
What is Network Switching
Network Switching
Network Switching works at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer) of OSI model. Switching is a process of receiving frame from one incoming port (ingress) and then forwarding it to as desired destination (egress).
Types of Network Switching
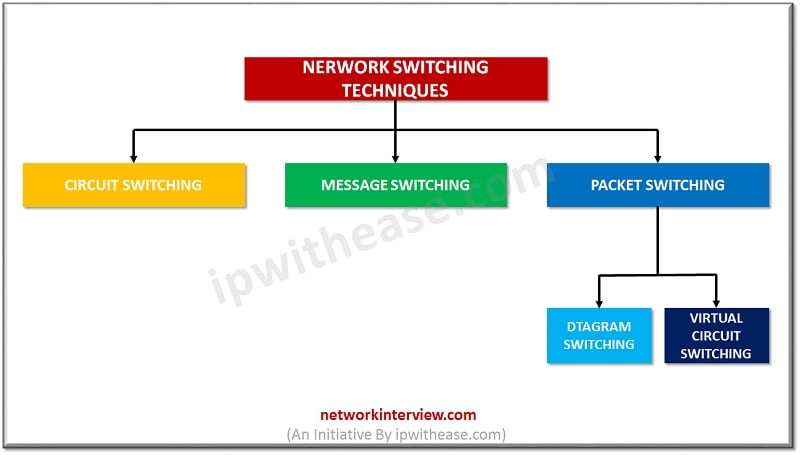
Switching is of 3 types –
- Circuit Switching
- Message Switching
- Packet Switching
Circuit switching
It is a switching method in which a dedicated physical path is formed between two points in a network i.e. between the sending and the receiving devices. These dedicated paths are created by a set of switches connected by physical links. Circuit switching is the simplest method of data communication that has a fixed data rate and both the subscribers need to operate at this fixed rate.
Message Switching
It is a switching method that was developed as an alternative to Circuit switching before the advent of Packet Switching. Message switching is a connectionless technique in which the entire message is routed from the source node to the destination node by one hop at a time, called hop-by-hop system. The distinctive features of message switching are:
Store and Forward network: The message is not discarded in case of non availability of the next hop. Rather, it is stored in a queue and is retransmitted when the required route is available .This is called store and forward network.
Message delivery: The entire information is wrapped in a single message and transferred from the source to the destination node as a “message” with a definite destination address in the header.
Packet switching
It is a switching method in which data is transferred in the form of small broken pieces of variable lengths. These broken pieces of data are called as packets. The data is transferred in the form of packets, transmitted to the network line and reassembled at the destination making a complete file.
Thus, Packet Switching method also uses Store and Forward technique. Each hop will store the packet and then forward the packets to the next host destination.
There are two types of packet switching :
- Virtual Circuit Packet Switching: VC Packet Switching is an approach in which a logical path or virtual circuit connection is done between sender and receiver. VC stands for Virtual Circuit.
- Datagram Packet Switching: In Datagram packet switching each packet has all the necessary information like Source address, destination address etc. So each packet is treated independently. Packets in this approach are called datagrams.
Related – Network Switching Basics
FAQs Related to Network Switching
Tag:Layer 2



