What is Fog Computing?
Introduction
Fog computing, popularly known as fogging is a concept that was released by Cisco in 2014. It was solely designed to connect the internet to devices at the periphery of the network. The main objective of fogging was to minimize the latency that beset cloud computing.
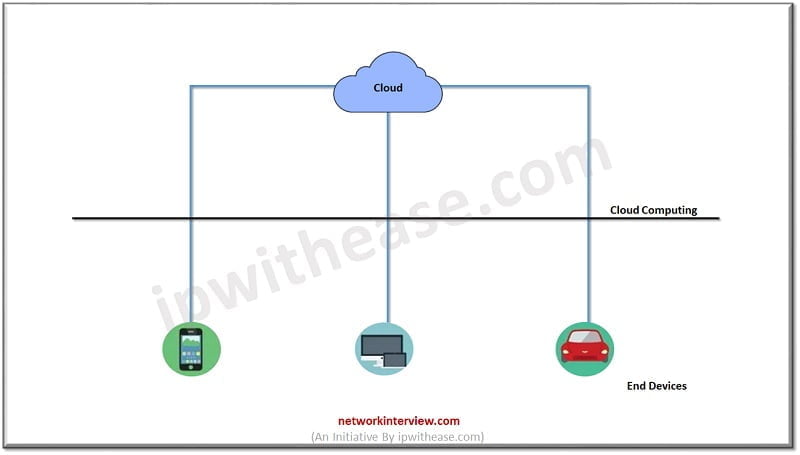
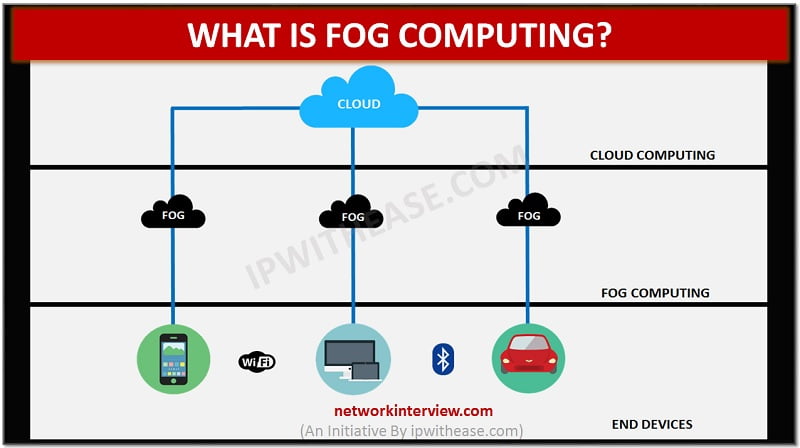
As we can see in the above scenario diagram, where we don’t have Fog computing setup, the data is sent from IoT (internet of things) devices to the cloud directly.
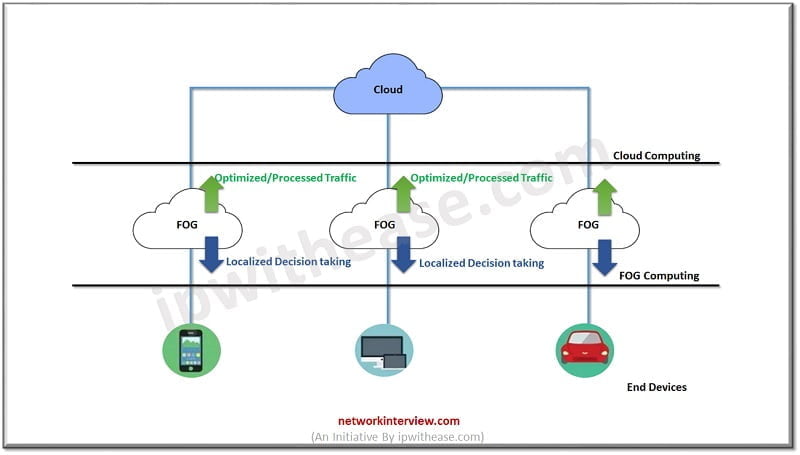
While Fog computing uses nodes to evaluate information on the edge of the network without transferring it back to the Cloud. The idea behind fog computing is to perform as much localized processing as possible using fog computing systems, which are much nearer to the data-generating devices. This assures that only processed or optimized information is forwarded to Cloud rather than raw data and hence the bandwidth requirements are reduced.
Therefore, we can call Fog computing as a decentralized computing structure located between the cloud and devices producing the data. Currently, fog computing is establishing its foundations, and its market is expected to be worth $6.4 billion in coming years. We can call Fog as the Sum of Cloud and IOT.
Watch this video for better understanding:
(or continue reading)
How it works?
Fogging functions by building nodes all through a network. Fog nodes can be devices such as switches, cameras, routers, and controllers. The nodes can be placed in target locales, including offices and vehicles. Thus, when an IoT device generates information, it is processed in one of the nodes without being sent back to the cloud. Fog computing offers decentralized local access, which majorly differentiates it from cloud computing, which provides centralized access. Data in fog computing follows the steps below:
- From device to automation controller
- Automation controller sends data via the protocol gateway or OPC server
- OPC server then converts the Data into an internet-based protocol
- Data is sent to the fog node for further analysis
Importance of Fog computing
Fog computing speeds up responses and awareness to events. Quick answers can boost service levels, increase safety and improve output in industries such as mining, public sector, transportation, oil and gas, manufacturing as well as utilities. It also creates new business opportunities, such as vehicle insurance and pay-as-you-drive. The significant benefits of fog computing include lower operating cost; elevated business alertness; more in-depth insight into privacy control and better security.
The concepts help the cloud to handle two Exabytes of information generated every day from the internet. Analyzing information close to where it is needed and produced helps solve issues of excess data volume, velocity, and variety. Fog computing catalyzes awareness by eliminating the round trip of data to the cloud. By offloading gigabytes from the leading network; it reduces costly bandwidth additions and protects sensitive data. Companies that use fog computing have better business agility, improved safety levels, and customer service. It keeps up with the growth of IoT devices, which has proved impossible through cloud computing.
Advantages of Fog Computing
- Low latency and drastic reduction in amount of data that is sent to the cloud.
- Since the distance to be traveled by the data is reduced, it results in saving network bandwidth.
- Improves scope for real time application and reduces the response time of the system. This results in enhancing user experience
- System security is improved in addition to better privacy since the data resides close to the host.
- Fog computing can provide better reliability due to reduction of data transmission burden.
Some of use cases of Fog Computing
- Smart cities equipped with fog computing will allow traffic regulation with smart traffic signals and road barriers.
- Smart System at home which have smart lighting, programmable shades and sprinklers and infact intelligent alarm systems.
- In Healthcare also, doctors can consider smart choices during a case of emergency, while being secured and with reduced delays in comparison to a cloud-based application.
- Fog computing has also been embraced by many other industries like agriculture, retail, oil & gas, Transportation and Energy.
Continue Reading:
Tag:New technology