Understand the difference between Microcomputer & Minicomputer
In this article, we will understand about some terminologies associated with computers. The categorization and classification is based on their size and data handling capabilities.
Let’s realise the difference between Microcomputer and Minicomputer.
Microcomputer
Microcomputers came into existence and become popular in 1970s and 1980s. The first microcomputer was the Micral based on intel 8008 chip. the Altair 8800 is considered first successful commercial microcomputer. The microcomputer was invented by Mers Kutt when he and his team at Micro computer Machines, Toronto introduced a desktop computer having intel 8008 chip.
Another commonly used name for Microcomputer is personal computer. Personal computers as the name suggest were designed for individual users to perform general functions or tasks. Majority of Laptops and Desktops are examples of Microcomputers. The microcomputer or personnel computer is comprising of components such as Central processing unit (CPU), Memory, storage, input, and output unit. These systems are ideal for personal work such as watching movies, listening to music, or office work like working on spreadsheets, typing a letter etc.
Microcomputer Characteristics
- Smallest in size among all other type of computers or systems
- Only limited number / type of software can be installed on personnel computers
- It is primarily designed for personnel work and single user interface
- Low cost and easy to operate
- No special skill or training is required to use it
- Having a single semiconductor micro chip
- Multitasking can be performed such as printing, scanning, Net browsing, videos etc.
Minicomputer
Minicomputers came into existence a way back in 1960s. The first Minicomputer was ‘Digital Equipment Corporation’ with PDP (Programmed Data Processor )and it was priced around USD 120,000. The minicomputers are characterized by small size but packed with power and multiple functionalities and are lightweight. Minicomputers are available in market today in the form of many electronic gadgets such as Smartphones, Tablet PC, iPAD, Drawing tablets , Desktop Mini PC and so on.
These small and powerful gadgets are packed with features and used for gaming, watching videos, net surfing, and a variety of computing tasks. Minicomputers were developed for tasks related to storage of records, calculations, controls etc.
Minicomputer Characteristics
- Smaller size than a mainframe computer
- Low in cost than a super and mainframe computer
- Less powerful than a super and mainframe computer but more powerful than microcomputers
- Perform multitasking and multiprocessing
- Suitable for individual use and small businesses
- Ease of use and maintenance
- Small and lightweight easy to carry
- Fast and reliable
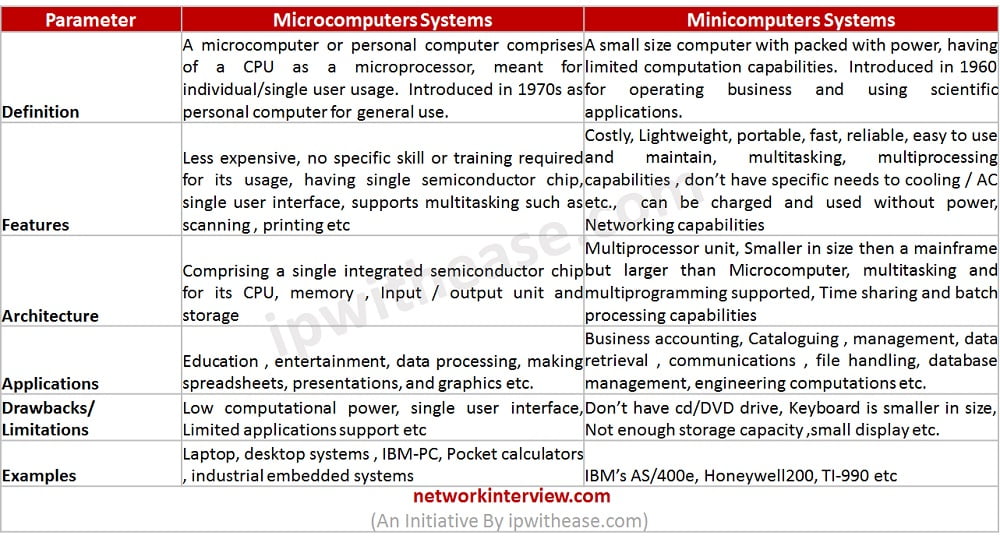
Parameter | Microcomputer Systems | Minicomputer Systems |
| Definition | A microcomputer or personal computer comprises of a CPU as a microprocessor, meant for individual/single user usage. Introduced in 1970s as personal computer for general use. | A small size computer with packed with power, having limited computation capabilities. Introduced in 1960 for operating business and using scientific applications. |
| Features | Less expensive, no specific skill or training required for its usage, having single semiconductor chip, single user interface, supports multitasking such as scanning, printing etc. | Costly, Lightweight, portable, fast, reliable, easy to use and maintain, multitasking, multiprocessing capabilities , don’t have specific needs to cooling / AC etc., can be charged and used without power, Networking capabilities |
| Architecture | Comprising a single integrated semiconductor chip for its CPU, memory , Input / output unit and storage | Multiprocessor unit, Smaller in size then a mainframe but larger than Microcomputer, multitasking and multiprogramming supported, Time sharing and batch processing capabilities |
| Applications | Education , entertainment, data processing, making spreadsheets, presentations, and graphics etc. | Business accounting, Cataloguing , management, data retrieval , communications , file handling, database management, engineering computations etc. |
| Drawbacks/ Limitations | Low computational power, single user interface, Limited applications support etc. | Don’t have cd/DVD drive, Keyboard is smaller in size, Not enough storage capacity ,small display etc. |
| Examples | Laptop, desktop systems , IBM-PC, Pocket calculators , industrial embedded systems | IBM’s AS/400e, Honeywell200, TI-990 etc. |
Download the difference table here.
Continue Reading:
Data Center vs Disaster Recovery Center
Tag:comparison, New technology