MAC Address vs IP Address : Know the difference
Introduction: MAC Address vs IP Address
All devices part of a network can connect and communicate with each other. However, when we try to put logic around the communication between these devices, the key query that always arises in our mind that how one device will uniquely identify and send data to the other device in the network. This can be possible only with the help of the MAC and IP addresses. MAC address is assigned to the NIC card by the manufacturer. IP address is a number assigned to the workstation’s NIC in a network.

We will follow below key sections during the course of this post to illustrate on MAC address and IP Address –
- Definition
- Key Differences
- Comparison Chart
- Conclusion
Definition
What is MAC Address?
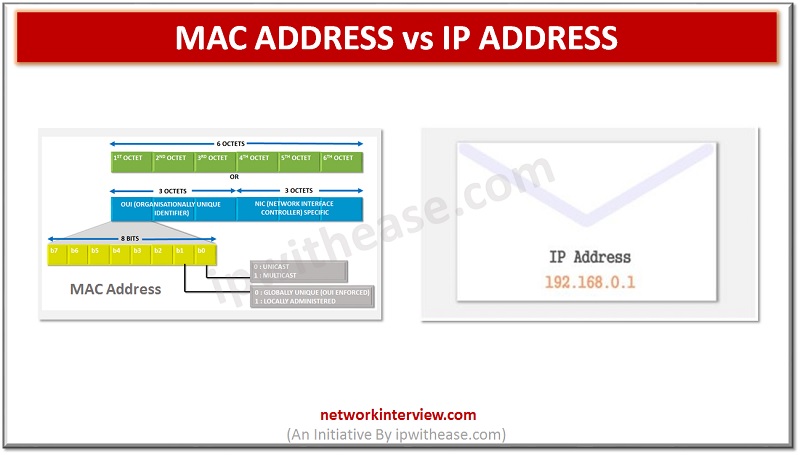
MAC (Media Access Control) address uniquely defines a hardware interface called MAC Address. MAC address is unique and assigned by the manufacturer and is programmed in the ROM of network interface card (NIC). MAC address is a 48-bit hexadecimal address. The format of a MAC address is xx:xx:xx:yy:yy:yy, where xx:xx:xx is a 3-byte address of the manufacturer. On the other hand, yy:yy:yy is a serial number of NIC card. Notable is that MAC address will change if NIC is replaced. MAC address works at the data link layer of OSI model. ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) is a protocol which does IP to MAC address mapping and henceforth is used to get MAC address of a device.
What is IP Address?
Internet Protocol (IP) address is an address which is allocated to every single computer. It is an address that is used to classify every node in the network. IP address provides the network node a location, so that it can connect with other nodes or networks. IP address is 32 bit, Version four of IP protocol. A newer version is IPv6 and it is 128 bit. IP address can be statically and dynamically assigned to a device.
- Static IP address – This will never change, and can be considered a perpetual internet address.
- Dynamic IP address – This is a provisional address that is allocated each time a computer or device connects to the network.
IPv4(Internet Protocol Version 4): IPv4 is a 32-bits address. This address is available in decimal form along with dots (.) in between. For Example – 192.168.1.1. The header field of the IPv4 is 20 bytes, and the checksum bits are present in the header for error control. The IPsec support (for security feature) is optional in IPv4. It supports a datagram up to size 576 bytes. The IPv4 addressing can be used for Multicasting and Broadcasting the data packets.
IPv6(Internet Protocol Version 6): IPv6 is a 128-bits address. This address is available in hexadecimal form along with semi-colons(:) in between. For Example: 2FFE:F300:0213:AB01:0132:7289:2134:ABDC. The header field of the IPv6 is 40 bytes, but the checksum bits are not present in the header file. The IPsec support (for security feature) is mandatory in IPv6. It supports a packet size of up to 1280 bytes. The IPv6 addressing can not be used for broadcasting.
Related – IPv4 vs IPv6
IP address classes
- Class A 0.0.1 to 126.255.255.254
- Class B 1.0.1 to 191.255.255.254
- Class C 0.1.1 to 223.255.254.254
- Class D 0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. It is reserved for multicast groups.
