Network Availability, Redundancy, Resilience, Diversity: What’s the difference?
As critical organization infrastructures are moving onto cloud and relying more on Internet networking services it is essential for networks to be resilient having ability to provide and maintain an acceptable level of service in the event of faults and challenges in normal operations. Resiliency enabling principles begin with enablers to fault tolerance, redundancy, availability and diversity of networks.
Today we look more in depth to understand network availability, redundancy, resilience and diversity enablers, how different they are from each other but still inter-related to each other.
Network Availability
Is network uptime which is a measure of how seamlessly clients could access resources such as servers, printers available on network. Network availability calculation is based on two key values:
- network uptime
- total duration of the given period
It is constantly monitored within organizations to maximize availability of their hosted services and applications. Determining overall availability and uptime requires tracking network devices for configuration errors, CPU over usage or other performance issues which could lead to network slowdown and failures. Network availability can be improved further by building redundancy of key components, diversification of them and self-recovery and self-healing resilient systems.
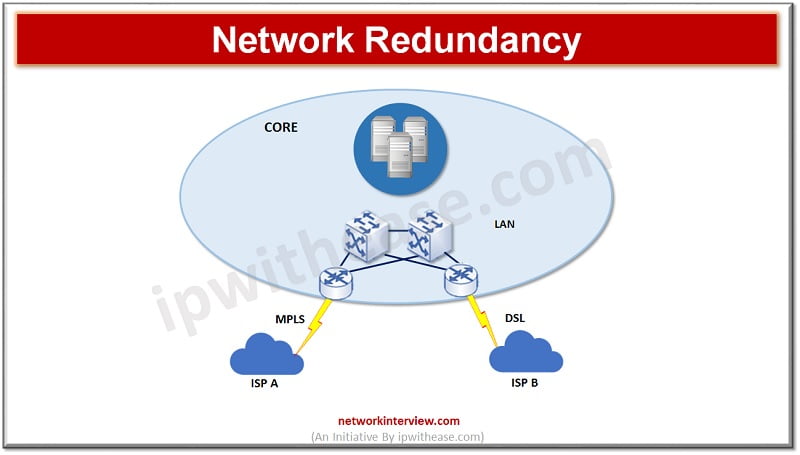
Network Redundancy
In network redundancy backup network resources are used to minimize or prevent downtime due to power outage, hardware issues, human errors, systems failure or cyber-attacks. Running critical core network services and building duplicate network infrastructure is required to achieve redundancy.
It ensures multiple pathways of data transmission are available to route traffic to alternate routes. If one path fails or becomes unavailable due to any said factors there is always an alternate path. But being redundant does not necessarily mean you are full proof from network outages. So we need to look at other enablers also to understand what role they play.
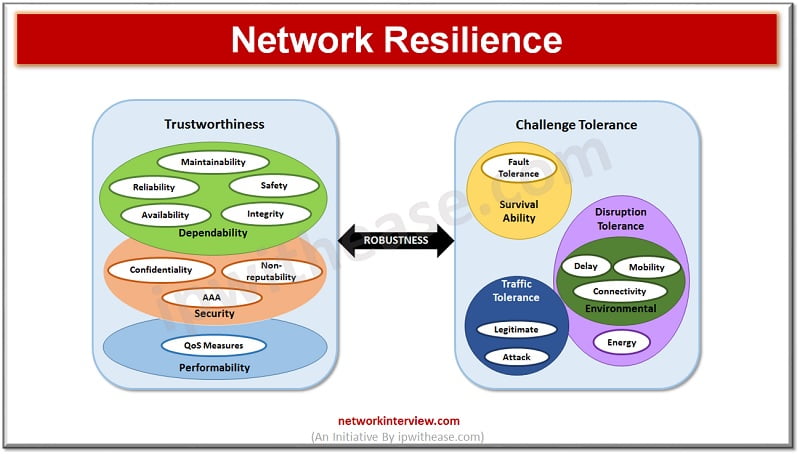
Network Resilience
Redundancy acts as a measure to enhance resilience which allows proactive or reactive response to changes which would impact systems. Requirements of resilience could be diverse and may be evolving, specifically in environments which are dynamic and scalable and any fault of one system would have a cascading effect on the entire chain of services.
Resilience is more prophetic in nature and involves forecasting of faults, isolating impacted components, providing protection against potential faults, removing faults and initiating recovery from fault state and restoring systems to optimal performance. Resilience is measured in terms of systems availability at any given instance, having frequency or delays in fault occurrences and speed of recovery from faulty state.
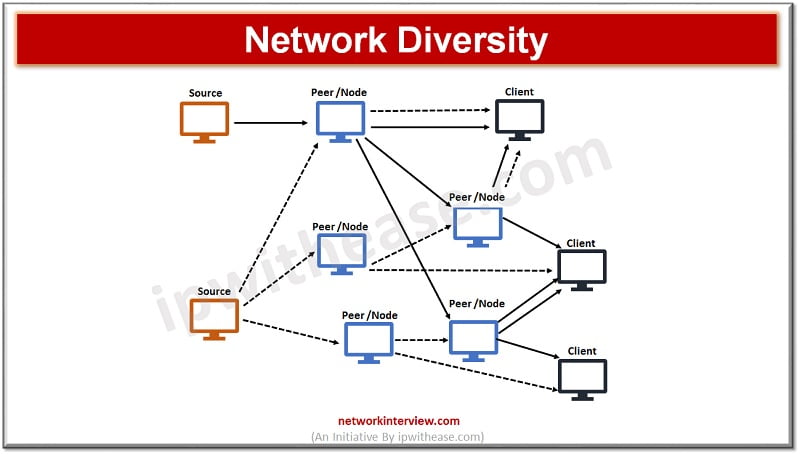
Network Diversity
A duplicate or alternate instance does not mean the organization network is fully protected so network diversity comes into picture here. It takes network redundancy to the next level while duplicating network infrastructure geographically on a diverse path in another data center or on cloud.
Geographically diverse networks protect against natural calamities such as weather events, construction and localized incidents at a single location. If a redundant site is in different city, or state or region then chances of incident impacting both locations at the same time is remote possibility, however to achieve near to absolute resiliency one can opt for cloud based disaster recovery solutions.
Conclusion
In a nutshell though network availability, redundancy, resilience and diversity seems differ from each other but these are crucial components of resilience disciplines as redundancy is for fault tolerance, diversity is for survivability, resiliency is self-healing and recovery from faults and end objective is to achieve network availability in a seamless manner.
Continue Reading:
Top 10 Trends Impacting Infrastructure & Operations
Colocation vs Carrier Neutral Data Center : Detailed Comparison
Tag:Infrastructure



