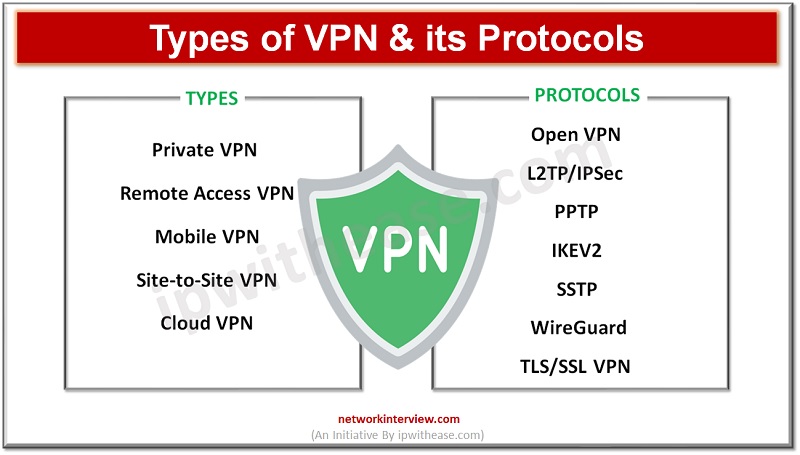
Types of VPN & its Protocols
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a technology that creates a secure and encrypted connection over the internet, allowing users to access the internet as if they were connected to a private network. VPNs are used for several purposes, primarily centered around security, privacy, and anonymity. You can get a VPN 7-day trial to understand the working of VPN in detail.
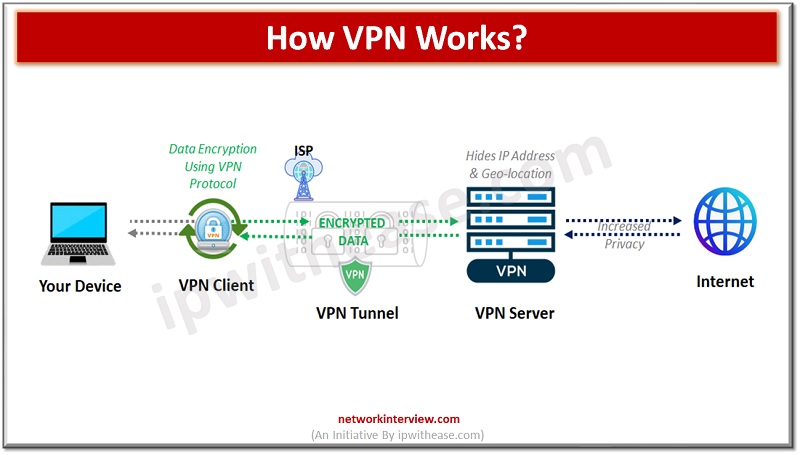
How VPN Works?
Encryption: When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic is encrypted, meaning that it is converted into a code that can only be deciphered by your device and the VPN server.
Tunneling: VPNs create a secure “tunnel” between your device and the VPN server. This tunnel ensures that your data remains protected as it travels over the internet.
Remote Server: Your internet traffic is routed through a remote VPN server located in a different location or country. When you access websites or online services, it appears as if you are doing so from the location of the VPN server, not your actual location.
Types of VPN
Lets discuss the major types of VPN:
Private VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Purpose: Private VPNs are designed for individuals or small groups seeking to enhance online privacy, security, and the ability to bypass geo-restrictions.
Usage: Typically used by individuals to protect their online activities, access blocked content, or secure their internet connections, especially when using public Wi-Fi networks.
Characteristics: Private VPN services often offer a choice of server locations, encryption protocols, and no-logs policies to safeguard user privacy.
Remote Access VPN
Purpose: Remote Access VPNs enable secure connections for remote employees or users to access a corporate network from outside the office.
Usage: Used by businesses to facilitate remote work, allowing employees to access company resources and data securely from home or other remote locations.
