Google NTP Server: Network Time Protocol
Introduction to NTP Server
NTP or commonly known as Network Time Protocol (NTP), is a networking type of protocol that is utilized for clock synchronization between computer systems, over packet switched data networks, with variable network latency. The NTP has operated since 1985 and it is one of the first Internet protocols that is implemented on the world-wide web. Historically, NTP was invented by Mr. David L. Mills, a scientist from the University of Delaware of the United States.
The main purpose of NTP is to synchronize all the connected computer systems, according to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) specifications, always maintaining a time difference of about a few milliseconds. The main theory of NTP is that It uses an intersection algorithm, known as a modified version of Marzullo’s algorithm, in order to choose the most accurate time servers available and it is designed to mitigate the problems of any variable network latency that may arrive.
Furthermore, NTP can maintain time differences, to a range of ten of milliseconds over the worldwide web and can sometimes perform even better than one millisecond accuracy in local area networks. Unfortunately, asymmetric routing and network random congestions can cause errors of 100 ms of delay or more.
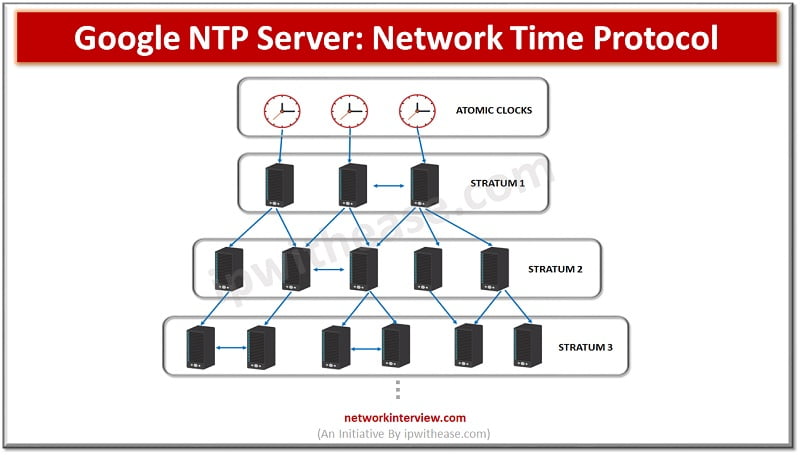
The NTP protocol’s architecture is usually explained in terms of the normal client–server model, but it can also be utilized in peer-to-peer negotiations, where both sides think that the other side can be a possible time source. In every day implementations, timestamps are being sent and received by utilizing the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) on port number 123. Timestamps can also use broadcasting or multicasting techniques, where client peers are listening to the time updates after the first round-trip exchange of calibration.
Finally, the NTP is able to supply an alert of any forthcoming leap of second adjustments but unfortunately, it cannot send any information about the local time zones or daylight saving time periods.
Technically, the international standard protocol that is used is version 4 (NTPv4), which is initially proposed under the documented RFC 5905 specifications form. Finally, it is essential to mention that it is backward compatible with version 3, that it is described in RFC 1305 specifications form.
How is Google NTP Server different?
Nowadays, there are many public NTP servers around the globe. Most of them are free of charge and the best priority of choice is the server’s physical location. Google’s public NTP server is distinguished from the competition because they serve what we call leap-smeared time since 2008.
Many organizations worldwide are using smeared clocks and it would be helpful if the smears were similar in every kind of implementation. In general, the purpose of clocks is to read the same time in different places of the world according to the specific time zone differences. Google also encourages users to smear leap seconds by introducing a 24-hour based linear smear system from noon to noon UTC.
This smearing system, combines the specifications that from experience has proved to perform well for most distributed computing applications:
- First of all, the longer the duration is, then results that the frequency changes are smaller. Usually, the change for the smear technique is about 11.6 ppm. This is in the range of the specifications followed by most manufacturers and various thermal errors of the machine’s quartz oscillators keeping the ratio below NTP’s 500 ppm maximum slew rate.
- Furthermore, by placing the smear in the center of the leap second, instead of setting it at the beginning or at the end of the leap second, results in minimizing the maximum usual offset.
- In addition, if we have a simple cosine smear system, we will find out that the linear smear method is a much simpler method, usually easier to calculate and minimize the maximum frequency differentiations.
- Finally, the 24-hour period duration has been widely adopted by organizations that implement smears in general. Google has previously used a 20-hour period smear duration, but chose to align with this more popular noon-to-noon interval period system.
Google plans to use the above smearing system for all the future leap seconds. Also, Amazon uses this smearing system in AWS. Finally, each user can use it in their systems by configuring them to use Google Public NTP server.
Conclusion on Google NTP Server
In this article, we discussed key attributes of NTP protocol and the historical evolution in time. Then we focused on Google’s NTP server and the advanced technologies they implement to the public community. Finally, we would like more public NTP Server’s to adopt leap-smearing methods to provide a better experience.
Continue Reading:
Web Server for Chrome: Google Chrome
Tag:services



