ISP vs VPN: Know the difference
Introduction to ISP & VPN
Internet service providers (ISP) facilitates internet navigation and helps in transmitting all your Internet packets however VPN creates a secure tunnel where data is encrypted during transmission. Often people get confused between the two terms and not clear on their purpose and not very sure what all getting exposed to the Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Let’s understand today the difference between the two terms more in detail.
What is ISP?
Internet service provider (ISP) is a company which provides ISP and Internet related services to its customers such as hosting services, browsing services, live streaming, Internet TV subscriptions etc. The ISP creates a link between systems and Internet. Whenever an instruction is sent from system to access information from Internet it first goes to ISP address and then hits their destination. Some common examples of ISP are VSNL, AT&T, Verizon etc.
The Internet access provided by ISPs can be divided into many types as under: –
Dial up Internet access – is the oldest form of technology to provide Internet access by using modem to modem connection using telephone line. The user system is connected via a telephone line and modem to Internet. It is very slow and used where broadband is not available.
Digital Subscriber line (DSL) – is advance version of dial up internet access. It allows Internet and phone connection both to operate simultaneously over high frequency.
Wireless Broadband – It gives high speed wireless Internet. This requires a dish which is place at high area and it points in direction of transmitter of Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP).
Wi-Fi Internet – it is also called ‘wireless fidelity’ and this provides high speed wireless Internet connection through radio waves. It is commonly used in public places such as Malls, airports, restaurants etc.
ISDN – stands for integrated services digital network and it is a telephone-based network which integrates with high quality digital transmission of voice and data on telephone lines.
Ethernet – it is a wired LAN where systems are connected in a limited physical space. Devices communicate using a protocol and it offers different speeds starting from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps.
How ISP works?
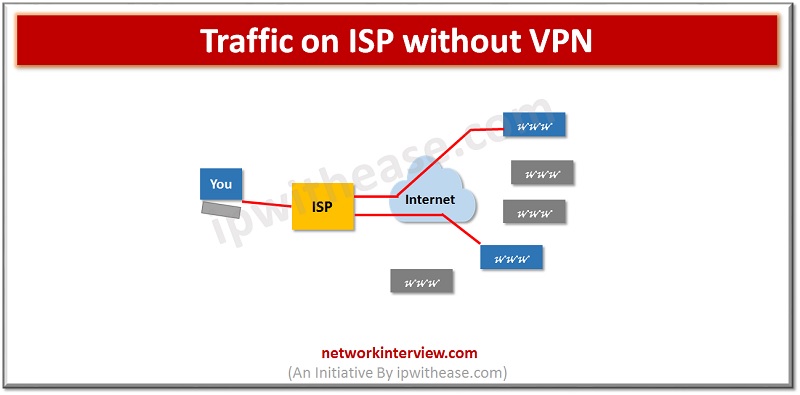
Internet service providers or ISP’s and analytical systems such as Google analytics captures all online activities performed by users. The ISP stores millions of user’s profiles in terms of age, gender, interests, preferences such as food, drinks, favourite music , movies, political preference etc. ISPs store and collect history of visited sites, when user types a URL in browser ISP analyses the contents of package you received. From the package all information related to login with passwords, search history etc. can be obtained (In case website is using unencrypted HTTP connection for authorization). The ISP knows where you are connecting and can read all unencrypted traffic.
About VPN
When the question or concerns arise on privacy of data over ISP then VPN (Virtual Private Tunnel) comes into the scene.
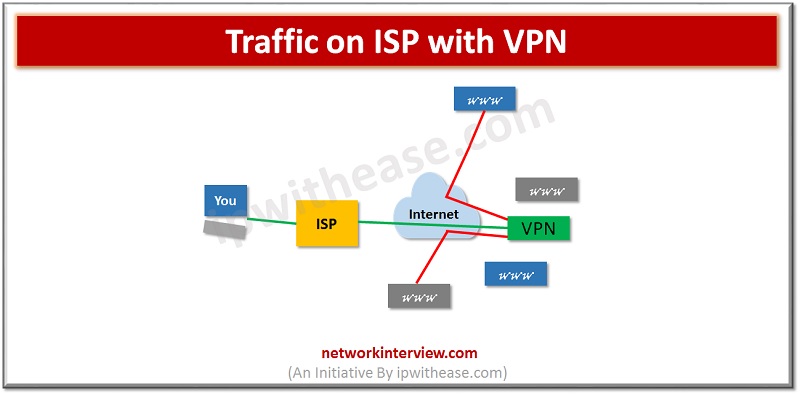
When online privacy is a major concern VPN is the answer to problem. VPN creates a virtual private tunnel between you and itself. Data passing thru tunnel is encrypted. A VPN application mask the actual IP address and replace it with virtual IP Address. When the system is connected via VPN tunnel the traffic passing through tunnel is not visible to the outside world.
