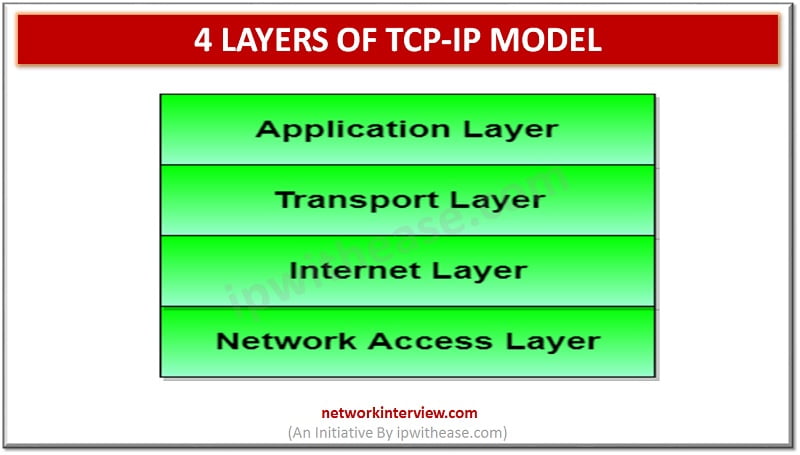
TCP stands for Transmission Control Program and IP stands for Internet protocol. TCP/IP model has a layered architecture and has four layers. The TCP/IP model is protocol-oriented standard. This model was developed by the Department of Defence (DOD) project agency. Internet protocols are a set of rules defined for communication over the network. TCP/IP is considered the standard model for networking and handles data transmission and IP handles addresses. The TCP/IP suite includes protocols such as TCP, UDP, ARP, DNS, HTTP, ICMP etc.
TCP/IP Model Features
- Multi-vendor support is available
- Used for around 35 years and most widely used protocol
- It supports interoperability
- It supports logical addressing
- It has routability feature
- It has name resolution feature
- Error control and flow control are supported features
About OSI Model
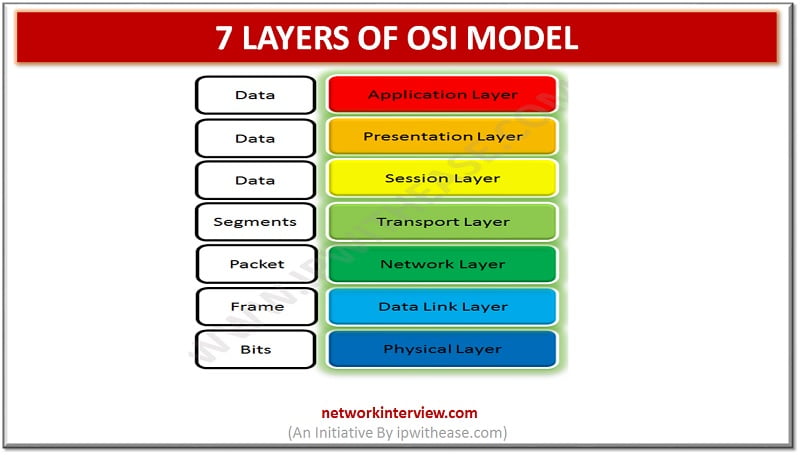
The OSI stands for Open System Interconnection, developed in the 1980s by the International standard organization. It is a conceptual model used in network communication. The OSI model consists of seven layers and each layer is connected to each other. The data moves through the OSI model from its start till end (Last layer of OSI model).
OSI Model Features
- Model to demonstrate how hardware and software work together
- Ease of troubleshooting (Each layer detects and handles error)
- Reduction in complexity
- Standardization of interfaces
- Facilitates modular engineering
- Provides interoperability between vendors
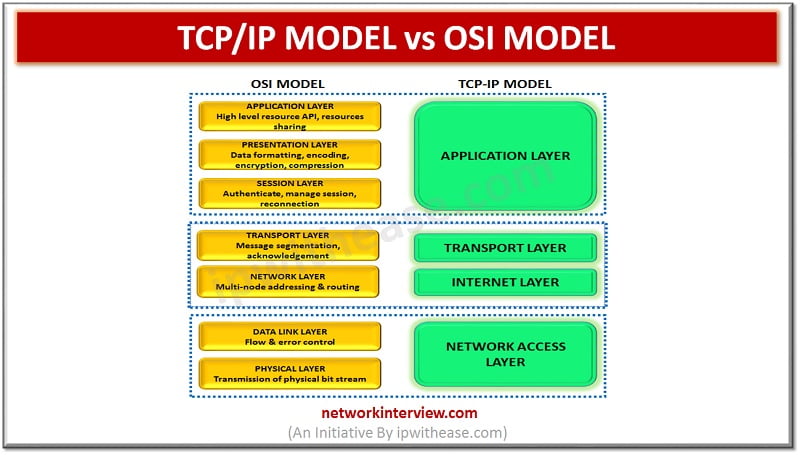
The application layer of the TCP/IP model maps to the first three layers i.e., Application, Presentation & Session Layer of the OSI model. The transport layer maps directly to the transport layer of the OSI model. The Internet layer maps to the Network layer of the OSI model. The last two layers of the OSI model map to the Data link layer and physical layer of OSI model. TCP/IP model is more widely used as compared to OSI model.
Similarities between TCP/IP and OSI Model
Common Architecture – both models are logical and have similar architecture based on layered approach.
Defined Standards – both models define the standard and framework for implementing the standards and devices.
Troubleshooting is simplified – by breaking complex functions at each layer into simple components.
Pre-defined standard – the protocols and standards are already pre-defined; and models do not redefine them, it just references it or uses it. Like Ethernet standards were already defined by IEEE before the origin of this model and it uses this in its reference at Physical layer or Network access layer.
Similar functionality at transport and network layer – function performed between presentation and network layer is similar to the function performed at transport layer.
Comparison Table: TCP/IP MODEL vs OSI MODEL
Below table summarizes the differences between the two:
FUNCTION | TCP/IP MODEL | OSI MODEL |
| Definition | TCP/IP stands for Transmission control protocol/ Internet protocol | OSI stands for Open systems Interconnection |
| Developed by | It is developed by DOD (Department of Defence) project agency. | OSI model is developed by ISO (International standard organization). |
| Technology/ Platform | It comprises of a set of standard protocols which lead to development of the Internet. It is a communication medium which provides connection between hosts. | It is an independent standard and generic protocol used as a communication gateway between network and end user. |
| Delivery of Packets | No guaranteed delivery of packets at transport layer. | Transport layer provides guaranteed delivery of packets. |
| Approach | Based on horizontal approach. | Based on vertical approach. |
| Application Layer | Session and presentation layers are not separate, both are included in application layer. | Session and presentation layers are separate |
| Type of Model | Implemented model of OSI model. | It is a reference model on which various networks are built. |
| Network layer | Network layer provides only connectionless service. | Network layer provides connection oriented and connection less services (Both) |
| Replaceable/ Non-replaceable Protocols | Protocols can’t be easily replaceable | In OSI model protocols are hidden and can be easily replaceable when technology changes occur |
| Number of Layers | Comprises of four layers | It comprises of seven layers |
| Protocol Dependent/Independent | Services, protocols, and interfaces are not properly segregated but are protocol dependent | Services, protocols and interfaces are defined and it is protocol independent |
| Usage | Widely used model | Limited usage of the model |
| Standardization of devices | Do not provide standardization of devices | Standardization of devices like router, switches, load balancers and other hardware devices |
Download the Comparison Table: TCP/IP MODEL vs OSI MODEL
Continue Reading:
Tag:comparison, protocol, routing



