Zigbee Protocol: Wireless Mesh Networking
Zigbee is a wireless protocol that enables smart devices to communicate with each other over a Personal Area Network (PAN). It is widely used in home automation systems to control various devices such as light bulbs, sockets, locks, motion sensors, and more. In this article, we will explore the features, advantages, and applications of Zigbee Protocol, as well as its compatibility with other technologies.
What is Zigbee Protocol?
Zigbee is a wireless protocol that enables smart devices to communicate with each other over a Personal Area Network (PAN). It is designed to be a low-cost, low-power solution for home automation and control. Zigbee operates in the 2.4GHz frequency band, the same as WiFi, and uses the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for physical and media access control.
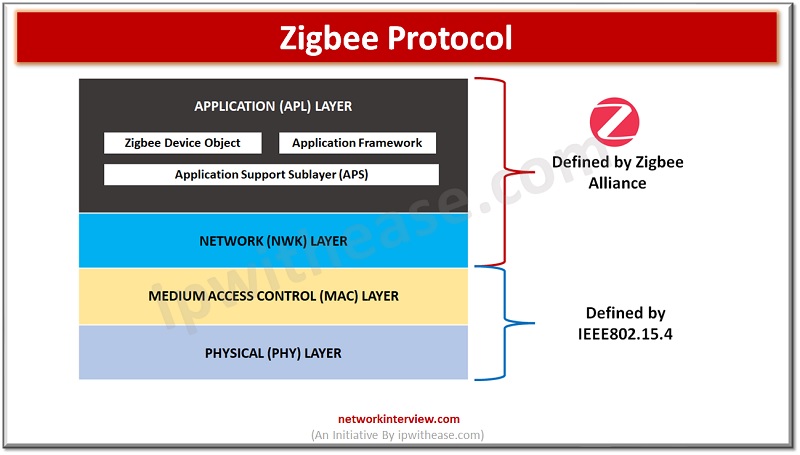
Zigbee Stack
The Zigbee protocol stack is comprised of four layers: the physical layer, the MAC layer, the network layer, and the application layer. The physical layer is tasked with transmitting and receiving data through wireless signals, while the MAC layer manages access control and data framing. The Zigbee network layer takes care of routing data between devices within the network, and the application layer defines the device’s specific functions and features.
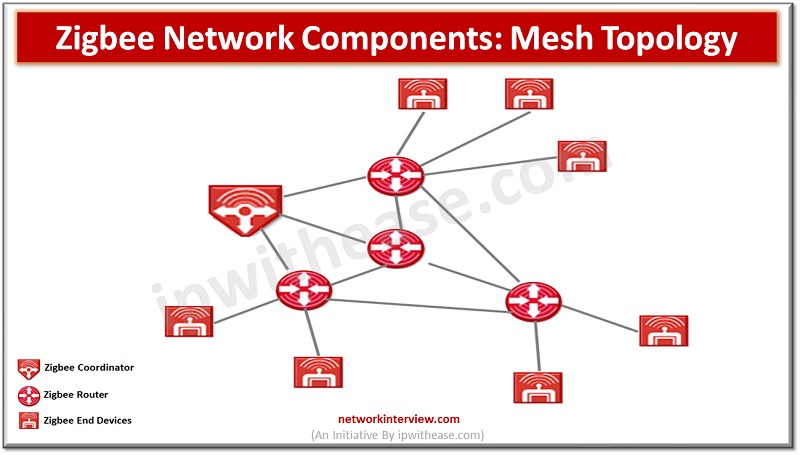
Zigbee Network Components
A typical Zigbee network consists of three main components: the Zigbee Coordinator (ZC), Zigbee Router (ZR), and Zigbee End Device (ZED).
- The Zigbee Coordinator is the central hub of the network and is responsible for setting up and maintaining the network, adding devices, and managing communications between devices. There can only be one Coordinator in a Zigbee network, and it must be permanently powered.
- Zigbee Routers are AC mains-powered devices that act as intermediate devices in the network. They provide the backbone of the Zigbee network by routing communications between devices to create a reliable and efficient network.