How VPN Technology works?
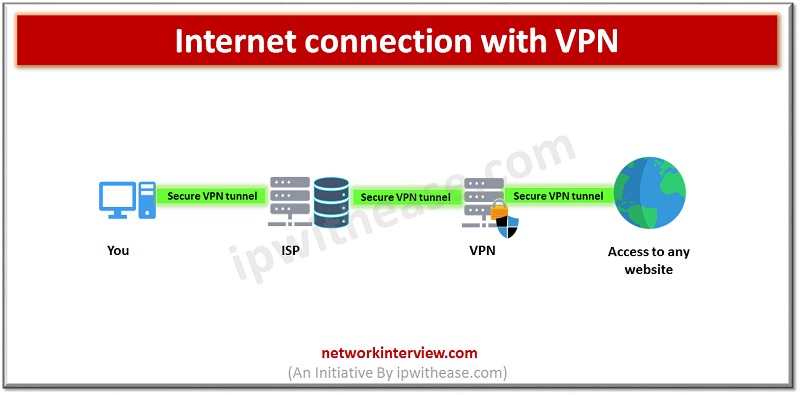
VPN route the device Internet connection through the chosen private VPN server instead of Internet service provider (ISP) so data transmitted to the Internet comes thru a Private tunnel it hides the actual IP address of system and protects the identity and since data is encrypted in transit it will be unreadable or can’t be intercepted until it arrives at its final destination. Encryption will hide data in such a way that it cannot be read until a strong password like key is available. The device is seen as being on same local network as the VPN and the IP address assigned is actually the IP address of VPN provider server.
Key Protocols used in VPN Technology
Some of the key protocols used in VPN technology now are days are:
- Point to Point Tunneling protocol (PPTP) – It is one of the oldest protocols used on Internet.
- Layer 2 Tunnelling Protocol (L2TP/IPSec) – This protocol is combination of PPTP and L2F protocol from Cisco. It is more secure than PPTP it does not have its own encryption capabilities, but it uses IPSec which is a security protocol.
- Secure Socket Tunnelling Protocol (SSTP) – This is created by Microsoft used by websites for encryption purpose. It is a very secure protocol.
- Internet Key Exchange, version 2 (IKEv2) – The more secure version of L2TP, IKEV2 made in collaboration between Cisco and Microsoft. It is bundled with IPsec and mainly used on mobiles.
- OpenVPN – it is an open source technology and it is one of the most popular protocols and considered most secure.
Benefits of VPN Technology
Some of the benefits of VPN are as under:
- It gives a secure connection and protect systems from hackers and other online threats
- It allows restricted access to websites
- It hides the actual IP address and protects your identity to outside world
- VPNs are significantly cheaper and easy to setup
- Ability to safely connect to public networks
Comparison Table: ISP vs VPN
Below table summarizes the differences between ISP and VPN:
PARAMETER | ISP | VPN |
| Definition | Internet service provider (ISP) is a company which provides ISP and Internet related services to its customers such as hosting services, browsing services, live streaming, Internet TV subscriptions etc. | VPN creates a virtual private tunnel between you and itself. Data passing thru tunnel is encrypted. |
| Features | ISP can see whatever you do, unencrypted traffic | Secure, data is encrypted, scalable, unrestricted access to websites, easier to setup and cheaper |
| Providers | AT&T, VSNL, Verizon , Comcast, Qwest, AOL etc. | Cisco VPN, Express VPN, Nord VPN, IPVanish etc. |
Download the comparison table: ISP vs VPN
Continue Reading:
Tag:comparison, Security



