Proactive Routing Protocol in Ad-hoc Network
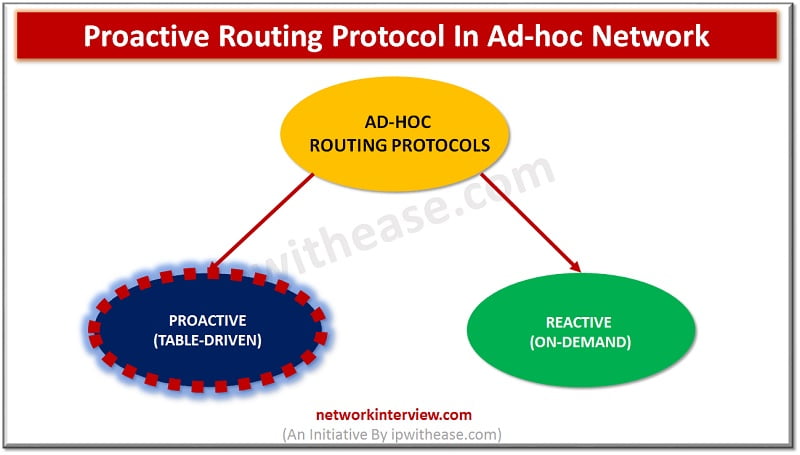
Proactive Routing Protocol
Introduction
Ad-hoc network is a collection of mobile nodes forming an instant network without a fixed topology. In such a network each node acts as both router and host simultaneously and can join or move out in the network freely. In Ad-hoc routing protocol, nodes take decision of routing among all nodes connected in a mobile ad-hoc network.
There are two variations of mobile network:
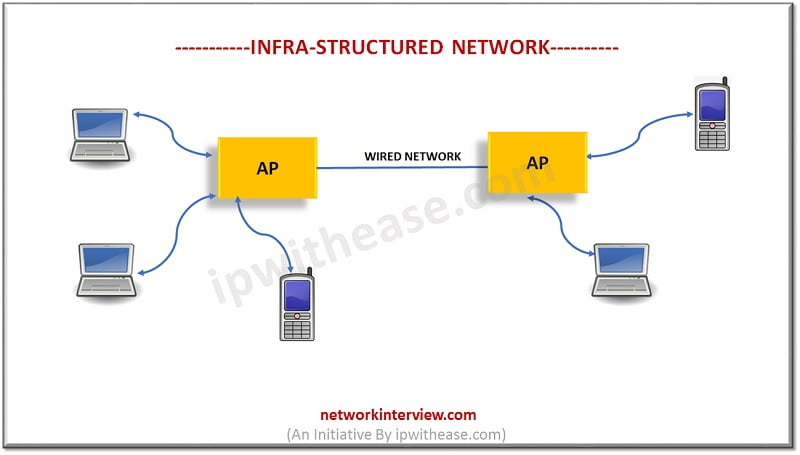
- Infra-structured network
- Ad-hoc network.
Infra-structured network are connections with fixed and wired gateways. Infrastructure mode wireless networking bridges wireless network to wired Ethernet network. Infrastructure mode wireless also supports central connection points for WLAN clients.
An ad hoc network typically refers to any set of networks where all devices have equal status on a network and networks are liberal to associate with any other ad hoc network devices in link range. Wireless ad-hoc networks can be further classified by their application, as follows:
- Mobile ad hoc networks (MANET)
- Wireless mesh networks (WMN)
- Wireless sensor networks (WSN)

Proactive Routing Protocol
In this type of routing protocol, each node in a network maintains one or more routing tables that are updated regularly. Each node sends a broadcast message to the entire network if there is any change in the network topology. However, it incurs additional overhead cost which arises since it maintains up-to-date information. As a result, throughput of network may be affected, but it provides the actual information to availability of the network. Below is the list of Proactive Protocols –
- Destination Sequenced Distance Vector (DSDV) protocol
- Wireless Routing protocol (WRP)
- Hierarchical State Routing (HSR) protocol
- Source Tree Adaptive Routing Protocol (STAR)
- Optimized Link State Routing (OLSR)
- Global state routing protocol (GSR) are the examples of Proactive protocol.
Each node maintains up-to-date routing information to all the nodes in the network whereas in case of on-demand routing protocol, a node finds the route to a destination when it desires to send packets to the destination. GSR is a protocol that uses destination sequence number to keep routes loop-free and up-to-date.
HSR are hierarchical routing protocol. WRP is a distance vector routing protocol. Each node in OLSR discovers and maintains topology information of network. It builds shortest path tree to achieve preferred paths to destinations. DSDV updates its Routing table by time to time transmitted throughout the network in order to maintain table consistency. Routers in STAR communicate to its neighbours their source routing trees either incrementally or in atomic updates. Source routing trees are specified by affirming the link parameters of each link which belonging to the paths used to reach every destination.
Related – Proactive vs Reactive Routing Protocols
Key points of Proactive Routing Protocol
- Low delay route setup process- all routes are immediately available.
- High bandwidth requirement- updates due to link loss leads to high control overheads.
- Low scalability- control overhead is proportional to the number of nodes.
- Slow reaction on restructuring and failures.
- High storage requirements- whole table must be in a memory.
- Respective amount of data for maintenance.
Applications of Wireless Ad Hoc Networks
- Tactical Networks – Military operations.
- Emergency Services – Disaster recovery, Patient records retrieval.
- Sensor Networks – Weather forecast and monitoring, Earth movement capturing, Ocean engineering, Collection of real time data.
- Cellular Networks and Bluetooth.
- Educational applications – Video conferencing, Virtual classrooms.
- Entertainment – Video and music on demand.



