What is BPM (Business Process Management)? A Comprehensive Guide
Business Process Management (BPM)
Business process management (BPM) is a regulation that uses different tools and methods to design, model, execute, monitor, and enhance business processes. A business process correlates the behavior of people, systems, information, and things to bring out the business outcomes in support of a business strategy.
It focuses on placing a congruous, automated process in place for routine transactions and human interactions. BPM helps to bring down the business’s operational costs by reducing wastes and by improving the overall efficiency of the team.
Types of Business Process Management Systems
BPM system can be divided into 3 categories based on the purpose they serve. They are as follows:
- System-Centric BPM or Integration-Centric BPM: This type of BPM structure handles processes that are mostly dependent on existing business systems like HRMS, CRM, and ERP without much human involvement. An integration-centric business process management software has large-scale integrations and API access. By using integrations and API access, we will be able to create fast and efficient business processes. We can consider online banking as an example for integration-centric process, which can incorporate different software systems coming together.
- Human-Centric BPM: Human-centric BPM are the processes that are mostly executed by humans, and automation cannot replace them easily. These continually have a lot of approvals and tasks which are performed by individuals. Providing customer service, on-boarding employees, conducting e-commerce activities, and filing expense reports are examples of human-centric processes.
- Document-Centric BPM: Document-centric BPM model emphasizes on the flow of documents from one team to another. This type of model is useful when the importance of documentation is high within the organization. It helps in the seamless and organized document flow thereby enhancing the overall process of the company.
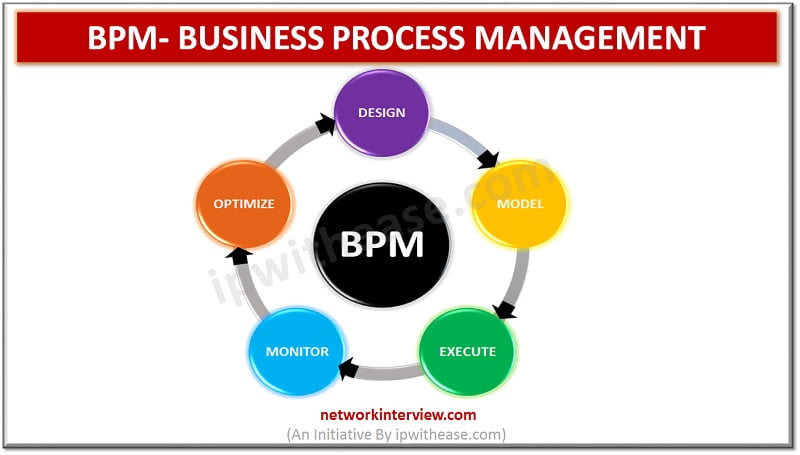
BPM Lifecycle
There are five Steps in Business Process Management. They are:
1) Design
Business analysts evaluate current business rules, interviews numerous stakeholders, and discusses desired outcomes with management. The main goal of the process design stage is to acquire an understanding of the business rules and make sure if the outcomes are in alignment with the organizational goals.
2) Model
Modeling interpolates to identifying, defining, and making a representation of new processes to assist the current business rules for numerous stakeholders.
3) Execute
The business process is executed by testing it with a small group of users first and then open it up to all users. In the case of automated workflows, artificially strangle the process to minimize errors.
4) Monitor
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are established and metrics are tracked against them using reports or dashboards. It’s important to focus on the macro or micro indicators.
5) Optimize
Business Process Optimization (BPO) is the redesign of the business processes to rationalize and improve process efficiency and strengthen the order of individual business processes with a comprehensive strategy.
Benefits of Implementing Business Process Management
Business Process Management helps organizations to advance towards total digital transformation and assist them to conceive bigger organizational goals. Some of the major benefits of using BPM in business are:
- Improved Business Agility: Optimizing and altering an organization’s business processes is mandatory to meet the market conditions. BPM permits organizations to halt the business processes, apply the changes, and re-execute them. Modifying workflows, as well as reusing the work flows and customizing them, makes business processes to become more responsive and gives the organization deeper understanding of the effects that process modifications have.
- Reduced Costs and Higher Revenues: A business process management tool eliminates bottlenecks, which remarkably reduces costs over time. One of the effect of this is depletion in lead time for product sales, providing customers quick access to services and products, which guides to higher sales and better revenue. It can also assign and track resources to lower the waste, which can also lower the cost and steer to higher profits.
- Higher Efficiency: The incorporation of business processes brings the potential for end-to-end development in process efficiency. If the right information is provided, process owners can closely observe the delays and allocate extra resources if needed. Removal of repetitive tasks and automation brings more efficiency in the business process.
- Better Visibility: Business Process Management software entitles automation while assuring real-time monitoring of key performance metrics. This improved transparency guides to better management and ability to change the structures and processes efficiently while tracking outcomes.
- Compliance, Safety, and Security: An exhaustive Business Process Management guarantees that organizations conform to the standards and stay up to date with the law. It also recommends safety and security measures by appropriate documenting procedures and facilitating compliance. As a result of above procedures, organizations recommend their staff to shield the organizational assets, such as private information and physical resources from misuse, loss, or theft.
Example Scenarios of BPM
Following are some of the examples of business processes where implementing BPM will emerge in a high return on investment.
- Dynamic processes that require regulative compliance changes, like a change in customer information management should follow changes in finance or privacy laws.
- Complex business processes which requires harmony and systematization across multiple business units, divisions, functional departments, or workgroups.
- Measurable mission-critical processes which straightaway improves a crucial performance metric.
- Business processes which require more than one legacy applications for their completion.
- Business processes with exceptions which are managed manually and require quick retraction.
Hope this article of Business Process Management (BPM) was helpful in providing knowledge of the topic and related nuances in addition to its benefits to customers.