- Zigbee End Devices are typically battery-powered devices that can only send or receive data. They cannot perform routing tasks and can only communicate with Routers or directly with the Coordinator. Examples of Zigbee End Devices include motion sensors, door sensors, temperature sensors, and door locks.
How Does Zigbee Work?
Zigbee builds upon the physical layer and media access control defined in the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. It uses a mesh networking topology, where devices communicate with each other through intermediate devices called Routers. This allows for multiple communication paths and increased network coverage.
Zigbee devices are designed to be simple and focused on specific tasks, such as motion sensing or dimming lights. This simplicity allows for better performance and reliability. The Zigbee network is self-configuring and self-healing, meaning that devices can automatically join and leave the network, and the network will adapt and reroute communication when needed.
Benefits of using Zigbee
There are several reasons why Zigbee is a popular choice for home automation systems:
- Lighting Options: Zigbee has a wide range of lighting options, including LED bulbs, color-changing LED strips, light switches, and dimmer modules. This makes it a versatile choice for creating different lighting scenes and effects in your home.
- Power Efficiency: Zigbee devices are designed to be energy-efficient, with some devices boasting up to 10 years of battery life. This makes Zigbee ideal for battery-powered devices such as motion sensors and door sensors.
- Optimized for Battery Devices: Zigbee is optimized for battery-powered devices by using a sleep mode when the devices are not in use. This helps to conserve battery power and extend the lifespan of the devices.
- Network Stability: Zigbee uses a mesh networking topology, which means that devices can communicate with each other through multiple paths. If one device goes offline, the network will automatically reroute the communication through another device, ensuring a stable and reliable connection.
- Security Features: Zigbee employs 128-bit AES encryption, the same level of security used in online banking services. This ensures that the communication between devices is secure and protected from unauthorized access.
- Firmware Updates: Zigbee supports over-the-air firmware updates, allowing devices to receive software updates without the need for manual intervention. This ensures that your devices are always up to date with the latest features and security patches.
- Scalability and Affordability: Zigbee networks can support thousands of devices in a single network, making it suitable for both small and large-scale home automation systems. Additionally, Zigbee devices are often more affordable compared to other technologies such as Z-Wave and WiFi.
Zigbee vs WiFi
Zigbee and WiFi are both wireless technologies, but they have different strengths and use cases. WiFi is well-suited for high-bandwidth tasks such as video streaming and online gaming, while Zigbee is designed for low-power, low-bandwidth applications.
WiFi networks are typically limited in terms of the number of devices they can support, usually between 32 and 64 devices. Zigbee, on the other hand, supports thousands of devices in a single network, making it ideal for home automation systems with a large number of devices.
When it comes to smart home applications, Zigbee is more power-efficient and can provide longer battery life for devices. Additionally, Zigbee’s mesh networking topology ensures better network coverage and stability compared to WiFi.
Zigbee vs Z-Wave
Zigbee and Z-Wave are two popular wireless protocols used in home automation systems. Both protocols have their own advantages and considerations.
Zigbee has a wider range of device options, especially for lighting applications. There are more Zigbee-based devices available in the market, including LED bulbs, light switches, and dimmer modules. Zigbee also supports a larger number of devices in a single network, making it suitable for larger homes or commercial applications.
Z-Wave, on the other hand, is known for its reliability and compatibility. Z-Wave devices typically have better range and signal penetration, making them suitable for larger homes with multiple floors or thick walls. Z-Wave also uses a different frequency band, which means it is less prone to interference from other wireless devices.
In general, it is recommended to choose a smart home controller that supports both Zigbee and Z-Wave to have the flexibility to choose devices from both protocols.
Conclusion
Zigbee is a wireless protocol that offers a range of benefits for home automation systems. With its extensive device options, power efficiency, scalability, and security features, Zigbee is a popular choice for creating a smart home ecosystem.
With Zigbee’s open standard and widespread adoption by major companies, it’s clear that Zigbee is here to stay and will continue to play a significant role in the future of smart homes.
Continue Reading:
Top 10 wireless technology trends
What is Wireless Mesh Technology?
Tag:New technology, wireless