Characteristics: Remote Access VPNs typically require client software or apps and strong authentication methods for user access.
Mobile VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Purpose: Mobile VPNs are designed for smartphones and tablets, ensuring secure and encrypted connections while users are on the move.
Usage: Often used by mobile workers and travellers to protect sensitive data when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks or accessing corporate resources remotely.
Characteristics: Mobile VPN apps are available for various platforms and provide seamless connectivity and data protection for mobile devices.
Site-to-Site VPN (S2S VPN)
Purpose: Site-to-Site VPNs establish secure connections between multiple networks or remote locations, allowing them to communicate as if part of a single network.
Usage: Commonly used by organizations to interconnect branch offices, data centers, or remote sites to share data, resources, and services securely.
Characteristics: Requires dedicated VPN gateways or routers at each location, and all data traffic between sites is encrypted.
Cloud VPN (Virtual Private Network)
Purpose: Cloud VPNs leverage cloud infrastructure to provide secure connections from remote users or sites to cloud-based resources and services.
Usage: Widely used by organizations adopting cloud computing, enabling secure access to cloud-based applications, databases, and services.
Characteristics: Utilizes cloud provider’s infrastructure, making it easily scalable, cost-effective, and suitable for remote access to cloud resources.
Below table gives a comparative analysis of the different types of VPN:
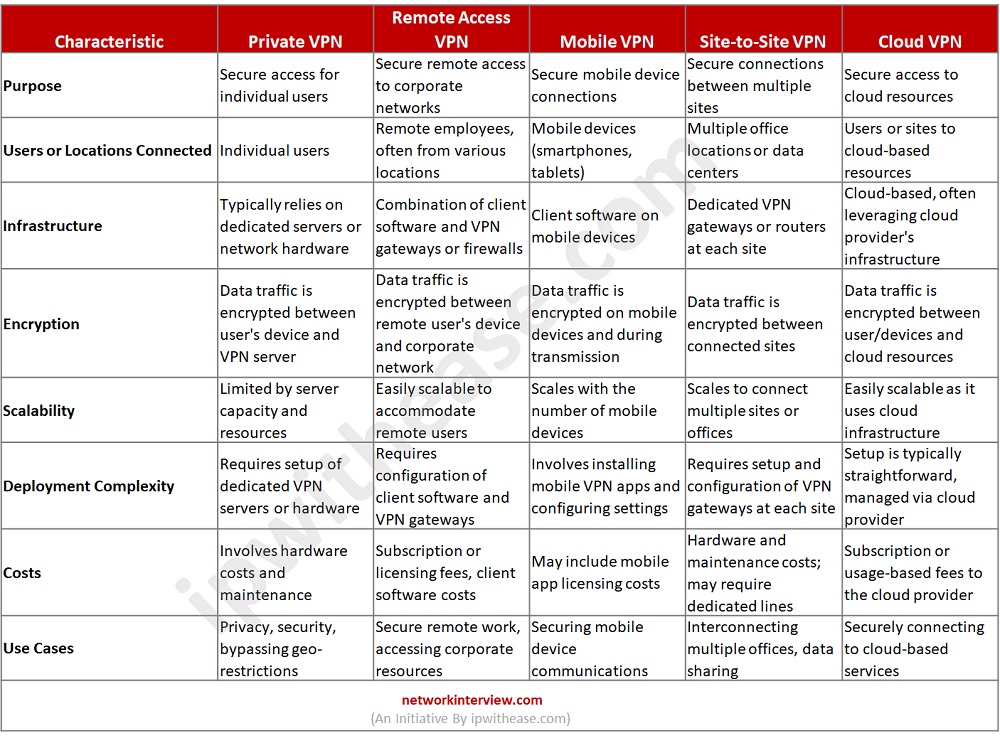
Download the comparison table: VPN Types Comparative table
Please note that the suitability of a specific VPN type depends on your organization’s needs, infrastructure, and security requirements. Each type of VPN serves a distinct purpose and may be used individually or in combination to meet your organization’s goals for secure and private communication.
