SNAT vs DNAT: What is the difference?
Introduction : SNAT vs DNAT
In our previous post, we discussed about the NAT in detail. NAT is abbreviated for Network Address Translation, so the key word here is translation, as it is the process that is responsible for translation of an IP address. The translation can be from a public IP address to a private IP address or vice versa.
In this post, we will focus on two terms i.e. SNAT and DNAT. Both SNAT and DNAT are related to NAT, so one should have an understanding of the concept of NAT beforehand.
What is SNAT?
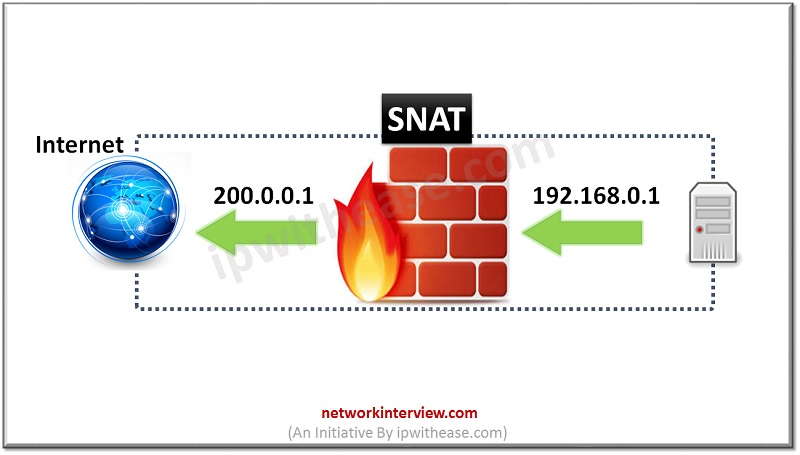
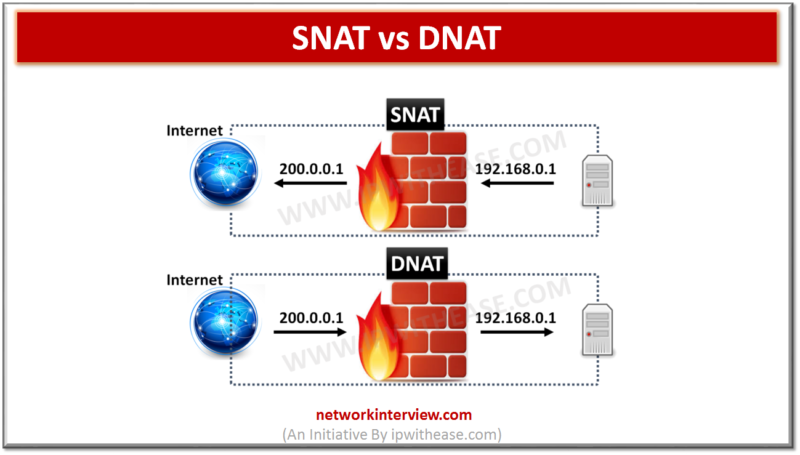
SNAT i.e. Source Network Address Translation as the name implies involves the translation of source IP address. Thus it allows the internal host to connect with the internet by translating its private IP address to public IP address. There are 3 types of SNAT:
- DIPP(Dynamic IP and Port): In this type of SNAT, multiple hosts can be allowed to have the same public IP address for their source IP addresses but with different port numbers.
- Dynamic IP: In this type of SNAT, one-to-one dynamic translation is allowed only of a source IP address (and not for port number) to the next available address in the NAT Address Pool.
- Static IP: In this type of SNAT, one-to-one static translation of source IP address is allowed, but the source port remain unchanged.
SNAT can also translate source port in TCP/UDP headers.
What is DNAT?
