FortiGate Packet Flow: Ingress And Egress
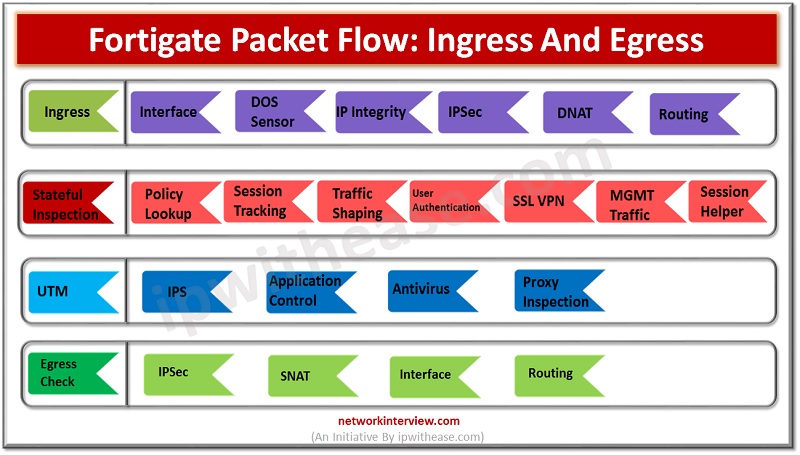
FortiGate packet flow is also known as Life of a Packet. This is the process when the packet enters the Ingress interface and exits from the Egress interface.
Stages of FortiGate Packet Flow
FortiGate packet flow consist of 4 stages which includes
- Ingress Check
- Stateful Inspection
- UTM
- Egress Check
Ingress Process: when packet comes on any Firewall interface, it extracts some layer 2/ layer 3 information and set information of interface on which it received.
Dos Policy: If you have configured DOS policy it checks by firewall here.
IP Integrity: Check if the packet is genuine or real/valid. If the packet is malformed or not able to pass IP integrity, the packet will be discarded by Firewall.
IPSEC VPN Decryption: If packet is VPN packet, it will be decrypted by firewall and get IP address detail of original source from TCP/IP stack.
You can see the image below with packet flow. Traffic enters in VLAN 2 with protocol 6, source IP address -> 10.1.1.1 and destination IP address -> 2.2.2.2 destination port 443 and sequence number of packet 22334455
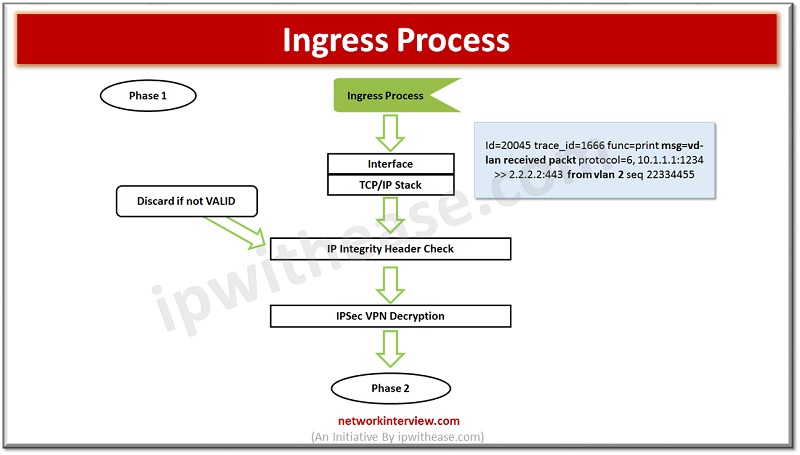
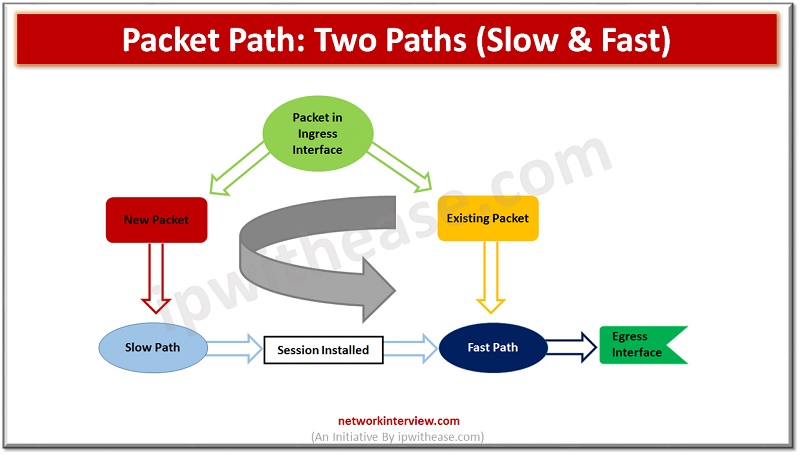
After the above checks the packet enters session table (Phase 2) and checks if it belongs to the existing session OR a new session.
