6 Types of Firewall: Network Security
Introduction to Firewall
In todays digital scenario, where businesses demand agility and information are hosted on cloud infrastructure security of data is one of the primary concerns of business and protection of data from unwanted sources is the prime objective. ‘Firewall’ is a specialized network device which prevents unauthorized access and keeps IT infrastructure safe.
Today we will learn about types of firewalls as well as understand the need of firewalls, how firewalls function? etc.
About Firewalls
A Firewall is a specialised network device or could be a software program which monitors, and filters incoming and outgoing network traffic based on a set of security rules. It acts as a fence between internet private company network and external outer world (Public Internet).
The firewall allows legitimate traffic to come in and prevent unauthorized or malicious data traffic to enter Private network thus protecting systems from viruses and cyberattacks. Firewall can be a network security device or could be a software program.
Firewalls could be hardware, software, and cloud-based firewalls. Cloud based firewalls are referred as FaaS (Firewall as a service). These can be managed centrally and provide perimeter security.
History of Firewall
The first firewall came into existence in late 1980s. Initial firewalls act like Packet filters their primary objective was to check for packets or bytes transferred between different systems.
The Stateful inspection firewall was introduced by Gil Shwed from Check Point Technologies in 1993 named Firewall-1. In year 2000 Netscreen came up with ‘Appliance’ firewall which supported increased internet speed, low latency, and high throughput at low costs.
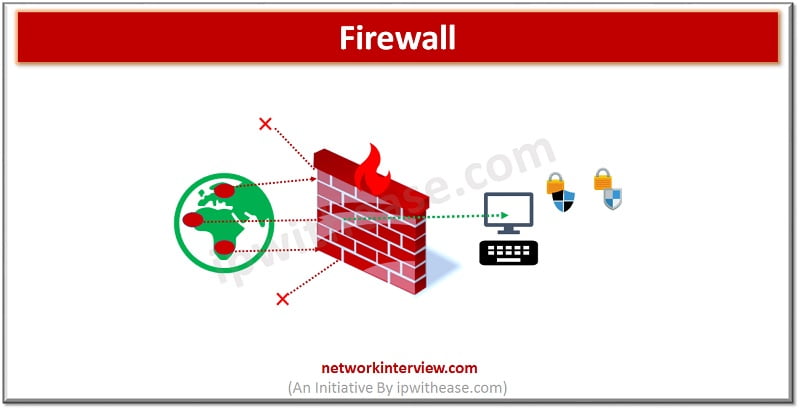
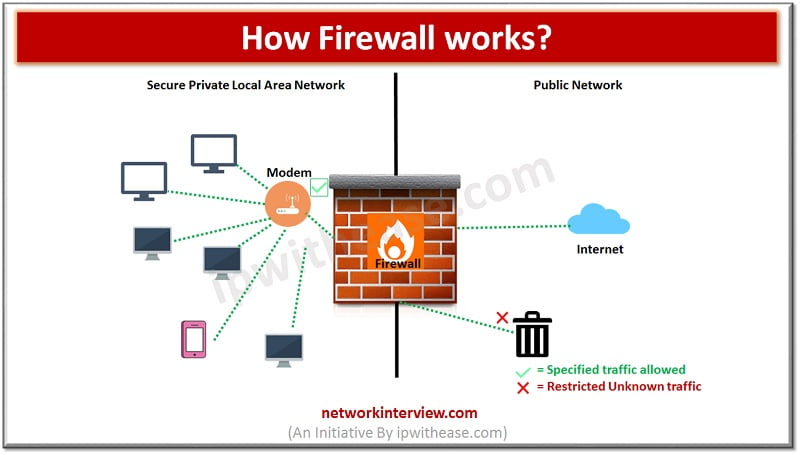
How Firewalls work?
A firewall analyses the traffic hitting the network based on pre-configured rules on firewall and filters the traffic based on pre-defined rules and prohibits traffic generating from unreliable and suspicious sources. It only permits traffic which is configured to accept as per firewall filter rules.
Firewalls intercept traffic at entry point, which is a port. Firewall allows or blocks specific data packets based on pre-configured security rules. Incoming traffic is allowed only thru trusted sources such as ‘trusted IP addresses’ or ‘Trusted source’ or ‘a specific port’.
