Business Intelligence vs Data Science
In the era of big data, where analysis of large amounts of data leads to world changing innovation. Organizations are hiring business intelligence experts and data scientists. Over the past few years the businesses have changed and more focused on data because organizations are generating more and more data in day-to-day operations and processes. Data is an intangible asset for organizations and they are using this data to gain real time analytics into their operations using data analysis. Data can be viewed as raw data from which information will be obtained which would be useful in solving business problems.
Today we look more in detail about two important technologies Business intelligence and data science , understand the difference between them, the purpose for which they are deployed and how use cases etc.
About Business Intelligence (BI)
Business intelligence is a set of technologies, applications, and processes which are used by organizations in business data analysis. It is used for conversion of raw data into meaningful information which will be used to make informed business decisions which are profitable. It may deal with structured or unstructured data sets and supports decision making based on actual facts derived from data sets and not on assumptions. It enhances the organization’s chances to enter new markets , mergers and acquisitions etc.
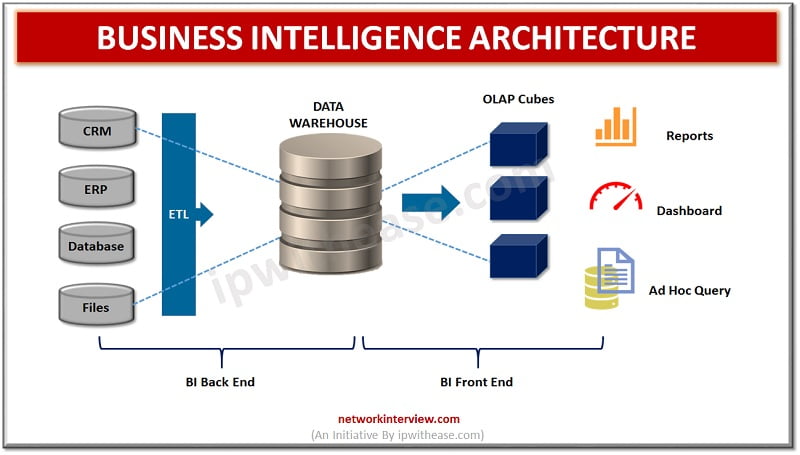
BI tools are used for analysis and reporting. They are also used to produce graphs, dashboards, summaries and charts to help in better decision making. BI data is stored in data warehouses and also supports real time data which is generated from services hence it helps in strategic decision making.
Uses of Business Intelligence
- Measurement of performance and quantify progress towards business goals
- Quantitative analysis via predictive analytics and modelling
- Data visualization and storage in data warehouses for further processing in OLAP
- Use of knowledge management programs to derive effective strategy to gain insight into learning management and raising compliance issues
About Data Science
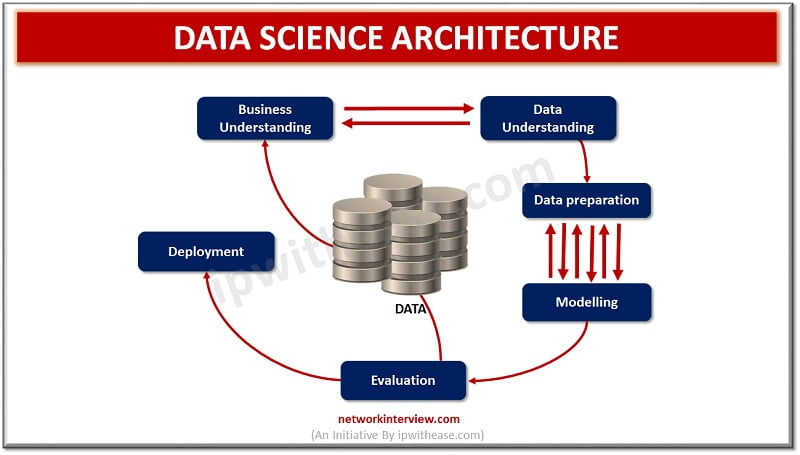
In the data science field information and knowledge can be extracted from the data using several scientific methods, algorithms, and processes. It is a combination of mathematical tools, algorithms, statistics, and machine learning techniques and identifies hidden patterns and insights into data which helps in facilitating decision making processes. Data science deals both with structured as well as unstructured data. It deals with both data mining and big data. It also involves historical trends study and use conclusions to redesign present trends and define future trends.
Data science focuses on generation of insight into the data which are resulting from complex predictive analytics and output is not presented as a report but as a data model. You can opt for a Data Science Online Course to get yourself acquainted with the Data Science technology.
Comparison Table: Business Intelligence vs Data Science
Below table summarizes the differences between the two terms:
FUNCTION | BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE | DATA SCIENCE |
| Definition | BI is accumulation of processes and technologies which takes raw data and derive something meaningful out of it | DS is all about gathering of raw data and analyse that data with statistical techniques and algorithms to bring out insight and conclusions |
| Scope | Analyses historical data to discover patterns and trends so business can take more informed decisions | It uses both historical and present data and uses it to create as much as impact possible onto business |
| Approach | Takes analytical approach to build decision making applications | Takes predictive and prescriptive analysis to generate insights into data and more complex in nature |
| Deals with | Deals with what has happened? | Deals with what will happen and what if |
| Type | Handles both structured and unstructured data sets which is static in nature (tabular data sets , relational models) | Handles both structured and unstructured data sets which are dynamic (text, audio, images, IoT signals etc.) |
| Focus on | Descriptive analytics: what happened why did it happen, what is the learning ? | Predictive and Prescriptive analytics : what will happen in future, how we prepare ourselves ? |
| Storage | Data is stored in data warehouses | Data is distributed in real time clusters |
| Procedure | Help organizations to solve questions | Used by data scientists (questions are curated and solved) |
| Goal | Identification of patterns and trends to turn raw data into insights | Test hypothesis using experimentation and iteration |
| Presentation | Findings are presented in the form of charts, dashboards, graphs, summaries etc | Findings are presented as algorithms and statistical models |
| Tools | MS Excel, SAS BI, Sisense, MicroStrategy, Cyfe, TIBCO Sportfire, Klipfolio etc | Python, R, Hadoop/ Spark, SAS, TensorFlow, BigML, MATLAB etc. |
Download the Comparison table: Business Intelligence vs Data Science
Continue Reading:
Data Science vs Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence vs Machine Learning
Tag:comparison, New technology



