Data Center vs Disaster Recovery Center: Sneak Preview
When we talk about IT Setups and IT infrastructure we come across some terms and we wonder what the difference between them could be.
Today we look at two common terminologies: Data center and Disaster Recovery Center, we come across in usual IT conversations.
Data Center
A data center is a centralized physical space to host computer systems and other infrastructure components such as network equipment, telecommunication links, storage systems etc. Data canters usually comprise of multiple power sources such as regular power supply from energy company, DG sets to provide power redundancy, multiple data communication links and other environmental controls such as air conditioning/cooling equipment, fire safety equipment’s, Security devices, access control equipment and so on.
Servers and network components are usually organized in ‘racks’.
Businesses in need of round the clock systems operations and high-speed connectivity requirements could depend on Data Centers for services to save running costs of IT operations.
Data Center – Types
Data Center design comprises of networking equipment such as routers, switches, firewalls. Storage equipment and Servers. Critical data and applications are hosted in Data Center to support business critical services hence data center security is very critical to Data Center design. Classification of Data Centers is determined by there ownership, technologies used for computing and storage , energy efficiencies etc.
Enterprise Data Centers are built and owned by organizations and optimized for their end users. They are usually in-house within company premises.
Managed Services Data Centers are managed by 3rd party service providers . Equipment is leased and not procured.
Colocation data centers are those where organizations rent space within Data Centers owned by other organizations. The infrastructure is provided by Data Center owner companies such as buildings, cooling , bandwidth , security (Physical / Logical) etc. and components such as Servers, Network equipment , storage etc. is provide by the organization.
Cloud data center – Data and applications are hosted on Cloud infrastructure such as IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure, or any other Public Cloud service provider.
Disaster Recovery Center
A disaster can strike at any point of time or anywhere. It may happen due to a network switch failure to physical calamity – Flood, fire etc. happened in Geographical area where Data Center is located. In most of the cases Disasters can’t be predicted but we can plan to minimize damage to business and recover critical business data with meticulous planning.
Disaster Recovery Centers are setup to address the uninterrupted Business continuity requirements of organizations. Disaster Recovery Center is a specialized data center where the replication of data and computer processing is setup at off-premises location to ensure the services are not impacted when disaster strikes. While designing a Disaster Recovery Centers several factors are taken into consideration such as Primary site and DR site should not be in same Seismic zones.
In today’s competitive world organizations required to provide on demand services to their customers and ensure availability of services round the clock and minimize the downtime.
Gone are the days of traditional On Premises Data Centers and these are replaced by Virtualized systems on a mass scale. Use of virtualization technology makes it easy to protect critical data and applications by creating VM based backups and replicas which can be stored off-site or at remote location. So, Production load of Primary data center can quickly be moved onto a Disaster Recovery site / Center to quickly resume business operations.
Setting up Disaster Recovery Center is subset of ‘Business Continuity’
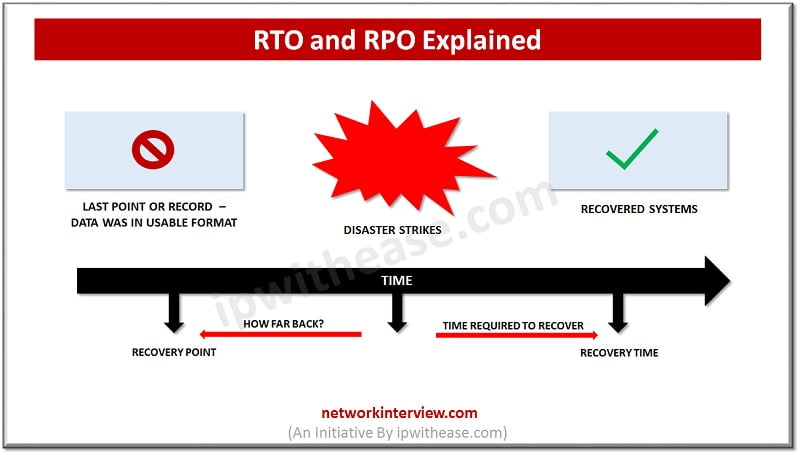
Disaster Recovery Center – RTO and RPO
RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) are two commonly used terms in Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery.
