Perimeter Firewall vs Internal Firewall: Detailed Comparison
Firewalls are the primary line of defense for organizations; they are there for more than three decades but evolved and came a long way with drastic features and also sold now as separate appliances and make smarter decisions about what network traffic is to allow and what to block.
But the question is do we need to secure Perimeter only or need to monitor traffic internally also; what if someone is sitting inside and launching an attack. Internal users or those inside the firewall are responsible for 60% of network attacks as per statistics.
Today we look more in detail about perimeter and internal firewalls, their key differences and which is suited for what kind of purposes.
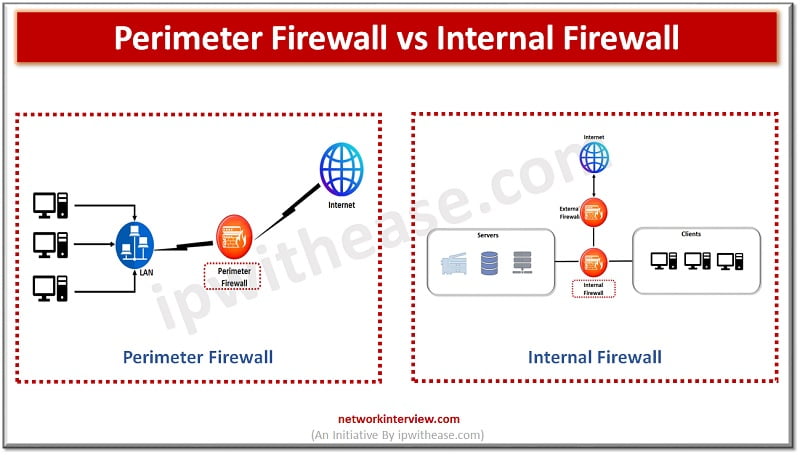
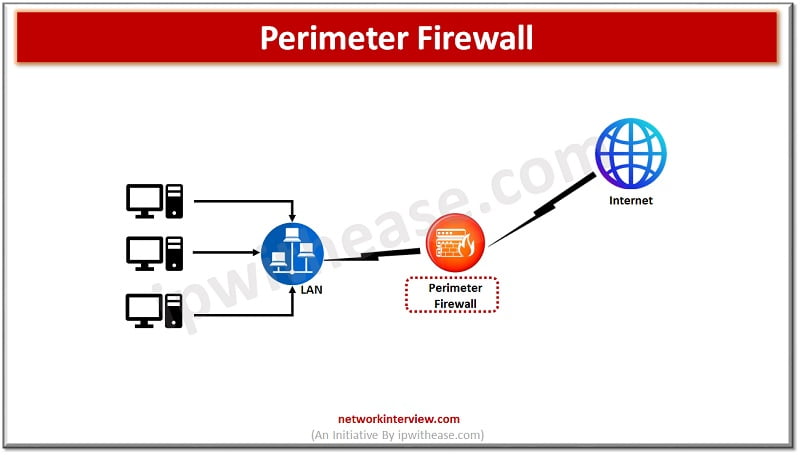
What is a Perimeter firewall?
Perimeter firewalls are external firewalls which are gateway to private networks as well as other public networks such as the Internet. The external firewall monitors and protects the network from external malicious traffic, harmful programs, and intrusion attacks. Perimeter firewalls come in a variety of capabilities like some are packet filtering firewalls they inspect contents of network packet and then allow/disallow based on access control lists.
Stateful firewalls in this category track current state of network connections and incorporate this information into access decisions. Proxy firewalls act as proxy for user connections and create separate connections between user and firewall and conceal IP address to protect privacy. Next generation firewalls or (NGFWs) are the latest in this brand and combine features of packet filtering and stateful inspection with other security capabilities such as intrusion detection, malware protection and so on.