Session path is further divided into TWO paths
- Slow Path->For new session
- Fast Path->For existing Session Or once new session created by firewall after completion of phase1
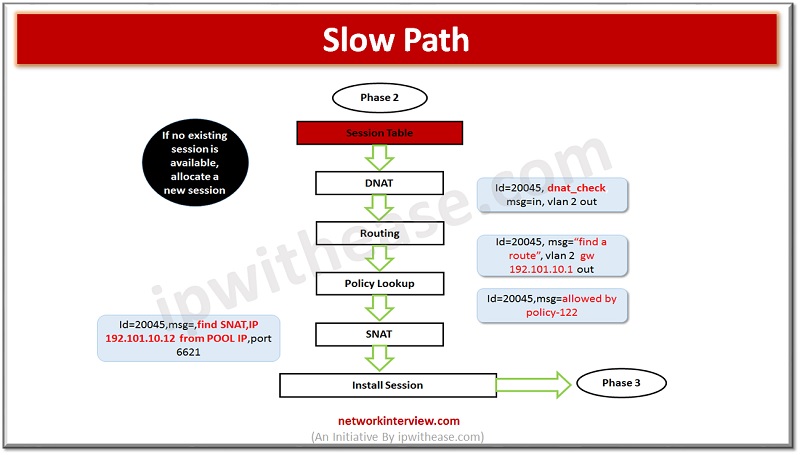
Slow Path
A new session to a new packet will be allocated by Firewall with a new session-id.
- DNAT -> Firewall check if the packet IP address is used in Destination NAT.
- Routing -> Find the Route for source
Why is Routing before Policy Lookup?
It saves process as routing policies are always less than Policies. Firewall can have 100-200 policies, but routing policies are less than 100. Hence routing is performed before policy lookup.
- Policy Lookup-> Check policy if source and destination is allowed by firewall else drop the packet.
- SNAT-> Check Source NAT to identify the original IP address.
Session Installed in session Table. You can see firewall packet messages in the below packet flow image.
Before sending a session in the next stage SSL decryption happens to identify the SSL traffic.
Now the session is installed in the firewall session table hence the packet moves to the Fast path of firewall packet flow.
Fast Path
- IPS-> Firewall check IPS signature against the packet of it contains any application traffic. IPS is the only UTM feature that gets triggered in a SYN packet. For other UTM features the packet must complete a 3-Way handshake. IPS is always FLOW Based. IPS further moves traffic to Application Control to identify which application it is.
- Application Control -> Check Application detail if it is yahoo, google, YouTube. Then packet moves to web-filtering stage
- Web filtering -> It checks URL, Category, domain-name. First it checks static/manual URL and then move to Category
- Then the packet is further processed for DLP and Anti-Virus.
Why does Anti-Virus come after Web Filtering?
Because first we browse any website and after that we download something from there. So, if content is malicious, it will be checked by Anti-Virus once downloaded from the website.
Note: If file size exceeds 10 MB it will skip by Firewall to perform Anti-Virus checks.