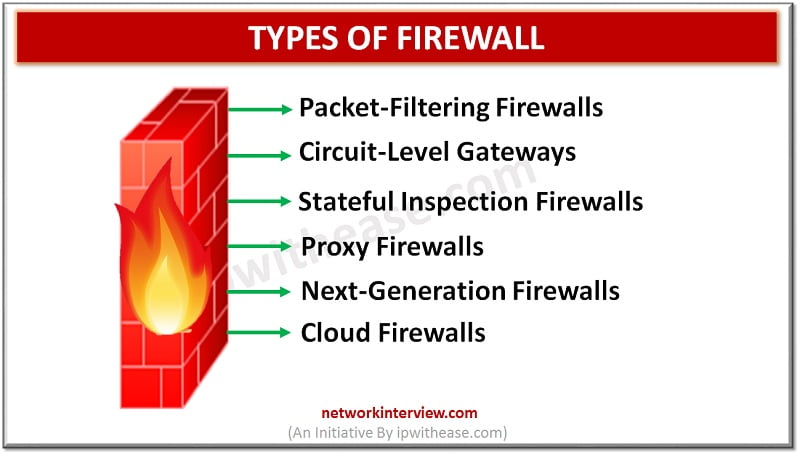
Types of Firewalls
Firewalls are categorized into below groups based on their structure and functionality.
Packet-Filtering Firewalls
Filtering incoming packets based on information they carry. Based on header information packet is allowed or denied as per firewall rules.
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient way of filtering headers
- Low costs
- Uses less resources
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to IP Spoofing
- No user authentication
- Can’t filter application level protocols
- No payload checks
Best suited for:
Ideal for traffic isolation within departments.
Circuit-Level Gateways
Work on session layer of OSI model TCP connections and sessions are observed.
Advantages:
- Cost and resource efficient
- Protect against address exposure
- Check TCP handshakes
Disadvantages:
- Do not support content filtering
- No application layer security
- Software modifications required
Best suited for:
Can’t be used standalone often used with application layer gateways.
Stateful Inspection Firewalls
Keeps track of the status of a connection by monitoring TCP-3-way handshake.
Advantages:
- Entire session is tracked
- Both inspected headers and packet payloads
- Operates with less ports
Disadvantages:
- Not a cost-effective solution
- No support for authentication
- Prone to DDOS attacks
- Slow performance due to high resource requirements
Best suited for:
Ideal for environment which require a balance between packet filtering and application layer protection.
Proxy Firewalls
Acts as intermediate device between internal and external systems over internet.
Advantages:
- Prevent contact with other networks
- User anonymity is ensured
- No Geolocational restrictions
Disadvantages:
- Reduction in performance
- Additional configuration required to perform overall encryption
- Incompatibility issues with some network protocols
Best suited for:
Ideal for web applications to secure servers from malicious users.
Next-Generation Firewalls
It is a security device which has functions combined from other firewalls. It has packer, stateful, and deep packet inspection.
Advantages:
- It has deep inspection, antivirus, spam filtering, application controls
- Automatic updates
- Network traffic monitoring from Layer 2 to Layer 7 of OSI model
Disadvantages:
- Highly priced
- Additional configuration required for integration with security management solutions
Best suited for:
Ideal for businesses require PCI or HIPPA regulatory compliance.
Cloud Firewalls
Cloud firewall is a FaaS (Firewall as a service)
Advantages:
- High Availability
- Scalable
- No hardware required
- Lower management and maintenance costs
Disadvantages:
- Pricing based on services offered
- Risk of loss of control on security assets
- Compatibility issues while migrating to another cloud provider
Best suited for:
Ideal for large businesses not having in house security team.
