VDC vs VLAN : Know the difference
Introduction : VDC vs VLAN
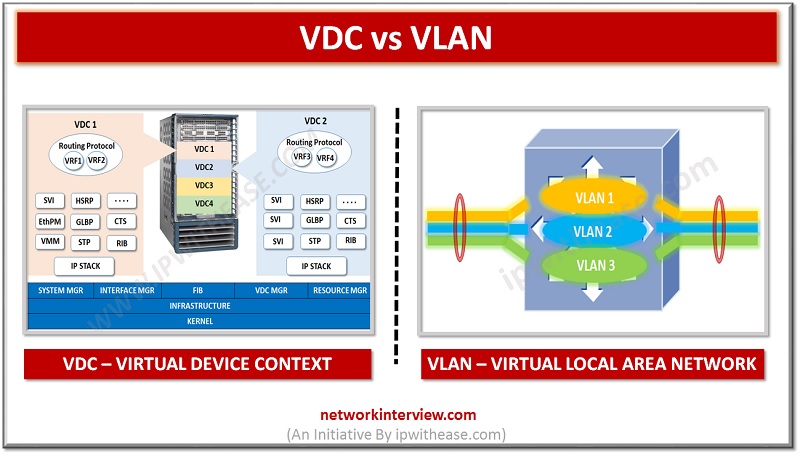
Virtualization in IT systems has helped Network estate immensely. 2 technologies which have helped networking across various segments are VLAN and VDC. While VLAN is short for Virtual Local Area Network, VDC means Virtual device contexts. VLAN divides the network into separate logical areas at the Layer 2 level and each VLAN is considered an individual broadcast domain. VDCs allows the switches to virtualize physical chassis.
In VLAN, unicast, broadcast and multicast packets are forwarded and flooded only to end stations in that VLAN. VLAN is considered a logical network and packets destined for stations that do not belong to the same VLAN (different subnet) must be forwarded through a router or Layer 3 device or entity.
VDC, presents itself as a unique device to connected users within the framework of that physical switch. VDC behaves as a separate logical entity within the switch, maintaining its own unique set of running software processes/configuration.
Virtual Device Contexts (VDCs)
The NX-OS supports Virtual Device Contexts (VDCs) feature, allowing the partitioning of a single physical Nexus 7000/7700 device into multiple logical devices i.e. Separate Management plane, Data plane and Control plane. This logical separation provides the following benefits:
- Administrative and management separation.
- Failure domain isolation from other VDCs.
- Address, VLAN, VRF, and VPC isolation.
Resource that can be shared in VDC –
- Single instance of the kernel which supports all of the processes and VDC.
- Hardware which can be shared i.e. Supervisor modules, Fabric modules, Power supplies, Fan trays, CMP, CoPP and hardware SPAN resources.
Resource that cannot be shared in VDC –
- CPU, Memory, TCAM Resources such as the FIB, QoS, and Security ACL.
- L2 Protocol i.e. VLAN, STP, LACP, UDLD and others.
- L3 Protocol i.e. Routing, VRF, PIM, SNMP and others.
VDC License requirement
To Create VDC, an advance license is required on Nexus switch. License is associated with serial number of chassis. Cisco provide 120 days grace period for trial.
Number of VDCs supported –
Number of VDC support depends on supervisor engine in Nexus chassis.
- Nexus 7000 Supervisor 1 supports 4 VDCs.
- Nexus 7000 Supervisor 2 supports 4+1 admin VDCs.
- Nexus 7000 Supervisor 2E supports 8+1 admin VDCs.
- Nexus 7700 Supervisor 2E supports 8+1 admin VDCs.
- Nexus 7700 Supervisor 3E supports 8+1 admin VDCs.
Types of VDC
Default VDC – VDC1 is said to be default. It is used for management of all VDC in Nexus. At first login in nexus switch user will be in default VDC. Default VDC is created by NX-OS boot up. In Default VDC, we can create/update/delete other non-default VDCs and allocate resources such as interface, memory to non-default VDC.
Admin VDC – It is created from initial configuration wizard. No resources is allocated to Admin VDC since it is not made to handle user data traffic. It is used for managing other VDCs and nexus chassis. Default VDC has been replaced with Admin VDC in SUP2/SUP2E with NX-OS 6.1. Default and Admin VDC cannot exist at the same time. VDC 1 can be either configured as default or Admin. We can convert to admin VDC by using this command #System admin VDC.
Non-Default VDC – It can be created from Admin or Default VDC. Changes made on non-default VDC does not affect other VDCs. Each VDC have its own configuration file. Non-default VDC is used to handle user data traffic as interfaces can be allocated to it.
Storage VDC, It is used when SAN function is implemented in Nexus. Two different types of interfaces are assigned ie FCOE and shared interface.
