
What is WAN? Detailed Explanation
Introduction to WAN
Computer Networks can be divided into various types depending upon their size and usability. The size of a network can be assessed by its geographical distribution. It can be as small as a room with a few devices/computers or as widespread as across the world, with a million of interconnected devices. Some of the most important types of computer networks are :
- PAN
- LAN
- WAN
- MAN
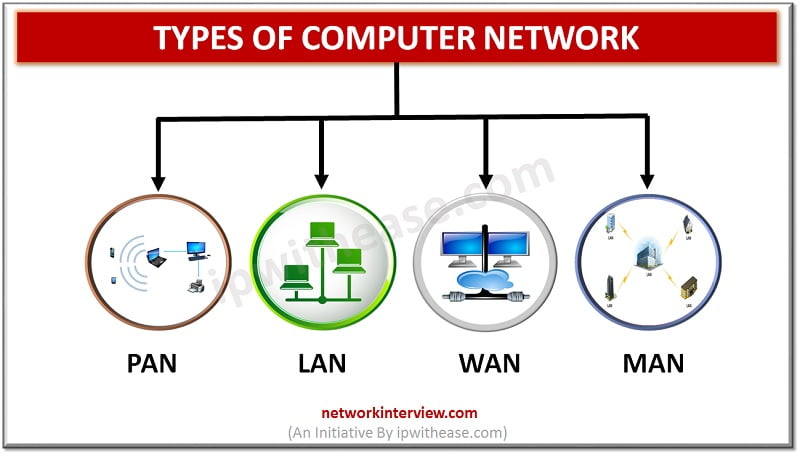
In this article, we will try to understand WAN in detail.
What is WAN?
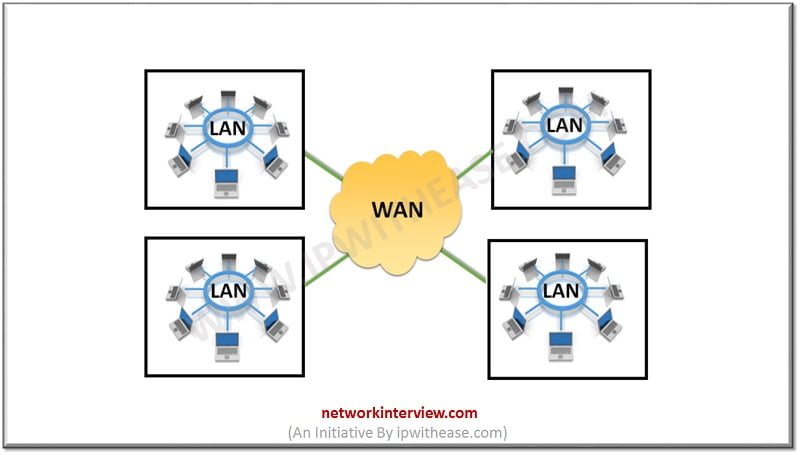
WAN is abbreviation for Wide Area Network. WAN is a network that covers a broad area and used to connect end devices like computers and printers which are distributed across long distance. WAN is used to connect different LANs , so it may also be called a network of networks. Internet is essentially a WAN only, that can be regarded as the largest WAN of the world.
History of WAN
WAN was first created by the U.S. Department of Defense. They developed ARPANET i.e. Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, the first ever wide-area packet-switching network with distributed control and the first ever network to implement TCP/IP protocol suite.
Characteristics of WAN
- It provides coverage over a large geographical area with a very broad reach ranging from a state, a country or entire world.
- It needs a public carrier for connection and transmission like a cable system, telephone network, satellites etc.
- It enables the remote access of computers by the users that provides an easier transmission and exchange of data and information.
- It facilitates the centralized storage of data because of remote access.
- WAN is maintained and operated by service providers who exist under distributed ownership.
Drawbacks of WAN
- High cost of initial setup.
- It is vulnerable to attacks and a strong security posture is required for its protection.
- Maintenance is difficult as it requires skilled technicians & network administrators.
- Data transfer speed is lower (upto 100 Mbps).
- High traffic congestion.
WAN Terminology
The various terms of WAN technology are:
Packet switching:
Packet Switching is a data transmission method, in which data is transmitted in the form of small packets. The message to be transmitted is broken into small parts called packets. Each packet is sent independently over the optimum route and all these packets then reassemble at the destination.
TCP/IP protocol suite:
TCP/IP i.e. Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol is a communication protocol that is used to interconnect the network devices.
Router:
It is a network device that is used to interconnect LANs to form a Wide Area Network.
Overlay network:
Overlay Network is a virtual network that is built top of another network.
PoS (Packet over SONET/SDH):
It determines the communication of point-to-point links while using optical fiber and SONET i.e. Synchronous Optical Network or SDH i.e. Synchronous Digital Hierarchy.
MPLS:
MPLS i.e. Multi Protocol Label Switching (MPLS). It is a technique used for the routing of network packets.
ATM:
ATM i.e. Asynchronous Transfer Mode is a switching technique that uses asynchronous time-division multiplexing to encode data into small, fixed-sized cells. It has largely been superseded by today’s IP-based technologies.
Frame Relay:
It is a technology that is used to transmit data between the LANs in a wide area network. The data is transmitted in the form of frames.
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN is Software Defined Wide Area Network. It uses virtualization and software platforms to provide a more efficient data transfer across WAN. It provides easier deployment, operation and management of WAN architecture.
Some of the prominent SD-WAN vendors available in the market are: VMware, Cisco Viptela & Meraki, Silverpeak, Fortinet, Citrix, Aryaka, Huawei and Riverbed SD-WAN.
Continue Reading:
To understand WAN technology in detail, check our video:
Tag:Layer 3