RTO defines timeframe within which systems need to be restored to their original state.
RPO defines how much data organization can afford to lose before it starts impacting the business.
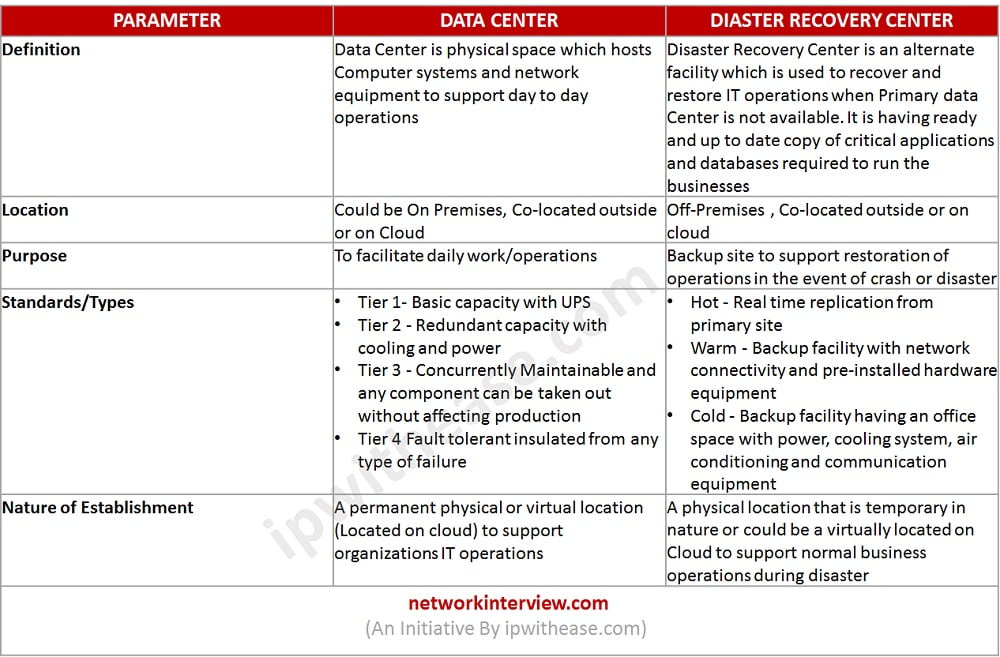
Comparison Table: Data Center vs Disaster Recovery Center
PARAMETER | DATA CENTER | DIASTER RECOVERY CENTER |
| Definition | Data Center is physical space which hosts Computer systems and network equipment to support day to day operations | Disaster Recovery Center is an alternate facility which is used to recover and restore IT operations when Primary data Center is not available. It is having ready and up to date copy of critical applications and databases required to run the businesses |
| Location | Could be On Premises, Co-located outside or on Cloud | Off-Premises , Co-located outside or on cloud |
| Purpose | To facilitate daily work/operations | Backup site to support restoration of operations in the event of crash or disaster |
| Standards/Types | •Tier 1- Basic capacity with UPS •Tier 2 – Redundant capacity with cooling and power •Tier 3 – Concurrently Maintainable and any component can be taken out without affecting production •Tier 4 Fault tolerant insulated from any type of failure | •Hot – Real time replication from primary site •Warm – Backup facility with network connectivity and pre-installed hardware equipment •Cold – Backup facility having an office space with power, cooling system, air conditioning and communication equipment |
| Nature of Establishment | A permanent physical or virtual location (Located on cloud) to support organizations IT operations | A physical location that is temporary in nature or could be a virtually located on Cloud to support normal business operations during disaster |
Download the comparison table here.
Disaster Recovery Center planning involves careful assessment of key points related to:
- Identification of critical business processes to continue its vital processes
- Identification of data that requires to be protected and develop a backup schedule
- Data recovery techniques suitable for business
- Location of data to be determined will it be stored on site or off site
- Training of staff to quickly recover from a disaster or supervision on how to work during disaster
- Test and update Data Center recovery Plans
Continue Reading:
Colocation vs Carrier Neutral Data Center
Data Warehousing and Data Mining
Tag:comparison