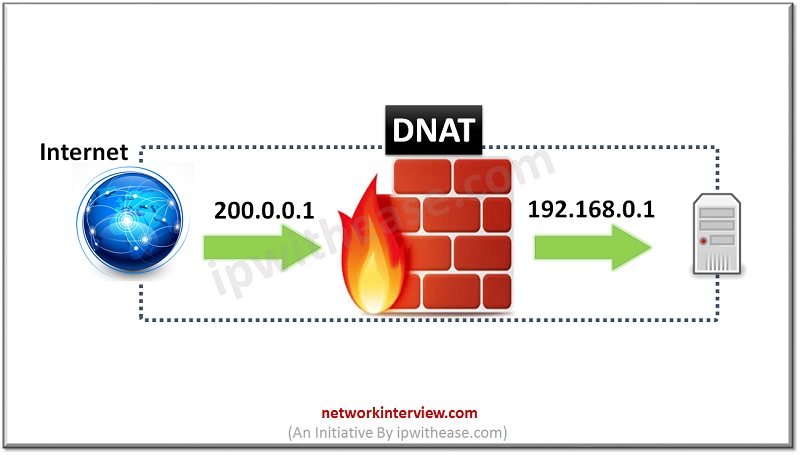
DNAT i.e. Destination Network Address Translation is used by an external host to initiate connection with a private network. So, it translates the public IP address of an external host to the private IP of internal Host.
DNAT can also translate destination port in TCP/UDP headers.
You can watch this video for better understanding:
(or continue reading)
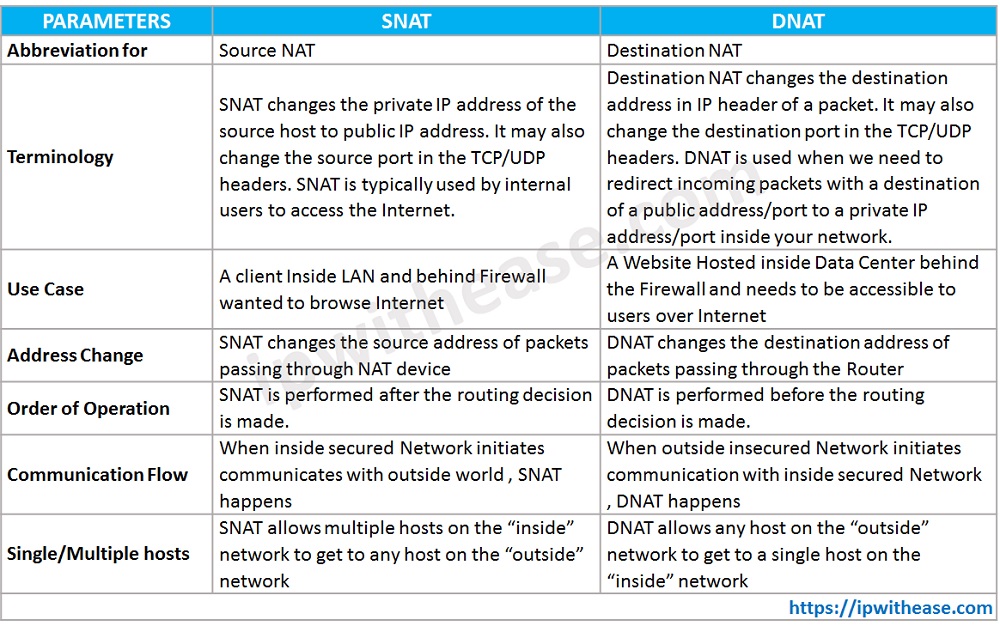
Comparison Table: SNAT vs DNAT
Below table summarizes the differences between SNAT and DNAT –
(Credit:ipwithease.com)
Conclusion : SNAT vs DNAT
In the nutshell, we can say the major difference between SNAT and DNAT is that, SNAT is used to allow the internal host to connect with the internet and DNAT is used by an external host to initiate connection with a private network.
Continue Reading:
If you want to learn more about NAT, then check our e-book on NAT Interview Questions and Answers in easy to understand PDF Format explained with relevant Diagrams (where required) for better ease of understanding.
Tag:comparison




