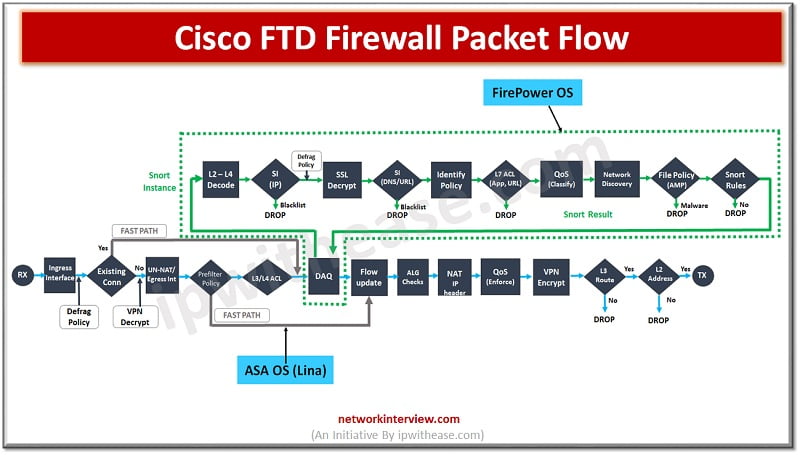
Cisco FTD Firewall Packet Flow
figure:1
As more and more systems are Internet facing due to high penetration of cloud and associates’ applications and services, the need for a very strong security system at perimeter or gateway to enterprises is becoming more and more crucial.
Earlier firewalls provided basic normal traffic filtering, and then intrusion detection systems were deployed by enterprises, soon they were replaced by intrusion prevention systems and now New generation firewalls with integrated threat management capabilities started their penetration, the boundary between hardware and software started to diminish and now integrative software image combining features of firewall, Intrusion detection / prevention came into existence.
In today’s blog, we will cover in detail about Cisco Firepower threat defence NGIPS systems and how packet flow works in them.
Cisco FTD Firewall Packet Flow
Cisco FTD as NGIPS shares a management console with Cisco firewall offering known as Firepower management center. Cisco had acquired SourceFire in November 2013 and rebranded it as SourceFire to FirePower on ASA platform. (Which is Cisco’s own firewall). FirePower on ASA is a next generation firewall with Anti-malware protection (AMP) for networks, next generation firewall on an existing platform.
The FirePower appliances run a special operating system known as FXOS. FXOS let you configure applications and decorators to interfaces. Apart from ASA application this also introduced a new application called FirePower threat defence or FTD as we know it in short.
The number of available security modules is dependent on FirePower appliance platform or ASA platform. The below figure depicts its architecture.
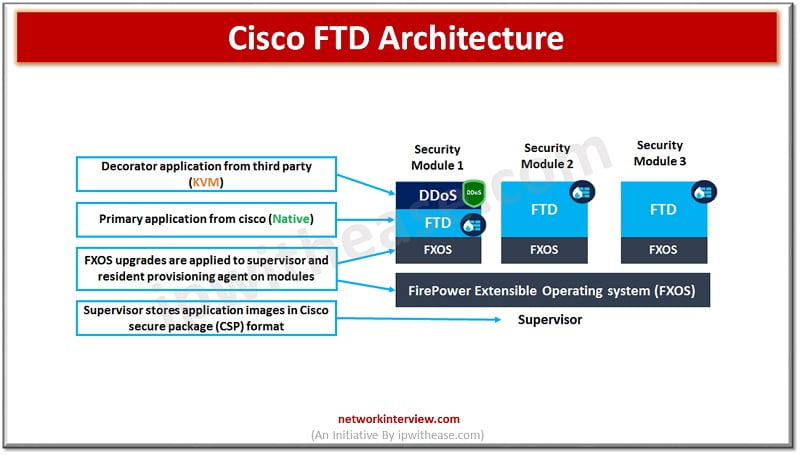
figure:2
FTD is when run on the FXOS environment, packet traverses through firewall in a different way and actually ASA features are like a service module inside the FTD environment. Understanding packet flow helps to troubleshoot and create true policy and help to analyse data and fine tune the security appliance.
There are two engines in the FTD unified software image ; Lina and Snort.
- Lina is the ASA code on which FTD runs on and
- Snort is the network analysis of packets which goes through Security Intelligence (SI) via ACP inspection of traffic by snort IPS rules.
Cisco FTD: Packet Flow
Cisco FTD firewall Packet flow goes like this:
- LINA engine handle packet which enters via ingress interface
- Packet inspection is performed by Snort so this can include inspections like SI, IPS, AMP, URL filtering etc.
- The Snort engine returns the result
- Snort engine does not drop anything but instead marks packet drop or forward based on snort analysis result
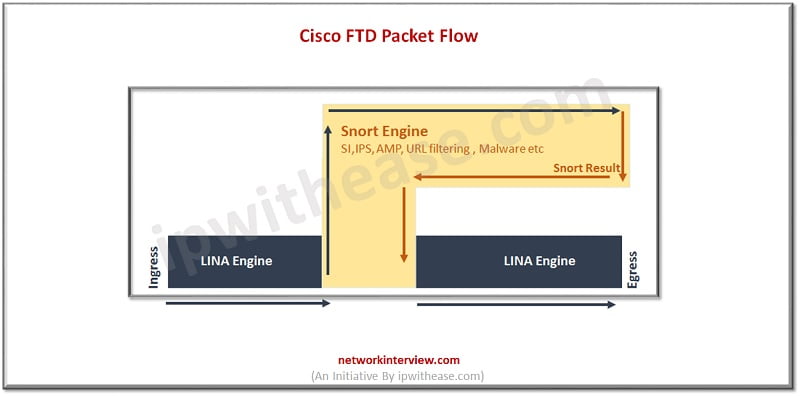
figure:3
Lina performs layer 2 processing, routing, NAT, VPN, Pre filter, and layer 3 – 4 access control policy rules check before Snort takes over. The Lina code takes over again after default action of Access control rule (ACP) and performs layer 2 routing, NAT , VPN etc.
Once a packet passes through Lina survived by Pre Filter or layer 3-4 ACP it will traverse the Snort process and go through layer 3 security intelligence white and blacklist post which application detection takes place if packet does not fall under blacklist or whitelist either. (Refer figure:1)
Packet will go further to L7 SI URL and DNS list and feed for authentication. Packets are finally compared to the rules in the main access control policy (L7 ACL) and from here they can be dropped, passed, or trusted and sent to the Egress engine. Based on configuration URL filtering and Malware policy will be enforced as well as the IPS rules on traffic. The packets are finally handed over to the Lina process for layer 2 routing, NAT, VPN etc.
Continue Reading:
Packet Flow in Checkpoint Firewall
Packet Flow in Palo Alto – Detailed Explanation
Are you preparing for your next interview?
Please check our e-store for e-book on Cisco FTD Interview Q&A. All the e-books are in easy to understand PDF Format, explained with relevant Diagrams (where required) for better ease of understanding.



