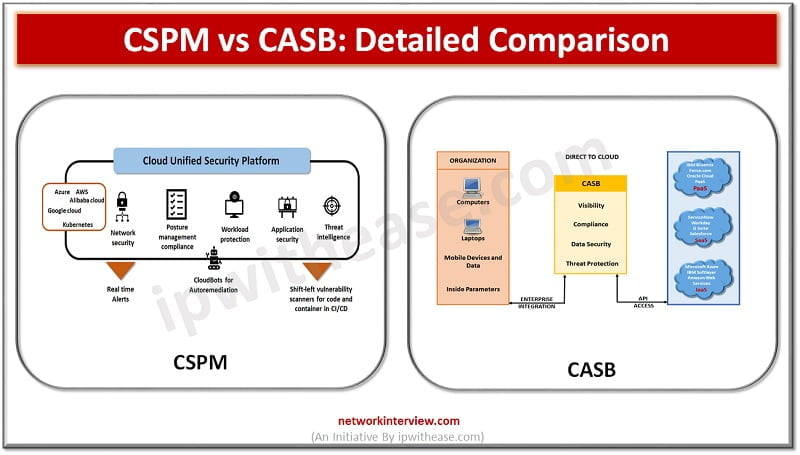
CSPM vs CASB: Detailed Comparison
Enterprises are moving their workloads on cloud infrastructure. Gartner forecasts that globally public cloud spending will increase by 18.4% in 2021 to a total of $304.9 billion. As organizations shift IT spend more and more on cloud services, they are facing more and more regulations, higher rate of data loss, and sudden surge in attacks on their cloud hosted applications. Visibility and security are of prime importance on cloud to confront these challenges.
Today we look more in detail about two important terminologies: Cloud security posture management and cloud security access broker, what is the purpose of each, advantages and disadvantages, use cases etc.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Cloud security posture management (CSPM) is meant for protection of workloads from outside by assessment of secure and compliant configurations on control plane in cloud platform. There are a set of tools which support monitoring of compliance, DevOps processes integration, incident response, risk assessment and risk virtualization.
It identifies unknown and excessive risk across an organization cloud plane including cloud services for computing, storage, identify and access management, and many more. It provides continuous compliance monitoring, configuration drift prevention, investigations in security operations center. Policies can be created at organization level to define desired state of configuration for cloud infrastructure; which CSPM product can use for monitoring based on those policies.
It enables enterprises to detect and take care of configuration issues which affect their cloud environments as per center for internet security benchmarks for cloud providers. CSPM tools can automatically detect the cloud environments non-compliance and security violations and provide automated steps to fix them. New risks for cloud environment, breach prevention, and uniform cloud configurations are manageable with CCPM.
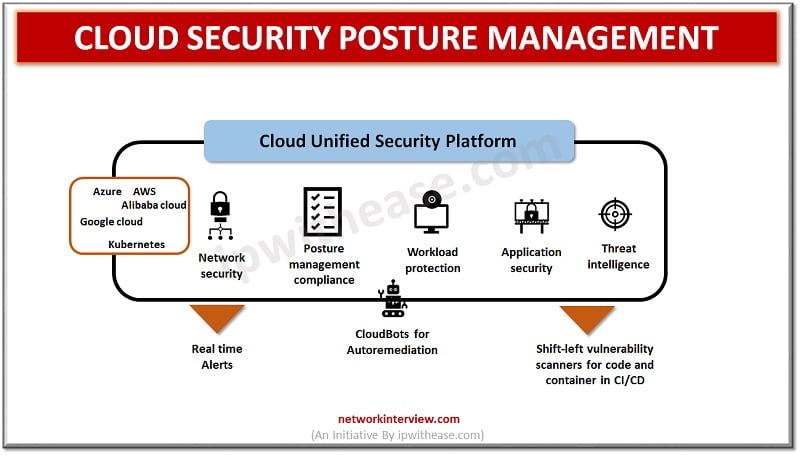
Features of CSPM
- Visibility and security controls enforcement across multi cloud providers
- Discovery and identification of cloud workloads and services
- Threat detection and alert prioritization
- Capabilities of Cloud risk management, risk visualization and risk prioritization
- Continuous compliance monitoring against different regulatory standards
Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
Cloud access security broker (CASB) is a firewall for cloud environment. It has a security policy enhancement gateway to make sure that users are compliant to organization policies and actions are authorized. It can identify all cloud services used by an organization, be it Shadow IT, unapproved or unmanaged SaaS and PaaS products. It enables alerts, cloud usage tracking, reporting, logging, assessment of risks posed by Shadow IT and event monitoring.
