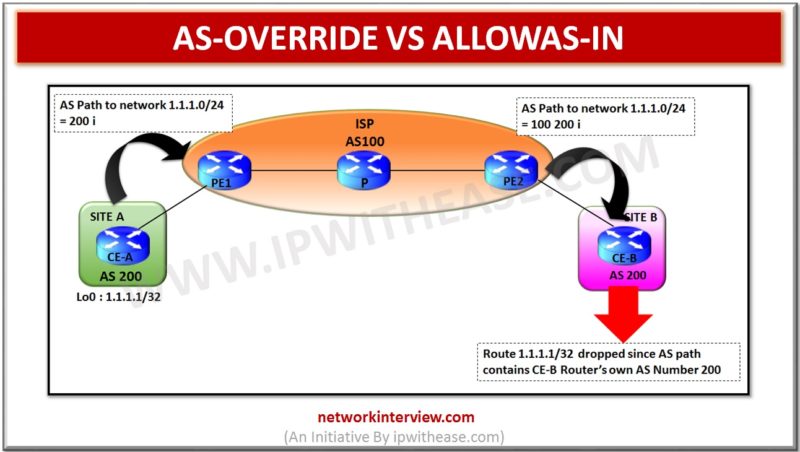
Below table describes the difference between AS-OVERRIDE and ALLOWAS-IN; PARAMETER AS-OVERRIDE ALLOWAS-IN Overview Used by PE to modify the AS Path so that prefix is not dropped based on BGP default behaviour to disallow its own AS number in the …
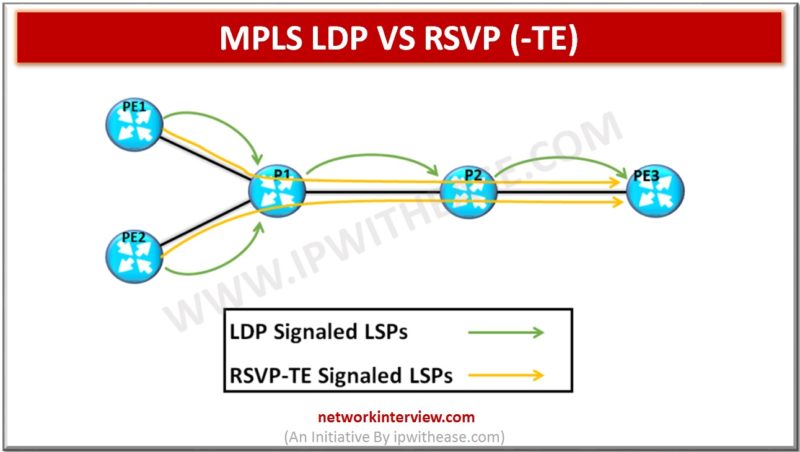
Comparison Table : LDP vs RSVP Below table describes the difference between LDP and RSVP: PARAMETERS LDP RSVP Abbreviation for Label Distribution protocol Resource Reservation Protocol Provisioning Easy to configure. We just need to enable on interfaces. Label bindings automatically …
Comparison Table : RD vs RT in MPLS Below table describes the difference between RD vs RT in MPLS: PARAMETER RD RT Abbreviation for Route Distinguisher Route Target Definition 64-bit identifier prepended to IPv4 route used to identify VPN the …
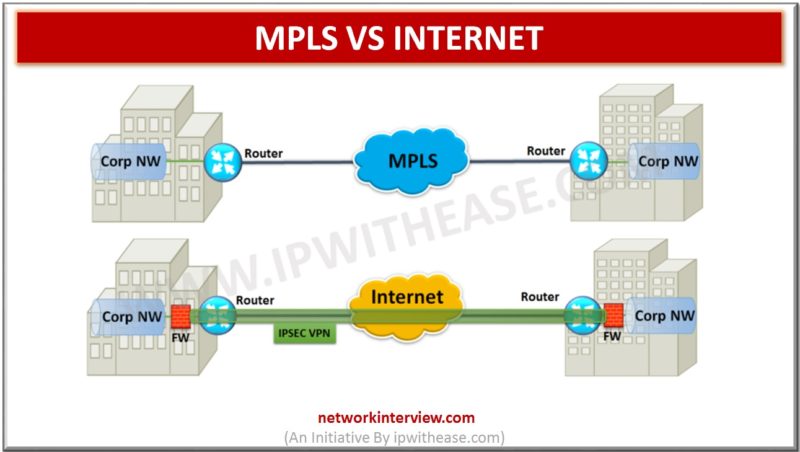
Comparison Table : MPLS vs INTERNET Below table describes the difference between MPLS and Internet: PARAMETERS MPLS INTERNET Carriers Single carrier provides MPLS connectivity for all the locations Not limited to single carrier. Different locations can be connected through various …
Comparison Table: MPLS vs VPN Below table describes the difference between MPLS and VPN: PARAMETER MPLS VPN Scope of Operation Operates on carrier provided Network (Logically segregated to support multiple customers) that will further connect to all customer sites. Operates …
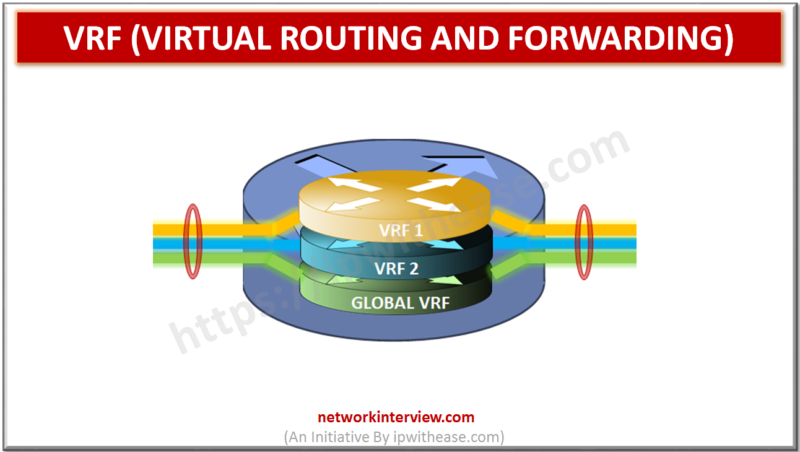