Creating VDC
Hostname#conf t
Hostname(config)#vdc (name) > Creates a VDC and enters the VDC configuration mode.
Hostname(config-vdc)#allocate interface ethernet slot/port > Allocates one interface to the VDC.
Initializing VDC
Hostname#switchto vdc vdc-name > Switches to the VDC.
Hostname-NewVDC#show vdc current-vdc > Displays the current VDC number.
Verifying VDC
Hostname#show running-config {vdc | vdc-all} > Displays the VDC information in the running configuration.
Hostname#show vdc [vdc-name] > Displays the VDC configuration information.
Hostname#show vdc detail > Displays the detailed information about many VDC parameters.
Hostname#show vdc current-vdc > Displays the current VDC number.
Hostname#show vdc membership [status] > Displays the VDC interface membership information.
Hostname#show resource > Displays the VDC resource configuration for the current VDC.
Related – VDC vs VRF
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
Virtual LAN (VLAN), divides the network logically on layer 2 (data link layer). VLANs also divide broadcast domain. It allows hosts to be grouped in a same broadcast domain even if they are not connected to the same switch. Two types of VLAN membership methods are Static and Dynamic.
In a Static VLAN, VLAN is manually created and then VLAN is assigned to respective switch ports. It is also called port-based VLAN. The port association with the VLAN does not change until the administrator changes the port assignment. End user device becomes the member of VLAN based on the physical switch port to which they are connected.
In a Dynamic VLAN, when a port is configured as dynamic, it receives VLAN information from VMPS server based on the MAC address. It reduces overhead of network administrator. When a workstation is connected to a switch port the switch queries a database to establish VLAN membership. VLAN database of a VLAN Membership Policy Server (VMPS) server is updated by administrator.
VLAN ranges
- VLAN 0, 4095: Reserved range.
- VLAN 1: Default or native VLAN of switches. By default, all switch ports are assigned in VLAN 1. This VLAN cannot be deleted/modified.
- VLAN 2 – 1001: Normal VLAN range. We can create/modify/delete these VLANs.
- VLAN 1002 – 1005: Reserved for FDDI and token rings. These VLAN can’t be deleted.
- VLAN 1006 – 4094: Extended range of VLAN.
Functions of VLAN
- VLANs increases the number of broadcast domains possible in a LAN by grouping various hosts with similar functions.
- Virtual LANs provide mechanism for making logical groups of end devices, though they are on different networks.
- Implementing VLANs reduces the security risks significantly, as the number of hosts connected on a broadcast domain decreases. This is done by configuring a separate VLAN for only the hosts with the sensitive information.
- VLAN offers flexible networking models which group different users based on their departments (job/function), rather than just physical locations of that network.
- Changing users/hosts on a VLAN is easy. All it needs is a new port level configuration. If a user wants to move from one VLAN to another, a new port needs to be configured on the desired VLAN.
Related – VLAN Interview Questions
Comparison
- A VDC virtualizes the device itself by segregating a single physical device into multiple logical devices. In case of VLAN, network is divided in a network switch on Layer 2 network.
- VDCs have Separate Administrative and management domains. In VLAN, we have separate broadcast domains.
- VDC feature is available on Nexus 7K only. In case of VLAN, this feature is available on every switch.
- Advance Services License is required to enable VDC feature set. VLAN doesn’t require any License to be enabled.
- An external connection needs to be made between ports of VDC to perform internal VDC (VDC to VDC) communication. In VLAN, SVI needs to be created to communicate between different network subnet.
VDC vs VLAN: Comparison Table
S.no. | VDC | VLAN |
| 1 | A VDC virtualizes the device by segregating a single physical device as multiple logical devices. | A VLAN divides network in a network switch. |
| 2 | Separate Administrative and management domains for each VDC. | VLANs have separate broadcast domain. |
| 3 | Feature available on Nexus 7K only. | VLAN feature is available on every switch. |
| 4 | Advance Services License required to enable VDC. | VLAN doesn’t require any License to be enabled |
| 5 | An external connection needs to be made between ports of VDC to perform internal VDC (VDC to VDC) communication. | VLAN SVI needs to be created to communicate between different network subnet. |
| 6 | Used in case of multi-tenant environment or when separate security Zone are required | Used to limit broadcasts and when multiple department or groups with separate security control |
| 7 | Scope limited to Data Center environment | Scope is very wide and VLANs can be seen in Data Centers, small to large offices and even Service provider networks. |
Conclusion
Both VDCs and VLANs are an integral part of a LAN network, and IT solutions would be incomplete without using atleast one of them. Virtualization is used by both discussed concepts where VDC came to fore pretty recently, VLAN has been there for quite long. VDC divides the physical chassis into multiple logical chassis, whereas VLAN divides physical switch network into logical parts.
Download the difference table here.
Tag:comparison