Comparison Table: Types of Firewall
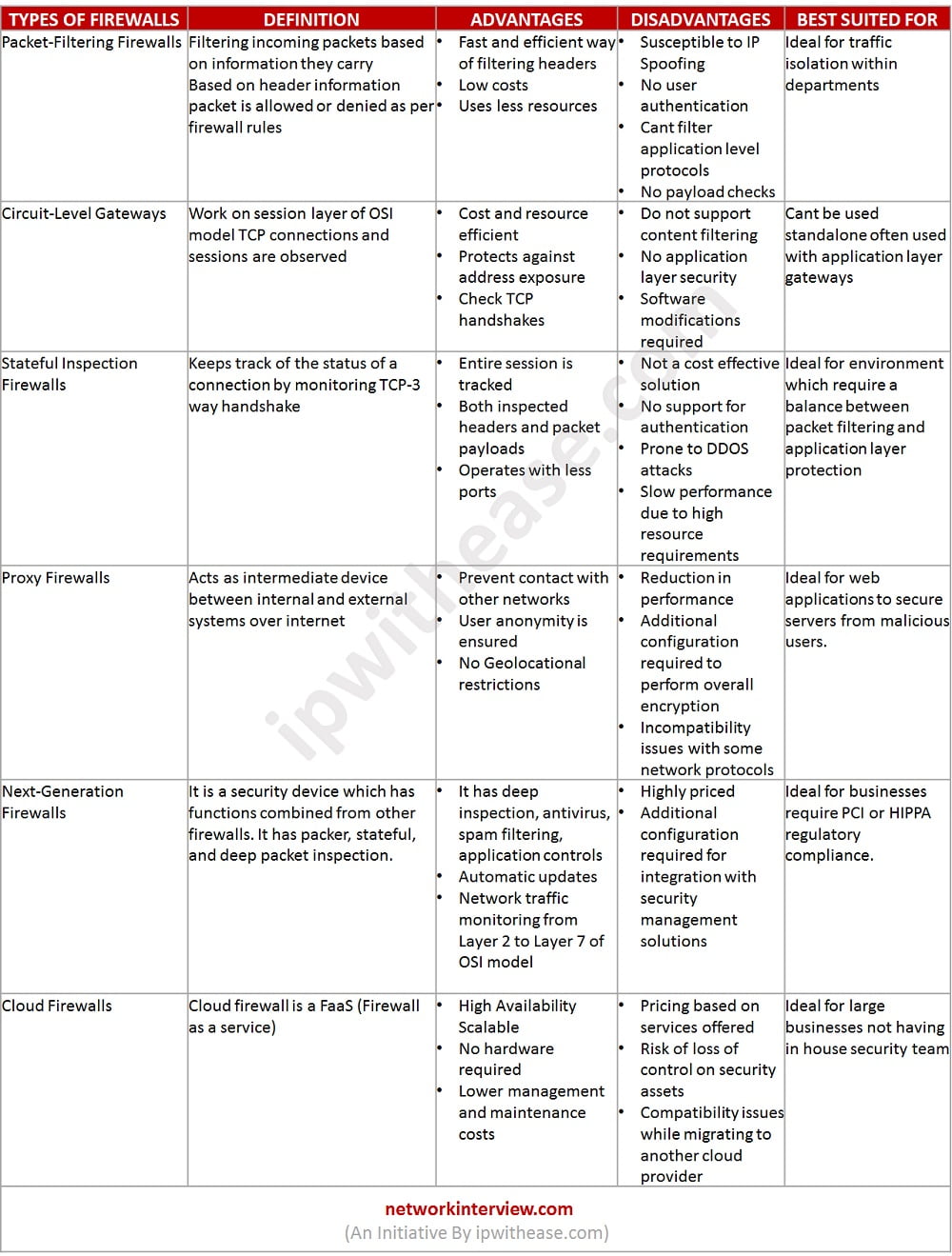
Download the comparison table: Types of Firewall
Key features of Firewalls
- Prevention of network threats
- Identity based control
- Hybrid cloud support services
- Scalable
- Performs access validation
- Control and Network traffic management
- Recording and reporting of events
Limitations of Firewalls
- There is no mechanism in firewall to prohibit user from accessing a malicious website
- Can’t prohibit transfer of virus infected files
- Can’t prevent misuse of passwords
- Can’t stop a breach if a security rule is misconfigured
- Can’t protect against social engineering attacks
- Already infected systems can’t be secured
- Can’t prevent attacks generating thru modems from dialling in to or out of the internal network
Continue Reading:
Palo Alto Firewall Architecture
Tag:Security



