What is Code Refactoring?
A successful software program requires the need for enhancing it, fixing problems and adding new features. Enhancements are applied on top of each other adding onto code complexity making it difficult new work or enhancement to a crawl. The end objective is to have a code which is more efficient and maintainable which in turn will reduce technical costs to do code clean up and pay hefty costs for that and avoid the dreaded code rot resulting from duplicate code, myriad patches, bad classifications, and other programming discrepancies.
In this article we will learn more about a discipline or technique called ‘code refactoring’ and will understand how it works, why it is used , its advantages and use cases.
Code Refactoring
Code refactoring is a discipline technique to restructure existing code alteration in its internal structure without making any modification in its external behaviour. It comprises a series of preserving transformations and each transformation is referred as ‘refactoring’, sequence of these transformations produce significant restructuring . The unit of transformation is so small that it does not impact the functioning of code and there are very bleak chances of system breakdown during restructuring.
Refactoring is not taken up as a separate activity but it is part of day-to-day programming activity. While adding any new feature to source code then it is analysed to understand whether existing code is structured in a way that making new change would be straightforward, if not then refactor required to existing code first to make way for adding new functionality in an easier manner.
Sometimes during modification code is checked to see if what we need is encoded in the program and if code has functions which can be easily called then refactoring is done to use that functionality in an easy way next time.
Advantages of Code Refactoring
- Simplified support and code Updation is easier
- Saves time and costs in future incur on technical glitches
- Reduction in complexity helps new developers to comprehend code and make required alterations faster
- Maintainable and scalable code
How to perform Code Refactoring?
Best time to consider code refactoring is while adding new updates, new features to existing code. There are different techniques to perform code refactoring some of the most popular ones are described below:
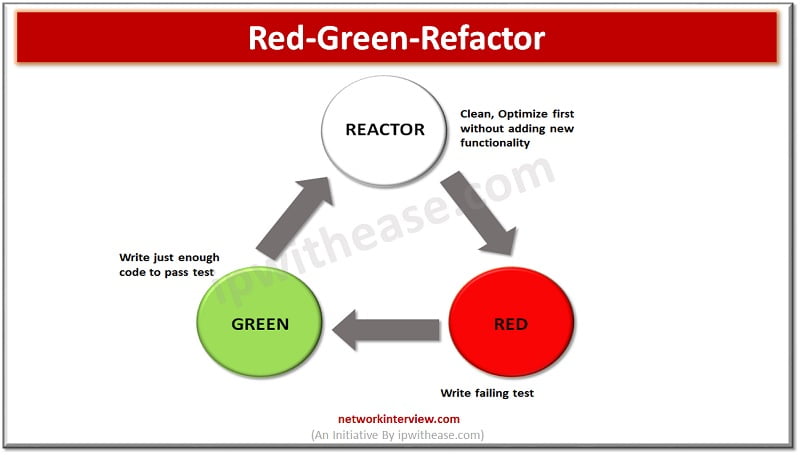
Red-Green-Refactor
One of the most widely used techniques for code refactoring is red/green process used in Agile test-driven environments. Developers break refactoring into three steps:
- Stop and consider what needs to be developed [RED]
- Pass the basic testing in Development [GREEN]
- Implementation of improvements [REFACTOR]
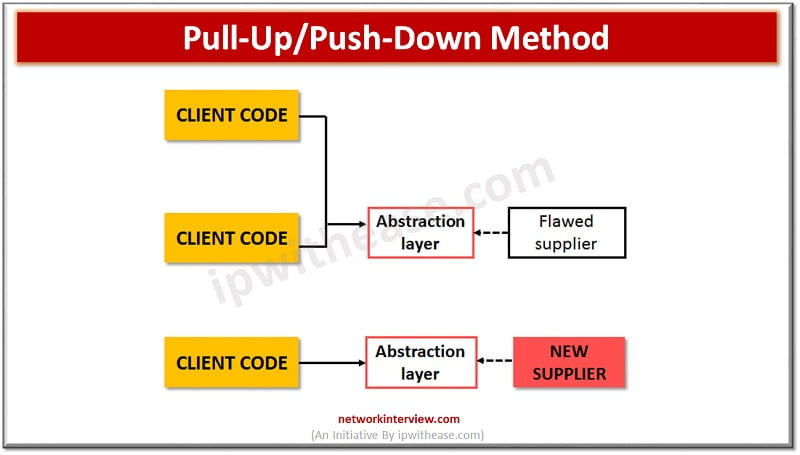
Refactoring by abstraction
It is useful when a large amount of data needs to be refactored. Abstraction involves class inheritance, hierarchy and extraction. The objective of this is to reduce duplications.
One example of such refactoring is the pull-up/push down approach. There are two opposite forms of refactoring involving classes. The pull up pulls code into superclass in order to remove code duplicity. Push down takes it from superclass and moves is down into subclasses.
Composing method
It involves streamlining of code to reduce duplicity. This is done using various methods such as extraction and inline methods.
- Extraction involves breaking down code into smaller parts to identify fragmentation. Extraction may involve class, interface, and local variables.
- Inline is a way to reduce the number of not so important methods to simplify code.
Simplifying methods
With the code getting older more complex and garbled it is. Objective is to make it simple by consolidation of conditional fragments and expressions and replacement of conditional with polymorphism. It involves tweaking between class interactions. Addition, removal, and introduction of new parameters along with replacement of parameters with explicit methods.
Moving features between objects requires creation of new classes and moving functionality between old and new classes. When one class has too much to perform then some of the code needs to move to another class or if a class is not doing much then code can be moved to another class and this one can be deleted.
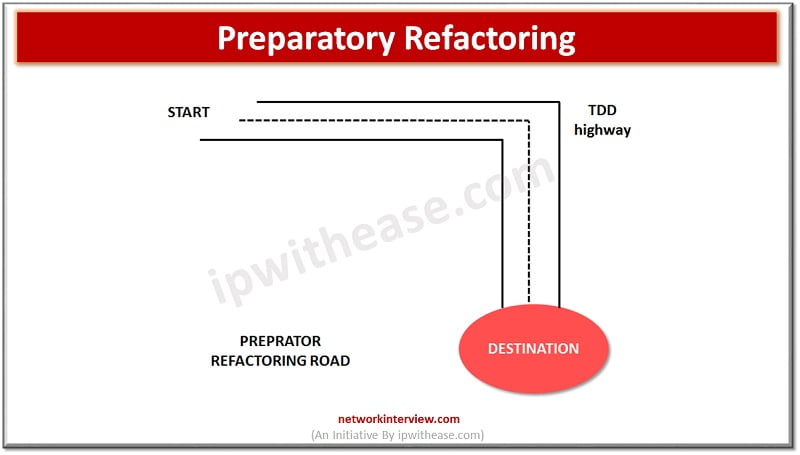
Preparatory Refactoring
When a developer notices that there is a need for refactoring before adding a new feature. Code needs to be updated at that moment to reduce future technical debt.
Conclusion
You can think code refactoring is similar to keeping your house clean and tidy. Where things are easy to locate and the same analogy applies here for code. Code also requires spring cleaning to ensure a better product and more productive environment.
Continue Reading:
What is Akamai NetSession Client?
Tag:software



