Decentralized Applications (dApps): Definition, Uses, Pros and Cons
Decentralized Applications are software programs that run on a blockchain or peer-to-peer network, enabling trustless and transparent operations without central control.
Web 3.0’s ultimate aim is to move the Internet from centralized model to decentralized model. Currently all big giants hold control over systems and applications and its data. This also makes software vulnerable to security threats and downtimes if the hosting server fails or gets compromised. Decentralized architecture puts an end to these kinds of issues.
It is just like a piece of open-source software which runs transactions on decentralized computing systems having no single authority. No single entity controls the application and data stored on distributed nodes thus making it more resilient to cyber threats.
Today we look more in detail about decentralized applications (dApps), what are they?, how they are used, what are their limitations and benefits etc.
What are Decentralized Applications
When you visit a website to reach or fetch its content at the backend it interacts with a centralized server to get you the desired content. Tech giants such as Meta (Facebook), Amazon, Google etc. feed on customer data and generate revenue. Decentralized applications on the other hand brings the freedom from this centralized control in a few hands. Instead of requests going to a centralized server , requests land up to blockchain for information. dApps are applications only without any central control.
App = Frontend + Backend → Hosted on Centralized Network Servers
dApps = Frontend + Backend + Smart Contracts → Hosted on Blockchain
Decentralized applications are software programs which run on blockchain or peer-to-peer(P2P) networks of systems instead of on a single system. dApps are outside the control and preview of single authority. dApps are built majorly on Ethereum platform and used for a variety of purposes including gaming, social media, and finance.
Ethereum network has several applications such as Smart Contracts. Smart contracts allow several parties to agree on conditions that will be coded in the self-executing program. This program automatically executes when coding conditions are met. A smart contract eliminates the dependency and trust on third parties, saves constant attention, time, and cost. Ethereum blockchain is an open-source development platform and environment to build Decentralized Applications (dApps) using Smart Contracts capability.
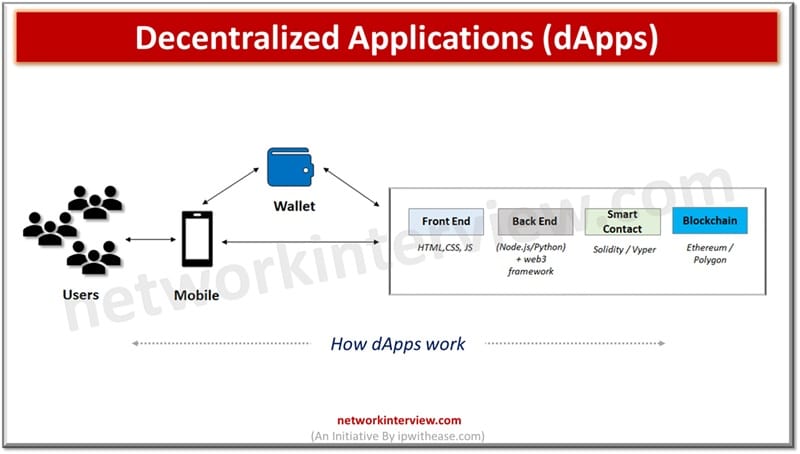
How dApps work
dApps interact with users on mobile or web browsers like a normal web or mobile application only. Users can connect or log in via wallet also to access the application. The dApp hosts are on the blockchain network and source code is available for verification in the network for each node. The front end of an application is coded in HTML, CSS, JS etc. and the backend is written using JS or Python. dApps can run on P2P networks or blockchain networks. Such as BitTorrent , Tor or Popcorn Time applications run on systems that are in a P2P network and allows multiple users to consume the content, feed and content seeding.
Pros and Cons of dApps
PROS
- No single party is authorized to control the application actions to maintain decentralization and equality
- Whole network is decentralized hence there is no single point of failure highly redundant in nature
- User privacy is better guarded as in decentralized application users not required to hand over any personal information
- Enhance possibility to deploy DeFi, which is decentralized finance, a system to ensure anonymous peer-to-peer financial transactions without the need for a middle party or third parties
- Automation of cumbersome processes such as agreement verification etc.
- Eliminate risks of data breach and hacking of personal data
CONS
- Might impact user experience and maintenance as no single party is responsible for upkeep
- Once a smart card is deployed in blockchain it is not possible to alter it
- dApps cloud lead to network congestion due to heavy computation
- Skill gap is a major concern for organizations who wish to switch over to blockchain based applications
- Developers cant alter the code once it is live and available publicly to everyone, some coding flaws and loopholes can be exploited by hackers to gain systems access
Uses of dApps
- Facilitate peer-to-peer financial transactions such as exchange currencies and asset transfers
- Tracking movement of goods in supply chain to ensure transparency and accountability
- Used to securely store and verify identity related information such as voter polls, passport applications, driving license applications etc.
- Facilitate buying and selling real estate directly between buyer and sellers and tracking property ownership and related documentation
- Store and track medical health records and facilitate communication and collaboration between healthcare professionals
- Use to create decentralized platforms for learning , allow user interaction and share content without need for a centralized authority
- Create decentralized platforms for predictive market analytics, let them predict on variety of topics
Tag:services