Types of VPN Protocols
VPN protocols are essential for establishing secure and encrypted connections between devices or networks over the internet. There are several VPN protocols available, each with its own set of characteristics, strengths, and weaknesses. Here are some common VPN protocol types:
OpenVPN
Security: Very secure, with support for various encryption algorithms and strong authentication methods.
Flexibility: Highly configurable and can run on multiple platforms, making it a popular choice for both remote access and site-to-site VPNs.
Open-Source: OpenVPN is open-source software, which means it can be audited for security and is often trusted for its transparency.
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security)
Security: Offers strong security through encryption and authentication protocols. It’s commonly used in site-to-site and remote access VPNs.
Compatibility: Supported by most operating systems and devices, making it a widely adopted standard.
Variants: IPsec has multiple modes, including transport mode and tunnel mode, to suit different deployment scenarios.
L2TP/IPsec (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol/IPsec)
Security: Combines the tunneling capabilities of L2TP with the security of IPsec, resulting in a secure VPN protocol.
Compatibility: Widely supported but may face challenges with network address translation (NAT) traversal.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol)
Security: Less secure than other protocols due to known vulnerabilities. It’s considered outdated and not recommended for sensitive data.
Compatibility: Widely supported but primarily used for legacy purposes.
IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2)
Security: Offers strong security and is known for its quick reconnection capabilities, making it suitable for mobile devices.
Performance: Fast and efficient due to its ability to re-establish connections seamlessly.
SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol)
Security: Provides strong security, as it’s designed to work with SSL/TLS for encryption. Commonly used in Windows environments.
Reliability: Known for its reliability and ability to traverse firewalls.
WireGuard
Security: Considered highly secure and efficient, with a minimal attack surface. It’s gaining popularity for its simplicity and speed.
Performance: Known for its excellent performance and low overhead, making it suitable for both mobile and desktop use.
Emerging Standard: While relatively new, WireGuard is being adopted as a modern VPN protocol due to its advantages.
TLS/SSL VPN
Security: Strong security provided by SSL/TLS encryption, making it suitable for securing web-based applications and services.
Ease of Use: Typically, does not require additional software installation, as it runs within a web browser.
The choice of VPN protocol depends on your specific requirements, including the level of security needed, device compatibility, and the purpose of the VPN (remote access, site-to-site, or other). It’s essential to select a protocol that aligns with your security and functionality needs while also considering factors like ease of configuration and ongoing maintenance.
Why People Use VPNs?
Security: VPNs enhance online security by encrypting your data, making it much harder for hackers and cybercriminals to intercept and steal your information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.
Privacy: VPNs help protect your online privacy by hiding your IP address. This prevents websites and online services from tracking your location and online activities. It also prevents your internet service provider (ISP) from monitoring your online behavior.
Anonymity: VPNs allow you to browse the internet anonymously. By masking your IP address and routing your traffic through remote servers, it becomes difficult for anyone to trace your online actions back to you.
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: Some websites and streaming services are restricted to specific geographic regions. By connecting to a VPN server in a different location, you can access content and services that might otherwise be blocked in your region.
Public Wi-Fi Security: When using public Wi-Fi networks (like in cafes or airports), your data can be vulnerable to eavesdropping. A VPN encrypts your traffic, making it safer to use public Wi-Fi.
Circumventing Censorship: In countries with strict internet censorship, a VPN can help users bypass government-imposed restrictions and access blocked websites and online services.
Remote Access: Businesses often use VPNs to allow remote employees to securely access company resources and data from anywhere in the world.
It’s important to note that while VPNs offer many benefits, not all VPN providers are equal. Some may have different privacy policies, logging practices, and performance levels. When choosing a VPN service, it’s crucial to research and select a reputable provider that aligns with your specific needs for privacy, security, and functionality.
Continue Reading:
Tag:Security



