What is Database Replication?
Database replication: Sneak Preview
Highly competitive and agile market demands businesses to run 24*7 and ensure data availability and accessibility with improved resilience and reliability.
Data replication technologies help businesses to quickly recover from a disaster , catastrophe, hardware failure, or a system breach in the event the data is compromised.
In this article, we will get deeper understanding about Database replication, why it is required? Its benefits and so on.
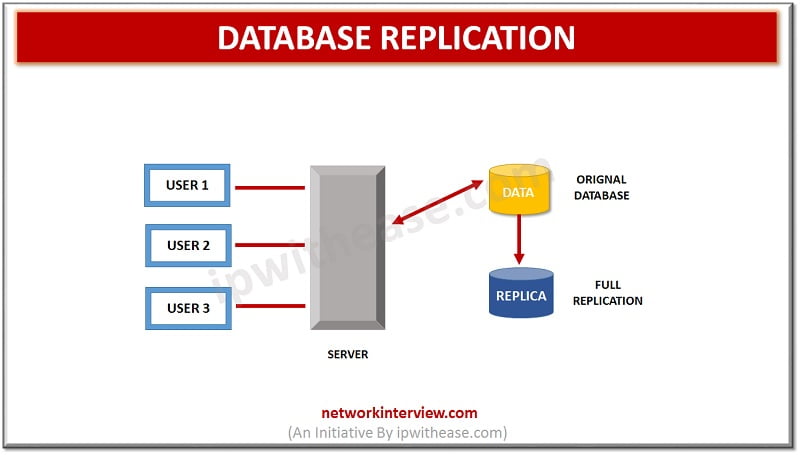
Database Replication
Database replication technologies facilitate the process of storage / retrieval of same data at many locations. Maintaining a replica of databases at multiple location also helps to access data faster hence improving user experience , running multiple replicas of same data on multiple servers enhance accessibility and also frees resource intensive Write operations onto replicas hence freeing processing cycles on Primary server.
Database Replication: Types
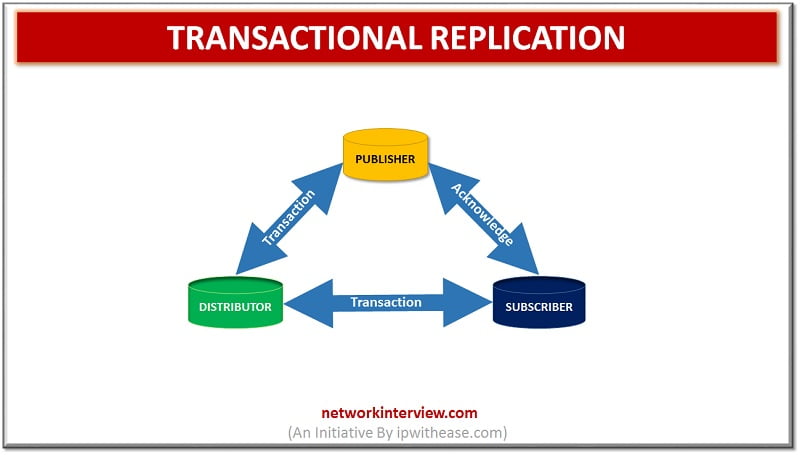
Transactional Replication –
Initial copies of full database is received by user and post that only updates are sent. The sender is referred as ‘Publisher’ and receiver is referred as ‘Subscriber’. Data copy happens in real time from Publisher to receiver in sequential order. Consistently and accurately all changes are replicated. It is a periodic in nature and more complex as complete transaction history on database replica is monitored. It is majorly used in scenarios where there are frequent data changes at the source.
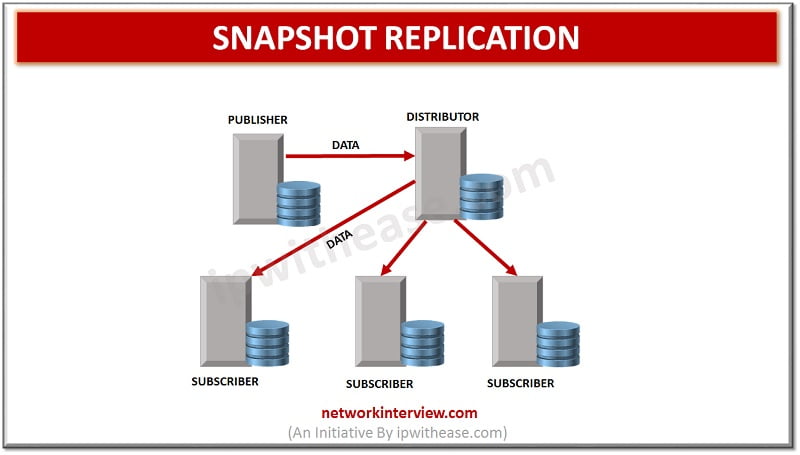
Snapshot Replication –
Snapshot as name refers is the actual snap of data at a specific time which is captured and send to users. Usually it is used to perform initial sync between publisher and subscriber. No change tracking happens in Snapshot replication and used where data changes are less frequent such as change in exchange rates or price lists are updated once a day and it gets replicated to branch servers from main server once a day.