VRF (Virtual routing and forwarding) is a technology that allows multiple instances of a routing table to co-exist within the same router at the same time. Overlapping IP addresses can be used without conflicting with each other as the routing …
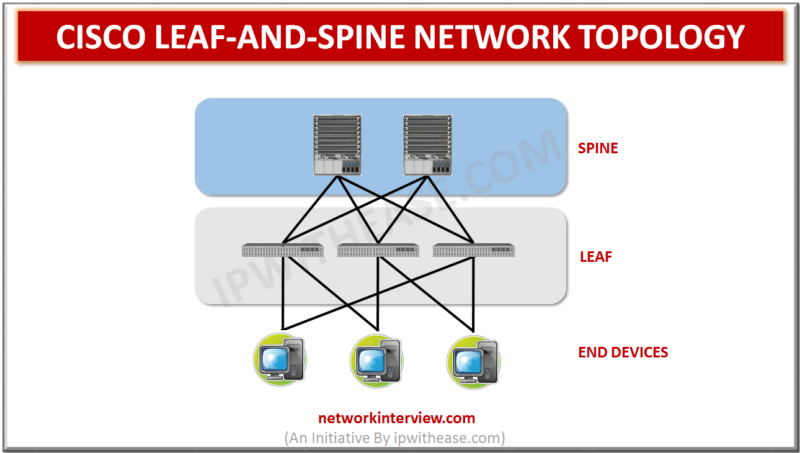
Network Topology Leaf-and-spine is a two-layer network topology composed of leaf switches and spine switches. We are all aware of the Cisco’s 3-tier network topology with the following 3 layers – 1)Access Layer 2)Aggregation/Distribution Layer 3)Core layer The Access Layer …
Introduction to LAN Computer Networks can be divided into various types depending upon their size and usability. The size of a network can be assessed by its geographical distribution. It can be as small as a room with a few …
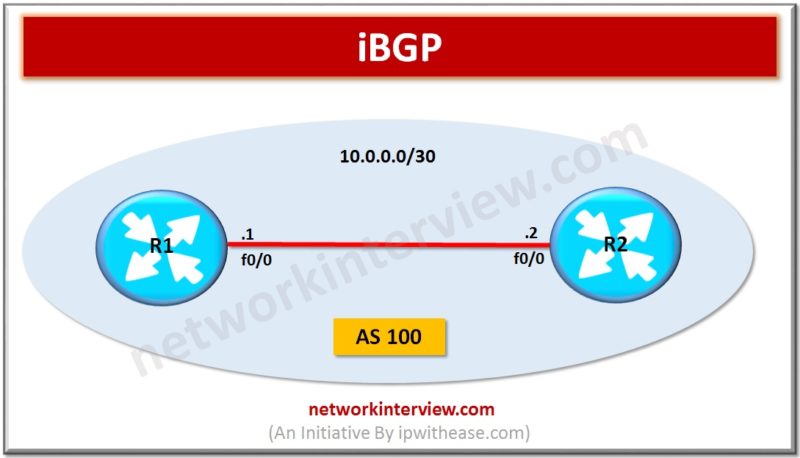
Introduction iBGP is abbreviation for Internal Border Gateway Protocol. iBGP protocol is used between the routers within the same autonomous system (AS). iBGP speaking Routers need to form full mesh to maintain full routing information. Full mesh (iBGP neighborship with all Routers …
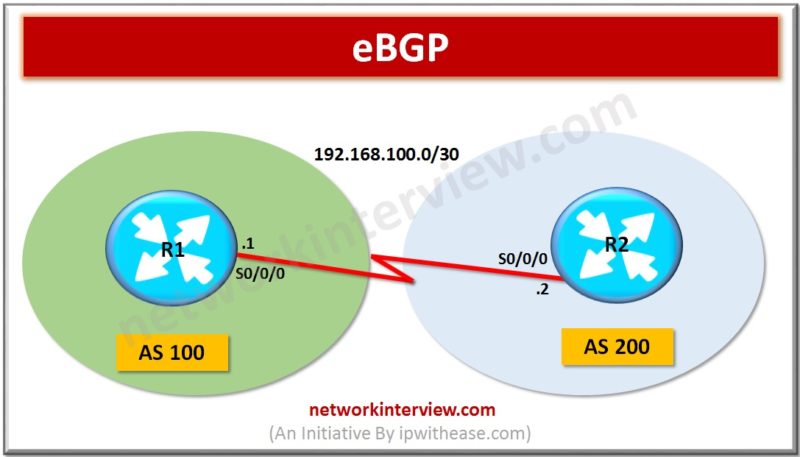
Introduction eBGP is abbreviation for External Border Gateway Protocol and is one of the flavors of BGP protocol. eBGP Routing protocol is used between BGP speaking neighbors which belong to different ASNs (Autonomous System Numbers). eBGP functions as the protocol for …
Network Switching Network Switching works at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of OSI model. Switching is a process of receiving frame from one incoming port (ingress) and then forwarding it to as desired destination (egress). Types of Network Switching Switching …