What Is A TOR?
TOR (The Onion Router) is a software and open network which allows the users to browse the Web anonymously. TOR makes it difficult, if not impossible, for any snoops to see our web mail, search history, social media posts or other online activity. Also no one can tell which country we’re in by analyzing our IP address.
TOR was primarily developed for the use by the US Navy so as to mask their IP addresses which could lead to theft of sensitive data. Later, TOR was released as an open source free software.
TOR is a network of servers that we communicate with anonymously. No one organization controls either the TOR software on our computer or the individual servers in the network. So, we don’t need to trust anyone to use TOR safely.
TOR was called The Onion Router because this software uses a technique known as onion routing to hide information about user activity.
How does a TOR work?
TOR network consists of thousands of independent servers run by volunteers around the world.Here’s what happens in a Tor network:
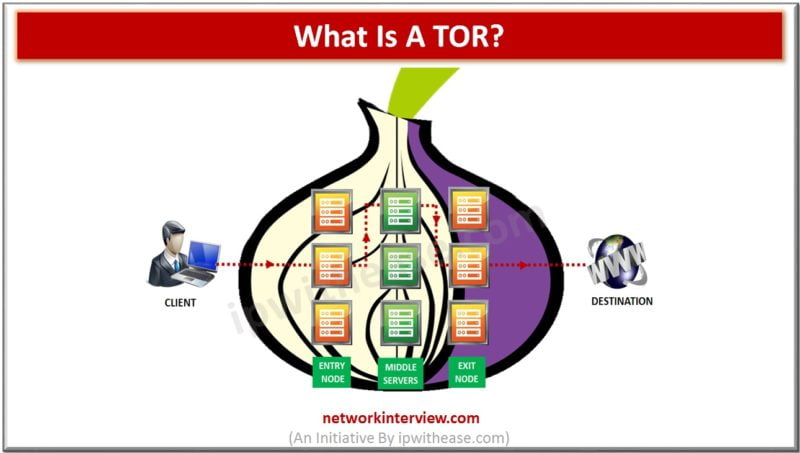
- We can divide the TOR network into : ENTRY NODE, MIDDLE SERVER and EXIT NODE for better understanding.
- The ENTRY NODE can see the IP address of our computer. But it doesn’t know what the exact message is , because of the additional layers of encryption. So the ENTRY NODE just receives a message from our computer using TOR and forwards that message to the MIDDLE SERVER(without actually knowing what’s in the message).
- The MIDDLE SERVER knows the message has come from the ENTRY NODE and that it has to forward the message received from the ENTRY NODE to the EXIT NODE. It can’t read the message because there is still one layer of encryption left. At the same time , the middle server doesn’t know who sent the message to the ENTRY NODE because that information is not passed through the TOR network.
- Now , the EXIT NODE knows what the message says because it has to peel off the final layer of encryption before the message can go out to the public Internet. But it doesn’t know the original source of the message. All it knows is that the MIDDLE SERVER has forwarded the message to it.
- Thus no one server knows or can know both where the message came from and what it says, providing anonymity.
Tag:Security



