
Palo Alto Packet Capture/ Packet Sniffing
Introduction to Packet Capturing
Before discussing Palo alto packet capture, let’s first understand the term packet capture. Packet capture is network interception of data packet which can be analysed , downloaded, archived or discarded. The reason for packet capturing is performed to identify threats, detect undesirable behaviours, network congestions, packet loss and analysis of network.
Packet capturing is performed in two ways
- one is by whole packet capturing and
- secondly by specific packet portion capturing.
There are several products available which let sniff or capture packets. Palo Alto network firewalls have capability to take packet captures of traffic and let them store to perform analysis.
In this article we will learn more about Palo Alto Packet capturing/packet Sniffing capabilities, its features , advantages and use cases etc.
Palo Alto Packet Capture
Palo Alto network firewalls have built in capability of packet capture (pcap) feature that allows capture of packets which traverse the network interfaces on firewall. Packets can be captured for troubleshooting purposes or create custom signatures.
Packet capturing is a CPU intensive activity and degrade performance of firewall.
Types of Packet Capture
There are several types of packet capture which we can enable based on the need as under:
Custom Packet Capture –
The firewall capture all traffic or specific traffic based on defined filters. For example, we can configure firewall to capture packet coming from a specific source and going to a specific destination or port. We can then use packet capture to troubleshoot network problems or to gather application attributes which enable to create custom application signatures or request and application signature for Palo Alto firewall.
Threat Packet Capture –
It captures when firewall detects a virus , spyware or vulnerability. Feature needs to be enabled in Antivirus, anti-spyware and vulnerability protection security profiles. Threat log will have a link to export packet capture. These packet captures provide context around the threat and help to determine if attack was successful or learn about methods used by attacker. It can be submitted to Palo Alto networks to determine if threat was false-positive or false-negative.
Application Packet Capture –
It is a type of packet capturing based on specific application filters. Traffic log has view or export feature as per rule definition to capture packet.
Management Interface Packet Capture –
