TCP Reset (RST) from Server: Palo Alto
Introduction to TCP RST
Protection of sensitive data is major challenge from unwanted and unauthorized sources. The next generation firewalls introduced by Palo Alto during year 2010 come up with variety of built in functions and capabilities such as hybrid cloud support, network threat prevention, application and identity based controls and scalability with performance etc.
Next Generation firewalls like Palo Alto firewalls include deep packet inspection (DPI), surface level packet inspection and TCP handshaking testing etc. These firewalls monitor the entire data transactions, including packet headers, packet contents and sources.
In this article we will learn more about Palo Alto firewall TCP reset feature from server mechanism used when a threat is detected over the network, why it is used and its usefulness and how it works.
Palo Alto Firewall – TCP Reset
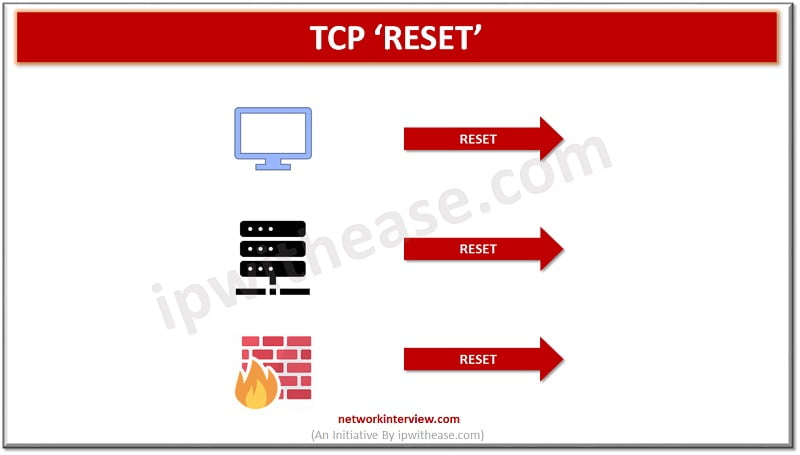
TCP reset from server mechanism is a threat sensing mechanism used in Palo Alto firewall. There could be several reasons for reset but in case of Palo Alto firewall reset shall be sent only in specific scenario when a threat is detected in traffic flow.
TCP header contains a bit called ‘RESET’. This ‘RESET’ will cause TCP connection to directly close without any negotiation performed as compared to FIN bit. TCP reset can be caused by several reasons.
TCP reset sent by firewall could happen due to multiple reasons such as:
- Configuration of access control lists (ACLs) where action is set to ‘DENY’
- When a threat is detected on the network traffic flow
Usually firewall has smaller session TTL than client PC for idle connection. The firewall will silently expire the session without the knowledge of the client /server. And when client comes to send traffic on expired session, it generates final reset from the client. Firewalls can be also configured to send RESET when session TTL expire for idle sessions both at server and client end.
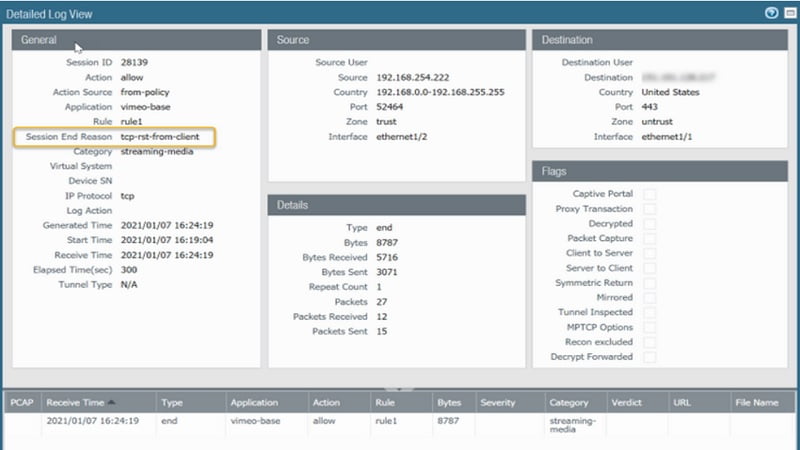
The TCP RST (reset) is an immediate close of a TCP connection. This allows for resources that were allocated for the previous connection to be released and made available to the system. The receiver of RST segment should also consider the possibility that the application protocol client at the other end was abruptly terminated and did not have a chance to process data that was sent to it.
TCP protocol defines connections between hosts over the network at transport layer (L4) of the network OSI model, enabling traffic between applications (talking over protocols like HTTPS or FTP) on different devices. TCP was designed to prevent unreliable packet delivery, lost or duplicate packets, and network congestion issues.
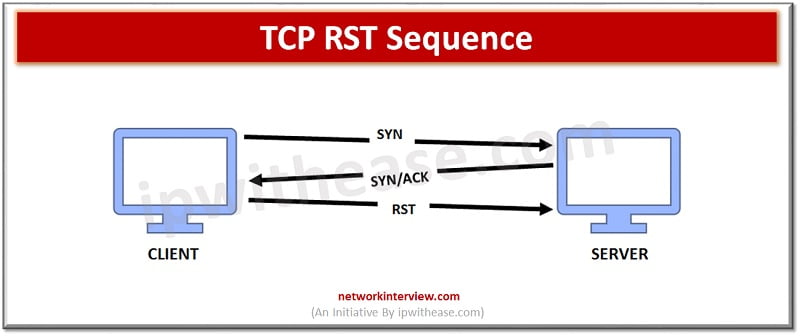
A TCP RST is like a panic button which alerts the sender that something went wrong with the packet delivery. An attacker can cause denial of service attacks (DoS) by flooding device with TCP packets. In case of TCP reset, the attacker spoofs TCS RST packets that are not associated with real TCP connections. TCP resets are used as remediation technique to close suspicious connections.
Continue Reading:
Palo Alto Packet Capture/ Packet Sniffing
Palo Alto Interface Types & Deployment Modes Explained



