
Wi-Fi generation comparison Wifi6 vs Wifi5 vs Wifi4
Wifi6 vs Wifi5 vs Wifi4
In the wireless world, Wi-Fi is the term that is similar in general to access of wireless. Although the fact is that this specific trademark is owned by Wi-Fi Alliance. This dedicated group takes care of Wi-Fi products certification when they meet the wireless standards of 802.11 set of IEEE. It is a bit complex in getting used to the standards naming scheme of IEEE and to make the process of understanding it easier, some simpler names haves been introduced by Wi-Fi Alliance. Under this convention of naming,
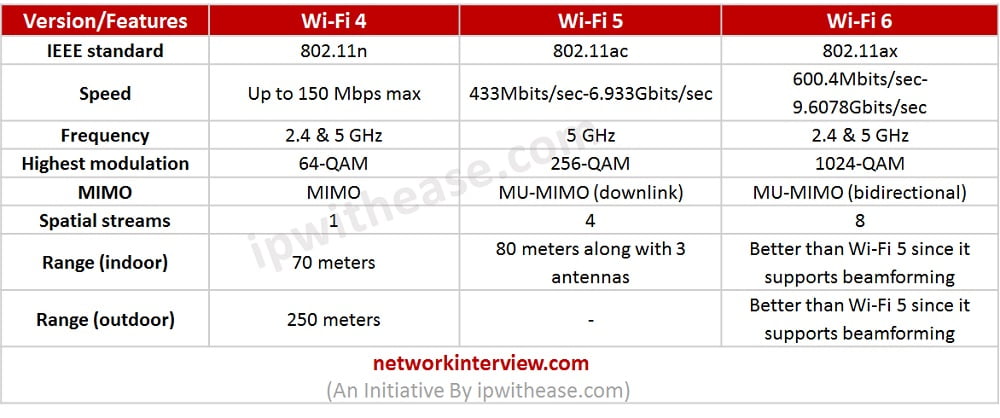
- Wi-Fi 4 is the name given to 802.11n
- Wi-Fi 5 is for 802.11ac
- Wi-Fi 6 is for 802.11ax.
Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n)
802.11n is the first standard in which MIMO is specified and usage is allowed by this in two frequencies- 5GHz and 2.4GHz having speeds ranging to 600Mbps. When the term dual band is used by vendors of wireless LAN, it reflects the ability of data delivering athwart the two frequencies. Wi-Fi 4 is the successor of Wi-Fi 3 i.e. IEEE 802.11g.
Introduction of MIMO has taken place in this Wi-Fi standard along with beamforming. However, testing of interoperability has not been done yet. Previous versions legacy fallbacks was also supported by it and bandwidths that is support are 40 MHz and 20 MHz It is also possible to achieve upto 150Mbps data rates due to higher bandwidth and use of MIMO.
70 meters is the range in indoor that could be supported by devices of WiFi-4 and in outdoor environments, it reaches about 250 meters. Wi-Fi 4 devices that offer support to MIMO configurations include 4T4R and 2T3R. The modulation schemes used in this are QPSK, BPSK, 64QAM and 16QAM.
Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac)
The wireless routers that are used in many homes at present are likely to have 802.1ac compliance operating in the frequency space of 5GHz. The data rates supported by this standard are up to 3.46Gbps with MIMO where speed is boosted and error is reduced by multiple antennas on the receiving and sending devices. This Wi-Fi standard stands as the first one in which feature of multi-user MIMO has been introduced.
On account of multi-user MIMO, higher bandwidths addition, more modulation schemes and spatial streams, higher throughput is supported by WiFi-5. 5GHz is its operating frequency and it offers support to modulation schemes of single carrier (CCK, DSSS), multi-carrier and types of baseband modulation (QPSK, BPSK, 256QAM and 64QAM).
Bandwidths of several channels are supported including 160 MHz, 20 MHz, 80 MHZ and 40 MHz Maximum data rate of 6.93 Gbps is also supported by Wi-Fi 5 along with approx. 80m of coverage range and 3 antennas. Multi-user as well as single user transmissions are also supported by this Wi-Fi standard.
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax)
802.11ax is also termed as WLAN of high efficiency since it aims at enhancing WLAN deployments performance in the scenarios that are dense such as airports and sports stadiums while it still operates in the spectrum of 5GHz and 2.4GHz. About 4X of improvement is targeted by the group in throughput in comparison to 802.11ac and 802.11n via utilization of spectrum that is more efficient. In comparison to the legacy Wi-Fi networks including Wi-Fi 3, Wi-Fi 4, Wi-Fi 5 etc. it offers greater range of coverage and higher speed. In both downlink and uplink directions in Wi-Fi 6, introduction of concept of OFDMA has taken place.
Beamforming, MU-MIMO, OFDM symbol of longer size, 1024-QAM, more spatial streams, scheduling of uplink resources with no contention etc. are the features introduced in this Wi-Fi generation. BSS coloring is the other specific feature present in this Wi-Fi generation. It is also referred as High frequency WLAN (HEW) on account of performance of high efficiency. Wi-Fi 6 generation offers better network capacity, efficiency, user experience and performance at reduced latency.
Related – Wi-Fi 6 Technology
Comparison : Wifi6 vs Wifi5 vs Wifi4
Tag:comparison



