Ring Network Topology
Network Topology refers to the physical or logical layout of a network.
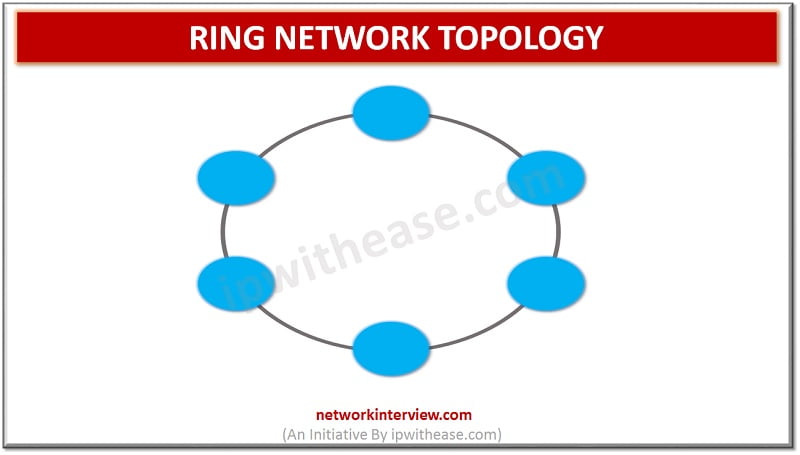
Ring topology is a type of network topology in which each network device is connected to two other devices, forward and backward forming a single continuous path for signal transmission. It forms a ring, as each network device is connected to the other with the last one connected to the first forming a ring network. In a ring network, data travels from one device to the next in the form of packets. Each device in a ring topology has a repeater, if the received data is intended for other device then repeater forwards this data until the intended device receives it.
Types of Ring Topology:
On the Basis of the data flow, ring topology can be of two types-
- Unidirectional Ring Topology
- Bidirectional Ring Topology
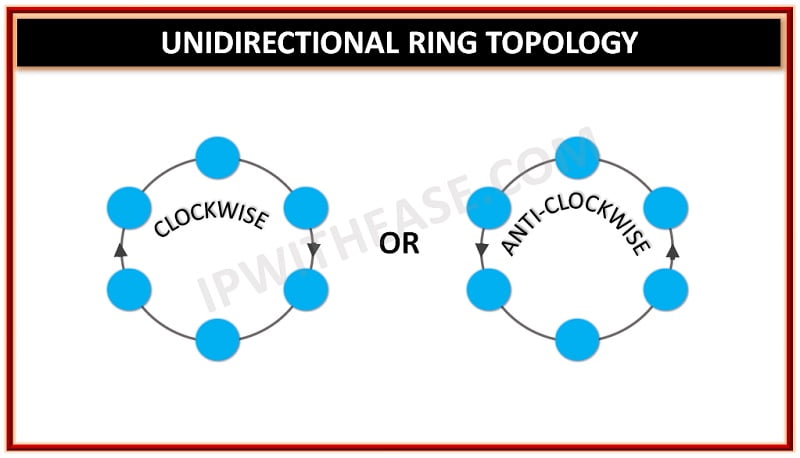
- Unidirectional Ring Topology : It involves data traffic in one direction, either clockwise or anticlockwise. This data network is also called a half-duplex network. E.g.- SONET network, SDH network etc.

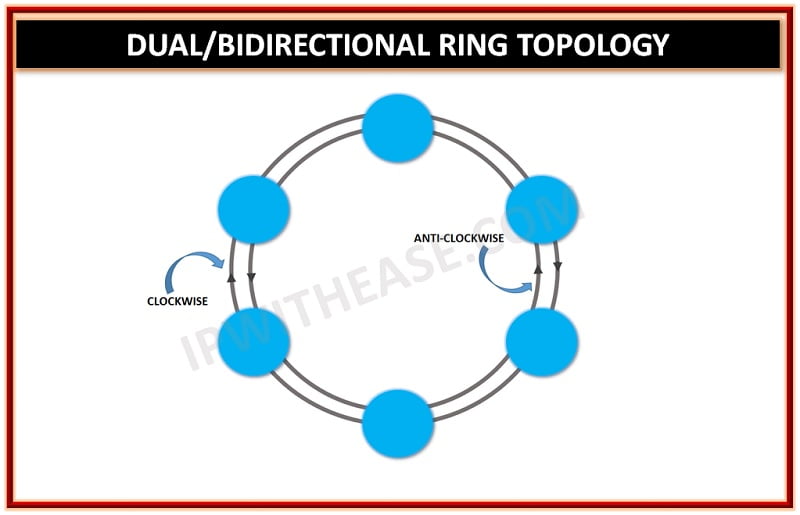
- Bidirectional Ring Topology : It involves data traffic in both the directions and is thus called a full-duplex network. Bidirectional data transmission is possible by having two connections between each network node, thus making two ring networks with data flow in opposite direction to each other. This type of topology with two rings is sometimes also referred to as the Dual Network Topology.

Advantages of Ring Network Topology:
- Easy to install.
- As the data flows in one direction, it reduces the chance of packet collisions.
- Performs better than bus topology under heavy traffic.
- No need of network server to control network connectivity between workstations.
- Additional devices can be added without impacting the performance.
Disadvantages of Ring Network Topology:
- The network requires to be shut down for addition or removal of nodes .
- A data packet must pass through all the nodes in unidirectional flow.
- Failure of one device disrupts the entire network.
Related – Star Network Topology
Tag:routing