Introduction to Juniper SRX Firewall
Network based security landscape is changing drastically and becoming more and more complex and dynamic in operations. New challenges in the cyber security domain related to web based and social network applications, sophisticated cyber-attacks, social engineering attacks are on rise due to increased use of web applications, Artificial intelligence, and machine learning adoption. Simple rule based stateful inspection firewalls are things of the past and no longer can provide protection against advanced threat landscape.
Today we look more in detail about the next generation firewall (NGFW) from Juniper, i.e., Juniper SRX, its architecture, working and how it protects against advanced threat landscape.
What is a Juniper SRX Firewall?
The early predecessors of SRX firewalls were ScreenOS products. First time introduced the concept of split OS and firewall software hence providing flexibility to choose the underlying OS it was comfortable with. Juniper SRX series is a next generation shift from ScreenOS platform built to provide scalable services. Service is an action or set of actions which are applied to network traffic such as stateful inspection and intrusion prevention (Referred here as service).
SRX firewall provides services on passing traffic which is scalable as well. Scaling provides an appropriate level of processing based on workload requirements. Placement of firewalls at data center and branch further have different sets of scalability requirements hence Juniper SRX series comes under two product lines – the branch SRX series and data center SRX series.
Juniper SRX (NGFW) Architecture
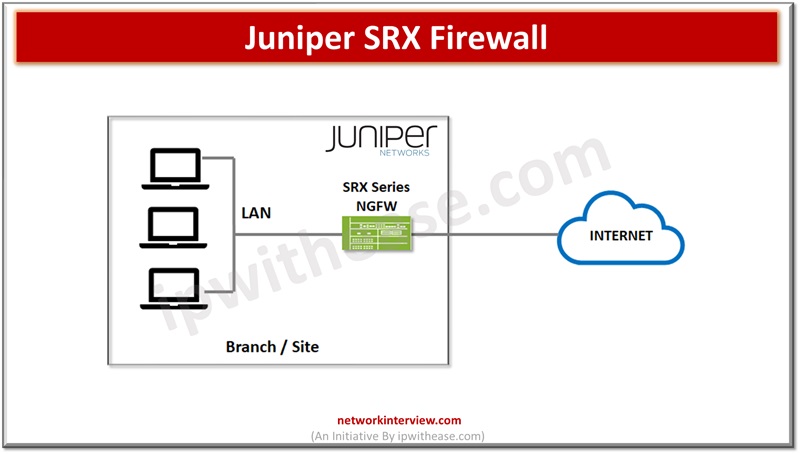
The network generation firewall architecture provides security services for remote sites, WAN connectivity. While using SRX device on premises site as a standalone NGFW the WAN routing functions are taken care of by SRX device itself. This architecture allows SRX device to perform all in-built security functions such as firewall and network address translation along with visibility to LANs which exist on spoke sites. Figure 1 shows SRX device connectivity to both onsite LAN and WAN.
SRX series devices can be used as standalone firewalls managed by Contrail Service Orchestration (CSO) which supports SRX 300+, SRX500+, SRX1500, SRX4100+ and vSRX series. NGFW provides multiple functionalities as mentioned under.
- WAN connectivity for sites – Provisioned NGFW for tenant allows any site belonging to that tenant to use NGFW device as its WAN link back to CSO.
- Automatic LAN connectivity – NGFW built in DHCP provide addressing capabilities for connected LAN
- Custom application signatures in firewall policies – In addition to support for existing SD-WAN policies CSO also supports custom application signatures in firewall policies
- Customized IPS signatures, static and dynamic groups – creation, modification, or deletion of customized intrusion prevention system (IPS) signatures, IPS signatures static and dynamic grouping. Cloning predefined or customized IPS signatures, groups (static and dynamic)
- Policy configuration import – Import of policy configurations from NGFW devices are supported.
Related: IPS vs IDS vs Firewall
SRX (NGFW) Security Features
The security device integrates network security and routing capabilities. Traffic which enters and exits a security device is processed as per configured features such as packet filtering, security policies, and screens. Software can determine if:
- Packet is allowed onto device
- Firewall screen applies to packet
- Which route to be taken by packet to reach its destination
- If need to apply NAT to translate packet IP address
- Does packet require an application layer gateway (ALG)
SRX supports next generation firewall protection having application aware security services, intrusion detection and prevention, role-based user firewall, unified threat management (UTM).
Let’s look at some of the security features more in detail.
Firewall User Authentication – additional layer of security by restricting or permitting individual users or groups.
Intrusion Prevention – enable selective enforcement of various attack detection and prevention mechanisms on network traffic passing through the IDP enabled firewall.
AppSecure – AppSecure detects behaviour of application and weaknesses which prevent application borne security threats detection and prevention though. Provides greater visibility of application. Stopping users from visiting inappropriate sites or downloading malware , traffic prioritization based on application type and bandwidth requirement, encryption and decryption using SSL-Proxy.
Unified Threat Management (UTM) – capability to protect against spam, viruses, worms, spyware, trojans and malware, content filtering to provide basic data loss prevention capability.
Continue Reading:
Introduction to Sophos UTM Firewall
NGFW: What is a Next Generation Firewall?
Tag:Juniper SRX, Security