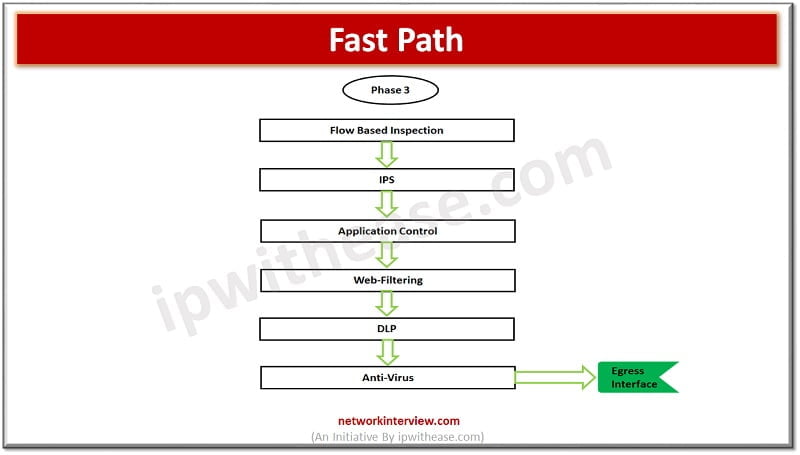
Once all above UTM features parsed by Firewall packet moves to Egress/exit interface.
This is the simplest form of FortiGate Packet flow.
Deep-dive: Packet Flow in FortiGate
You can read the article below for a better understanding of FortiGate packet Flow.
Ingress Process & Network Interface -> when packet comes on any Firewall interface, it extracts some layer 2/ layer 3 information and set information of interface on which it received.
Dos Policy-> If you have configured DOS policy it checks by firewall here. It stops DOS attacks.
IP Integrity ->Check if the packet is genuine or real/valid. If the packet is malformed or not able to pass IP integrity, the packet will be discarded by Firewall. It ensures the packer header is correct and valid.
IPSEC VPN Decryption -> If packet is VPN packet, it will be decrypted by firewall and get IP address detail of original source from TCP/IP stack.
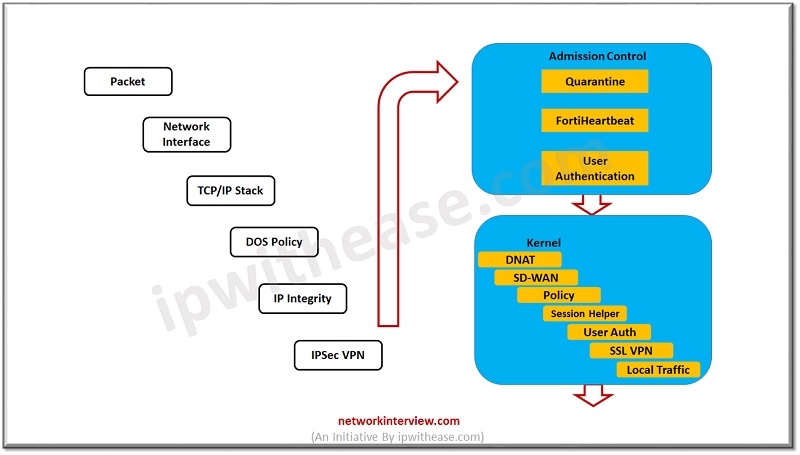
ADMISSION CONTROL -> It verifies if the traffic is non malicious and not belongs to the QUARANTINE List,
- Quarantine->Files which contains viruses are placed in Quarantine list to avoid any direct contact with normal traffic.
- FortiHeartbeat -> Quarantine packet can only be accessed by FortiApp
- User Authentication ->User is authenticated by using Captive portal.
After authentication, the packet moves to Kernel Level process.
- Destination NAT -> If destination NAT is applied on packet IP address, then NAT table is checked, and packet IP will be changed to assigned Destination NAT IP.
- Routing -> here routing table will be checked for packet, depending on source or destination address traffic redirect to the next step. Based on source address and interface routing decisions will be made in the FortiGate firewall.
