What is Augmented Reality? Everything You Need to Know
Just in time access to information, anywhere, everywhere is the focus of businesses. Enhancing customer experience by increased engagement and interaction to provide richer user experience, increasing the perceived value of brands and products with access to detailed analytics is key requirements on which today’s businesses are focusing on.
Technologies like virtual reality which was coined sometime in 1957 has been quickly taken over by its variation augmented reality which was an enhanced version of real-world environment which blended interactive digital elements into physical objects for better user experience.
In today’s article we would venture more in detail about augmented reality technology, who coined this term, why it is getting so popular, its use cases and future of augmented reality technology etc.
What is Augmented Reality?
The term ‘Augmented Reality’ and first true device of its kind was created in 1990 by Boeing researcher Tom Caudell and his colleague David Mizell. These two scientists used this as a solution to simplify the jobs of workers in manufacturing units. The rudimentary device created a see-through display to be worn on the head that superimposed computerized images of the airplane schematics to guide workers during the assembly process of wiring for 777 jetliners.
Two years after this Louis Rosenberg created Virtual Fixtures, the first AR system for use by the US air force. Since then, Augmented technology has taken a big leap in terms of performance and usability.
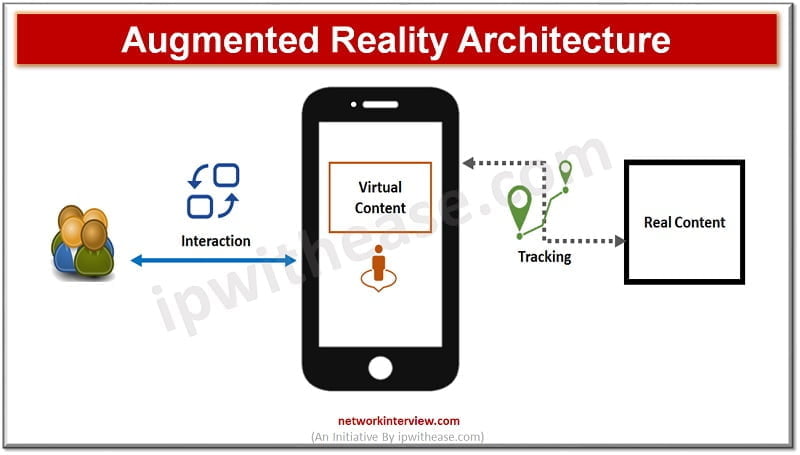
It is an essentially interactive experience of a real-world environment where objects are improved upon using computer generated perceptual information across multiple sensory faculties such as visual, auditory, haptic, somatosensory or olfactory. Digital elements are infused / used to enhance the real world.
Features of Augmented Reality
- Increase in engagement and interaction to provide rich user experience.
- Increase in perceived value of brands and products.
- Inexpensive alternative to other media platforms as no specific media is required.
- Detailed analytics to enable their audience.
Use cases
- Automobile industry – AR in car dashboards to provide wide range of technical and travel information
- Virtual instructor for everyday maintenance such as oil change, tyre pressure etc.
- Marketing – Product sales via activation of additional brand content such as music videos, TV footage etc.
- Virtual product demos
- Banking – AR activated bank accounts to check account details such as balance, latest transactions etc.
- Hospitality – Virtual tour guides for specific city tours
- Healthcare – Practising surgery by medical students in controlled environment
Challenges of Augmented reality
- Data overload due to creation and data sharing is all time high
- Can cause perception impairment
- Privacy threats
- Cyber security risks
Augmented Reality Working
On using a device or application which is AR enabled,
- The hardware of the device or application clicks an image of the object and shares it with a computer vision program.
- Computer vision program processes the image and collects all information pertaining to it such as object measurements, its surroundings, distance to other objects.
- Post applying these insights the AR enabled device builds up virtual information which is superimposed over real objects to have a unique user experience.
- In AR the user sees both natural and artificial light with a layering effect.
- The real-world acts as the first layer.
- The camera recognizes the target and processes the image and then augments digital assets onto their image.
Types of Augmented Reality
There are four types of Augmented reality each having its own unique function and application:
1. Marker based
It is also known as image recognition & uses a smartphone camera and visual marker which produces an augmented reality on sensing by camera. The marker can be a QR code or a specific image such as a movie poster, having distinct visual points.
Markers can be used to bring still images to life or provide customers additional details. Such as for an upcoming concert one can market it by creating a poster that on scanning shows set list and plays music from the line-up.
2. Market less
Market less augmented reality uses GPS, digital compass, or accelerometer to provide data based on location and speed to a device. Useful in showing physical objects in relation to other objects such as sizing furniture for houses on IKEA application.
3. Projection Based
Projection based augmented reality or spatial augmented reality (SAR) projects artificial light onto a real surface. Usually done on a larger scale for a conference or event can be interactive using sensors and 3D. helps to showcase large objects like cars
4. Superimposition Based
Superimposition based augmented reality uses object recognition. The original image is replaced by augmented image partially or fully. Majorly used in the medical field to superimpose an x-ray onto a patient body.
Quick facts !
The Augmented Reality market is expected to grow to $340 billion by 2028.
Continue Reading:
Top 10 Networking technology trends
Top 10 Trends of Software Development
Tag:New technology