- Class E 240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.254. It is reserved for future use, or research and development purposes.
Key Differences
- MAC address uniquely identifies a device, whereas an IP address uniquely defines a device connection to a network.
- MAC address is 48 bit long hexadecimal whereas IP address has two versions, IPv4 a 32-bit address and IPv6 a 128-bit address.
- MAC address is assigned by the manufacturer. On the other hand, IP address is assigned by the network administrator.
- ARP obtains MAC address whereas RARP obtains IP address.
- MAC Address operates in the data link layer whereas IP Address operates in the network layer.
- MAC Address of computer cannot be changed with time and environment whereas IIP Address modifies with the time and environment.
- MAC Address can’t be found easily by third party whereas IP Address can be found by third party.
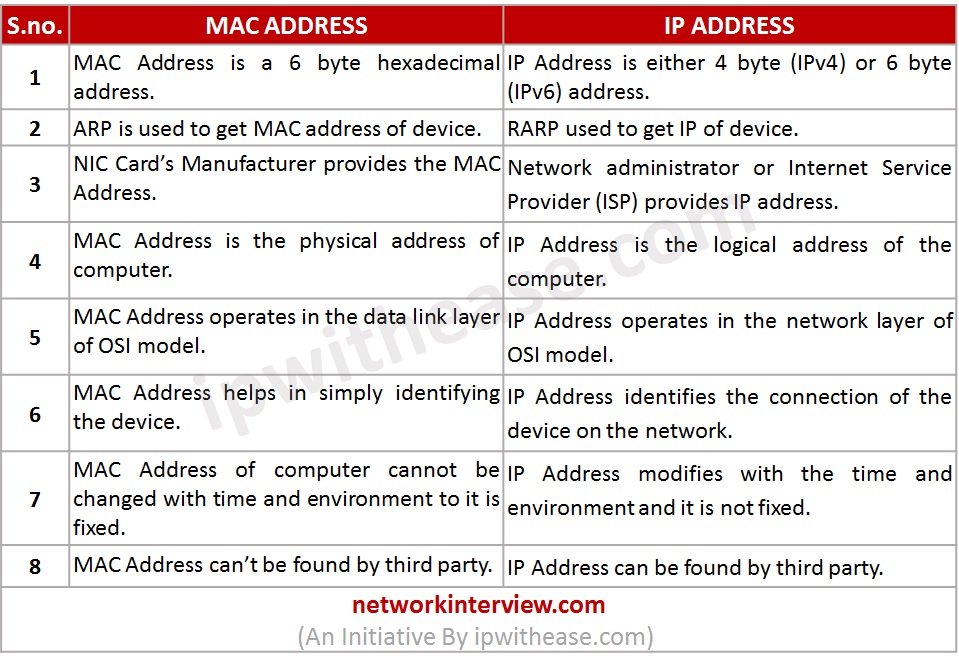
Comparison Table : MAC Address vs IP Address
S.No. | MAC ADDRESS | IP ADDRESS |
1 | MAC Address is a 6 byte hexadecimal address. | IP Address is either 4 byte (IPv4) or 6 byte (IPv6) address. |
2 | ARP is used to get MAC address of device. | RARP used to get IP of device. |
3 | NIC Card’s Manufacturer provides the MAC Address. | Network administrator or Internet Service Provider (ISP) provides IP address. |
4 | MAC Address is the physical address of computer. | IP Address is the logical address of the computer. |
5 | MAC Address operates in the data link layer of OSI model. | IP Address operates in the network layer of OSI model. |
6 | MAC Address helps in simply identifying the device. | IP Address identifies the connection of the device on the network. |
7 | MAC Address of computer cannot be changed with time and environment to it is fixed. | IP Address modifies with the time and environment and it is not fixed. |
8 | MAC Address can’t be found by third party. | IP Address can be found by third party. |
Conclusion
MAC and IP address both are equally required when a device communicate with another device in a network.
Download the difference table here.
Continue Reading:
Ways to find MAC Address of Remote Computers
For a better understanding of IP Address, please watch our related video:
Tag:comparison