It is defined as capturing of packet on management interface (MGT). It is useful to troubleshoot services which traverse the interface such as firewall management authentication to external authentication services, software and content updates, log forwarding, SNMP servers communication, authentication requests for GlobalProtect and captive portal.
GTP Event Packet Capture –
Firewall captures single GTP event such as GTP-in-GTP , IP spoofing on end user, abnormal GTP messages, Making troubleshooting easier for mobile network operations.
How to capture packets in Palo Alto firewall?
To capture packets on Palo Alto firewall, go to Monitor à Packet capture à click Manage filters (hyperlink)
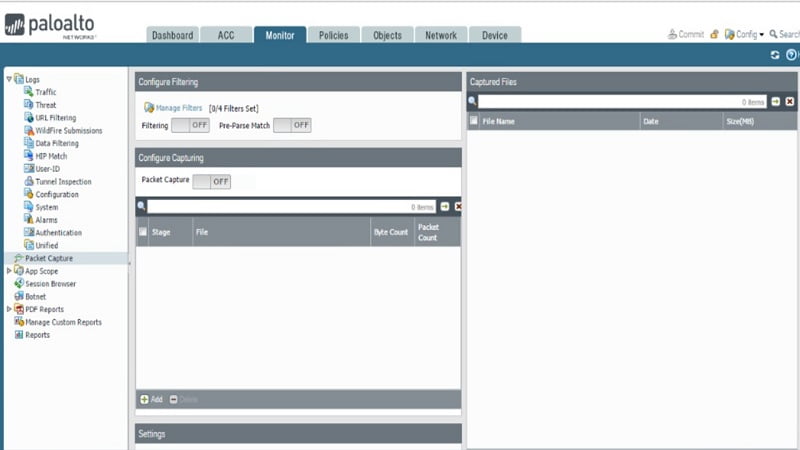
Click Add and in ID column select 1
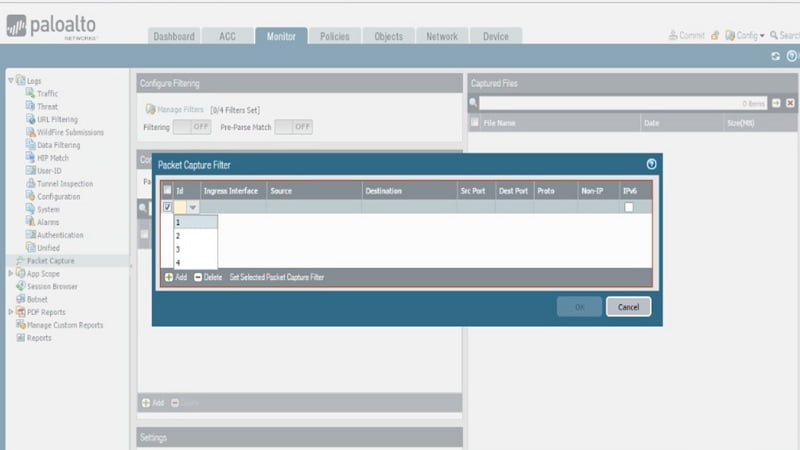
Under Ingress interface column à choose Ethernet ½ (inside security zone)
Under source column type source 192.168.1.20 (inside client machine) > type destination 192.168.50.10 (DMZ machine) > under Proto > type 1 (ICMP)
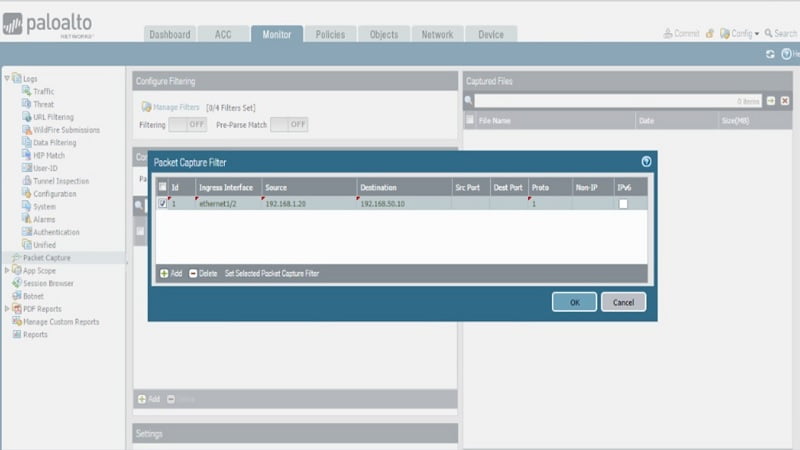
Click toggle to make filtering ON
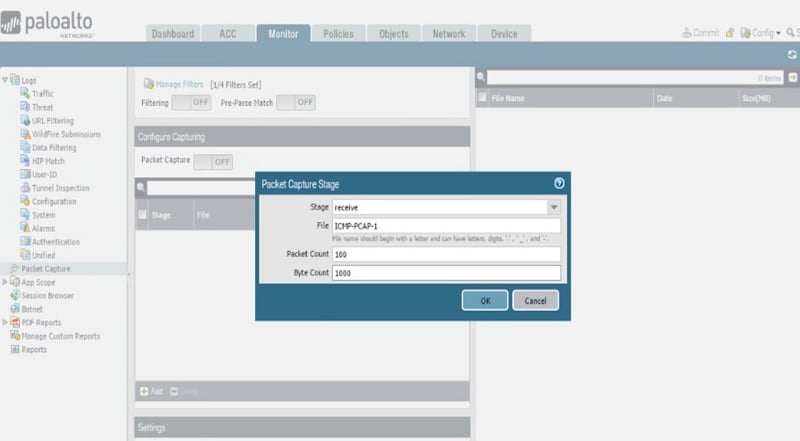
Under configure packet >stage>Add > Select stage : receive
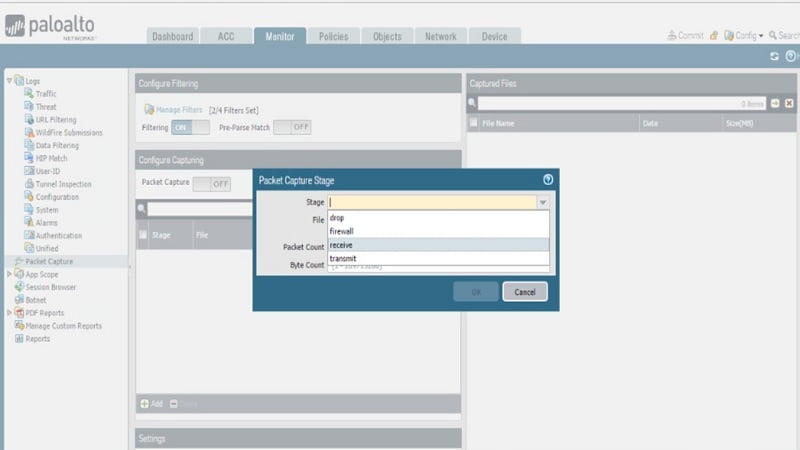
Type name for file (ICMP -PCAP-1) > type packet count : 100>type byte count >1000> click Ok
The packet capture will automatically stop if packet count hits 100 or byte count hits 1000. It is advisable to keep size of packet capturing file small so as to have less impact on CPU and memory of firewall.
Click on Packet capture (OFF) to make it ON (Toggle) and initiate packet capture
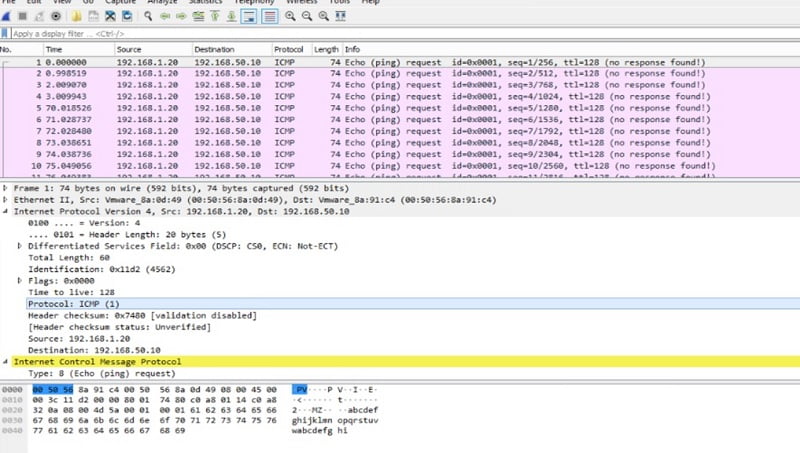
Click ok to continue on warning message, Packet capture file will show on the left side under capture files. Click on captured file (ICMP-PCAP-1) and download the Pcap file. Wireshark network protocol analyzer is required to open pcap file.
At least one capture stage is required to be selected. Stage indicates the point at which packet capture is to start.
Drop – when packet processing encounter error packet drops
Firewall – when packet has session match or first packet with session is created successfully
Receive – when packet is received on dataplane processor
Transmit – when packet is transmitted on dataplane processor
File – mention capture file name
Packet count – specify maximum number of packets post which capturing will stop
Byte count – specify maximum number of bytes post which capturing will stop
Continue Reading:
Why you should be worried about Network Packet Loss?