It has auditing and reporting tools for regulatory compliances, in addition to cloud stored areas. This provides user authentication, authorized applications, anti-phishing, account takeover, URL filtering, malware detection, and sandbox protection.
CASB can also monitor access to data and with granular access controls it can enforce data centric security policies and policy-based encryption.
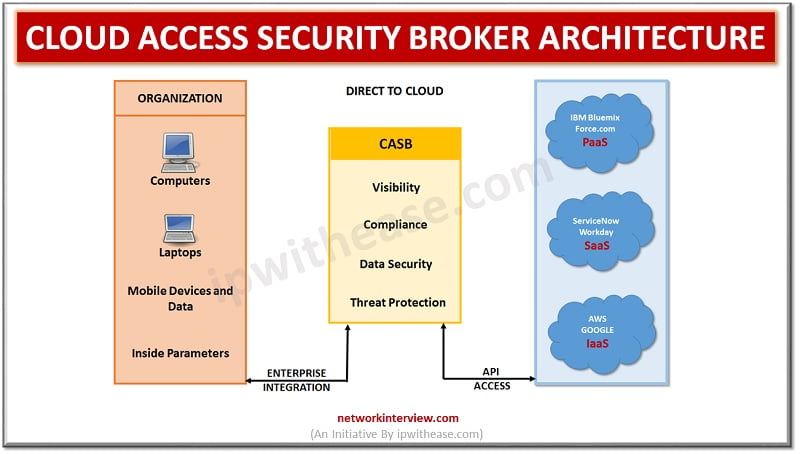
Features of CASB
- Detection of shadow IT
- Usage tracking in cloud services
- Reporting and logging
- Alerts generation
- Enforcement of regulatory requirements
- User behaviour analysis
- Malware detection
- Encryption and tokenization
- Enforcement of data loss prevention policies
Comparison Table: CSPM vs CASB
Below table summarizes the difference between the two:
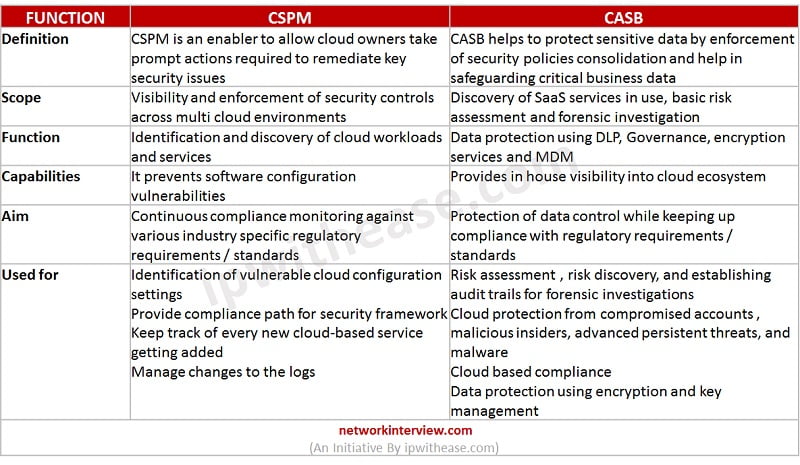 Download the comparison table: CSPM vs CASB
Download the comparison table: CSPM vs CASB
Conclusion
The recent cloud breaches are forcing organizations to double their security and it is a domination conversation across board meetings. Cloud security means all procedures and technologies which secure the cloud computing environment against internal and external threats and ensure adherence to regulatory requirements which may differ from country to country. Both CSPM and CASB are needed to secure a cloud computing environment. CASB acts as a security policy enforcement gateway to ensure users are compliant to policy requirements whereas CSPM is required to ensure continuous compliance monitoring.
Continue Reading:
What is CASB (Cloud Access Security Broker)?
Tag:cloud, comparison, Security