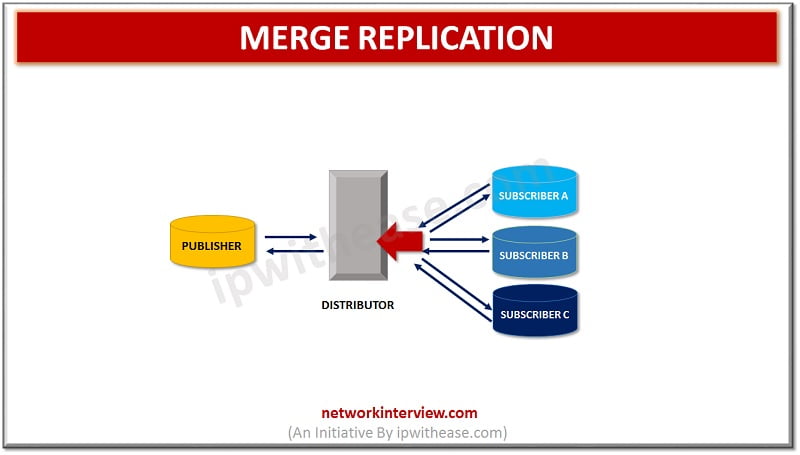
Merge Replication –
Multiple databases are combined into one single database. In Merge replication changes are sent from one publisher to multiple subscribers. It is a bi-directional replication in a server-client environment and connection is not continuous. Whenever the network connectivity is established replication occurs by Merge agents. This is one of the most complex type of replication and a typical scenario where it could be used is a central warehouse connected to stores so informed requires update in central database and store databases on inventory, delivery etc.
Advantages /Disadvantages of Database Replication
Below table describes the advantages and disadvantages of Database replication:
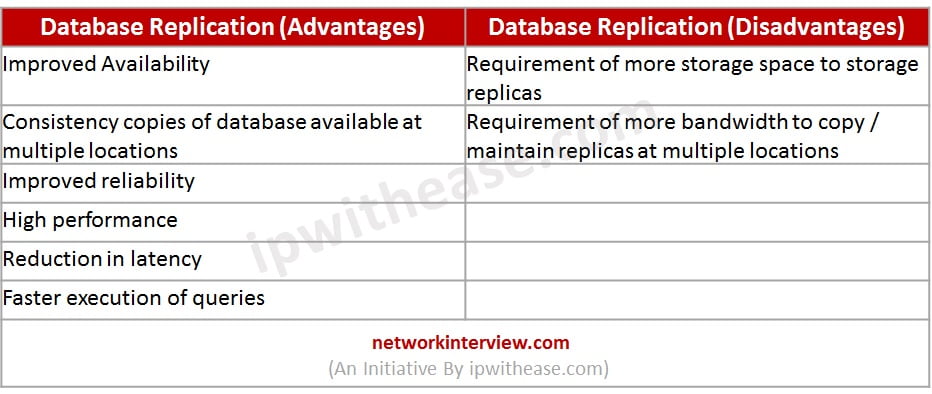
Database Replication (Advantages) | Database Replication (Disadvantages) |
| Improved Availability | Requirement of more storage space to storage replicas |
| Consistency copies of database available at multiple locations | Requirement of more bandwidth to copy / maintain replicas at multiple locations |
| Improved reliability | |
| High performance | |
| Reduction in latency | |
| Faster execution of queries |
Download the table here.
Comparison of different types of Replication
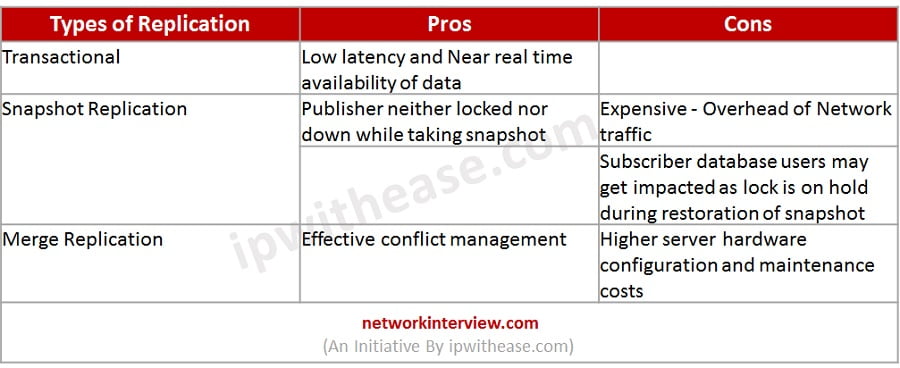
Types of Replication | Pros | Cons |
| Transactional | Low latency and Near real time availability of data | |
| Snapshot Replication | Publisher neither locked nor down while taking snapshot | Expensive – Overhead of Network traffic |
| Subscriber database users may get impacted as lock is on hold during restoration of snapshot | ||
| Merge Replication | Effective conflict management | Higher server hardware configuration and maintenance costs |
Download the table here.
Database Replication on Cloud
Widespread data availability, Analytics , data integration across multiple platforms, are some of the key reasons for choosing a Cloud based replication.
Data residing on a cloud instance(Primary instance) is replicated or copied to another cloud instance (Standby instance) . Data transmission mechanism can be synchronous or asynchronous depending on the Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) requirement of the organization.
In the event of disaster , it is vital that the secondary instance is in a different geographical region from Primary instance (Cloud instance connected over WAN link).
Cloud based replication keeps data offsite so in event of major disaster like fire, flood, earthquake etc. when primary instance is unavailable still the secondary instance is operational over cloud and data and applications can be recovered.
Cloud based replication costs are less as compared to in-house data center . Building a secondary site is a costly affair and organizations can save costs incurred on hardware, maintenance, and support.
On demand scalability s another reason organizations prefer to maintain business agility.
Data replication happens on cloud to that providers can assure their users high availability and Disaster recovery.
Continue Reading:
Data Center vs Disaster Recovery Center
Tag:storage