- Policy Lookup -> Policy checks will be performed by checking stateful packet table in firewall.
- Session Helpers -> These helpers are used for dynamic ports or dynamic application like VoIP, SIP. FortiGate extracts information from the packet to check if the traffic belongs to a dynamic application and requires session helpers. Session helpers are
- PPTP
- H323
- FTP
- TFTP
- SIP etc.
- User Authentication-> User authentication is checked again
- SSL VPN-> if traffic has SSL traffic, then it will be checked by firewall.
- Local Management Traffic-> if firewall management by any management device, then traffic check performs for the same.
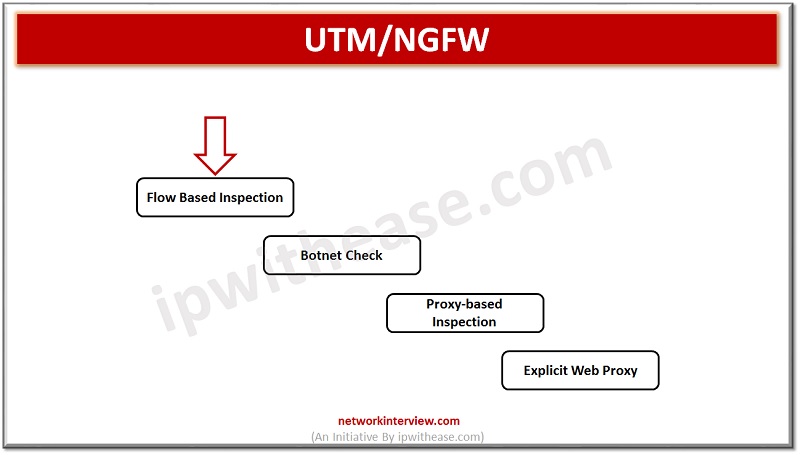
Now traffic moves to the UTM/NGFW mode
- FortiGate supports flow-based or proxy-based inspection
- Flow based is for single-pass processes
- Proxy-based inspection is for explicit tor transparent traffic.
- Botnet is checked against the traffic by using UTM feature of firewall
- IPS checks are performed in UTM/NGFW mode
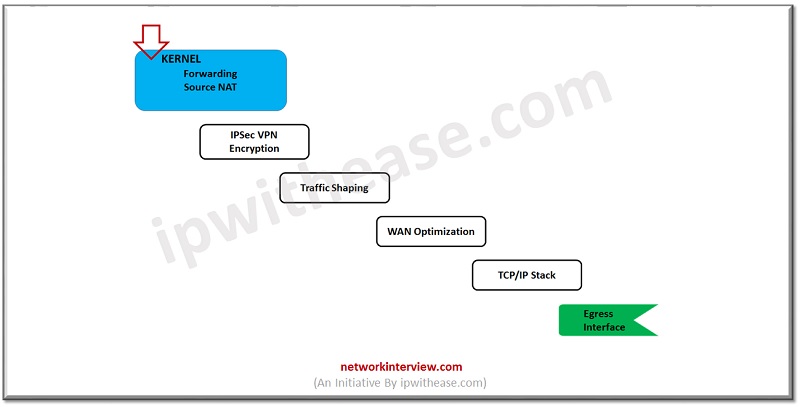
Now traffic moves to another Kernel stage
- Source NAT -> here source NAT will be checked, and routing table is used to verify the correct exit interface of firewall.
- IPSec Encrypted -> If traffic/packet belongs to IPSec tunnel then firewall performs encryption for the same.
- Traffic Shaping-> QoS/Cos (Quality of Service & Class of Service) will be performed on packet.
- WAN Optimization-> It imposes if traffic shaping is configured
- TCP/IP Stack-> Re-verification of packet, if packet checksum is correct or malformed.
- Network Interface-> Egress Interface
Continue Reading:
Packet Flow in Palo Alto – Detailed Explanation