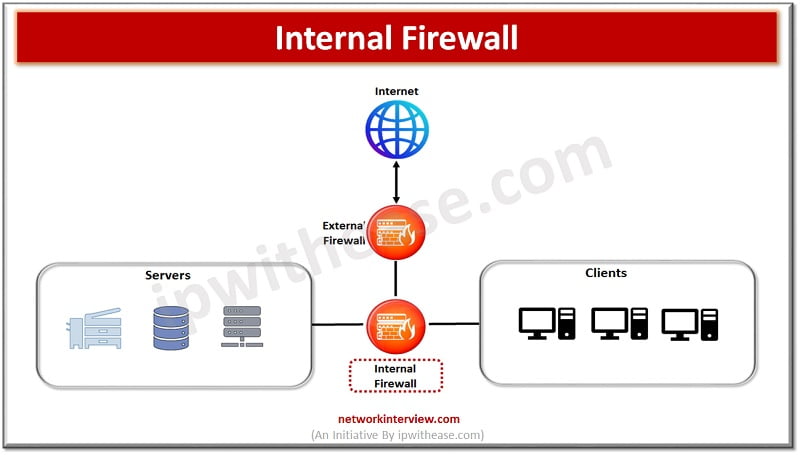
What is an Internal firewall?
An internal firewall protects a network from attacks which have passed the perimeter by controlling network traffic between two internal devices such as workstations and servers. An internal firewall has more complexity in terms of its application as a firewall and placed inside the internal network and employs a Zero Trust network access (ZTNA) to isolate insider attacks and reduce the impact of harm.
Traffic patterns in IT or hosted environments are classified based on:
- North to South – Traffic from internet network (LAN) to Internet and vice versa.
- East to West – Intra-organization traffic which routes server-to-server, client-to-client but does not go outside the organization perimeter. It may occur between IP subnets or routed VLAN interfaces.
Perimeter Firewall vs Internal Firewall
Below table summarizes the differences between the two types of firewalls:
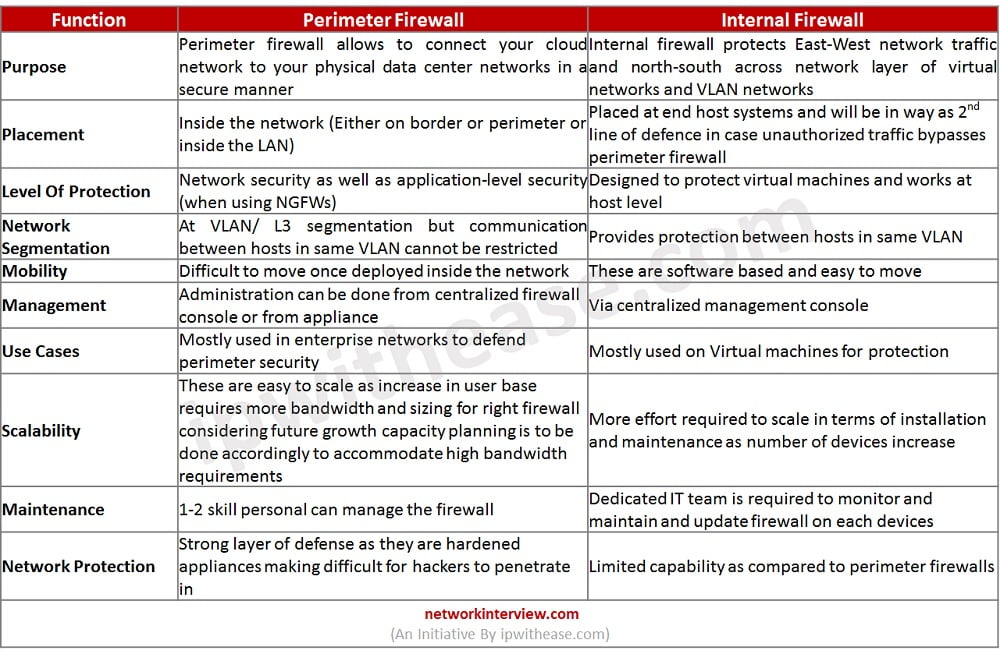
Download the comparison table: Perimeter Firewall vs Internal Firewall
Continue Reading:
6 Types of Firewall: Network Security
Tag:comparison, Security



