ISP Terms & Terminologies
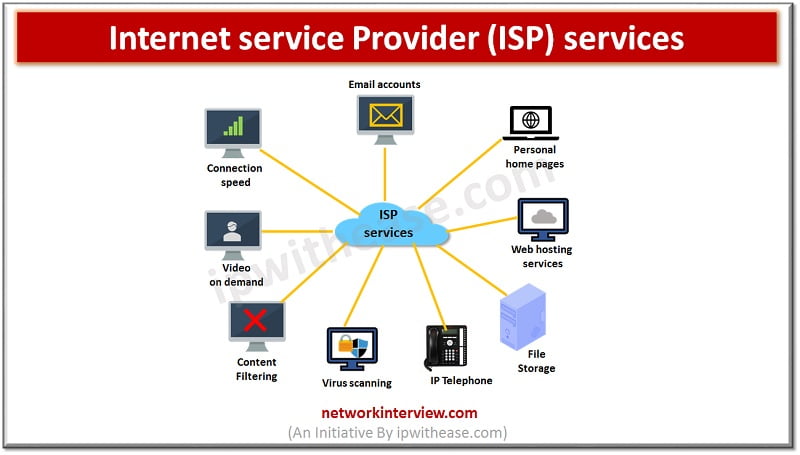
ISP stands for Internet service provider they offer a wide variety of Internet services related to browsing, Email services, faxing capability, audio and video communications and hosting services etc.
Let’s look more in detail about Internet service provider (ISP) and terminologies associated with it.
ISP Terms & Terminologies
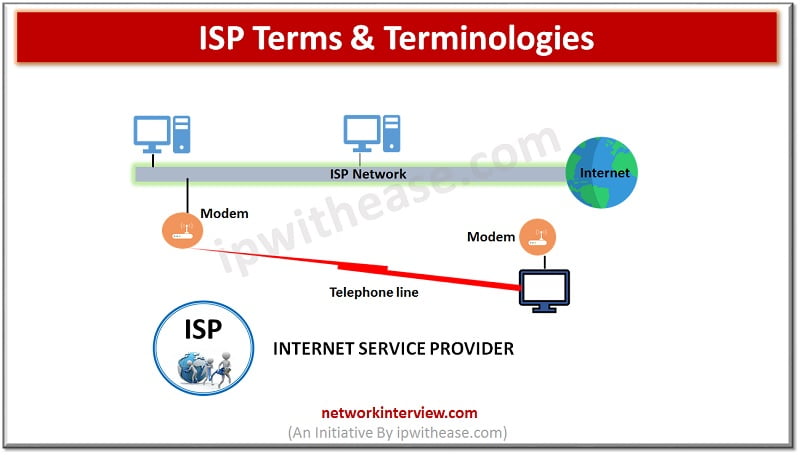
Internet service providers are companies which offer internet access for its customers and provide wide variety of services – streaming, Live TV, Browsing, Domain name registration, web hosting, Usenet services etc. An ISP can be provider of information, storage service provider, internet network service provider (INSP) or could be a mix of services provider.
Initially ISP’s provided internet access using dial up connections over regular phone line restricting speed limit to 56 Kbps. Later, in late 1990s ISPs started offering broadband internet services via DSL and cable modems. Now a days some ISPs offer high speed fibre connections which provide Internet access over Fibre optics. ISPs act as hub of internet and they are directly connected to Internet backbone.
There are various terminologies associated with ISPs we would look more in detail about them:
ADSL –
Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line is a high-speed internet connectivity also known as DSL. ADSL is asymmetric so download speeds are higher than upload speed. DSL allows high speed communication over normal twisted pair copper writing. It has distance limitation so the farther the equipment the speed is slower.
Cable modems –
High speed internet access can be achieved using cable modems. The speed ranges from 500 Kbps to 30 Mpbs.
Network backbone –
It is a component of computer network infrastructure which connects several different networks and connects different local area networks in offices, buildings etc. Several interconnected local area networks are called wide area networks (WAN) or a metropolitan area network (MAN) where services are restricted within the city.
DSL –
Stands for ‘Digital subscriber line’ it is an advanced version of dial up internet access methodology. It uses high frequency to execute a connection over the phone network facilitating both internet and phone connection to run simultaneously on same phone line. It offers Asymmetric Digital Subscriber (ADSL) line and Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) line.
Wireless Broadband (WiBB) –
Wireless broadband is designed to impart high speed internet and data services using wireless networks. Wireless broadband networks could be fixed or mobile.
Wi-Fi Internet –
In short form is also known as ‘wireless fidelity’. This wireless technology provides high speed wireless internet connection using radio waves.
ISDN –
It stands for ‘Integrated services digital network’. It integrates a high-quality digital transmission of voice and data over standard phone line. Voice and data both transfer over same line.
Ethernet –
Is a wired LAN (Local area network) and enables communication between devices using a protocol (set of rules or uniform network language) within a limited physical space.
FTP –
File transfer protocol used for transfer of files between client and server in a computing network.
Network service provider (NSP) –
It is a company which provides backbone services to Internet service provider (ISP).
Website –
It is a collection of related information, having multimedia content.
HTTP –
Hypertext transfer protocol is an application layer protocol for collaborative, distributed information.
Wireless application protocol (WAP) –
It is a standard for mobile wireless network to access information.
URL –
Uniform resource locator is a standard naming convention for referring to documents accessible over Internet and Inter company network.
Hosting ISPs –
These ISPs provide hosting services related to email, web hosting, or online storage services ,cloud services etc
Transit ISPs –
Like customers pay to ISP for usage of services similarly ISPs pay to their upstream ISPs for internet access. A single connection is established with upstream ISP and used for data transmission beyond the ISP’s home network.
Access Providers –
These ISPs provide basic services like internet access.
Mailbox access –
Hosting services for email services is provided by mailbox access providers and storage space for mailboxes such as gmail.com, outlook.com, AOL mail etc.
Virtual ISPs –
Purchase services from another ISP and known as wholesale ISP.
Free ISPs –
Provide services free of charge these are also known as freenets.
Wireless ISP –
It has a network based on wireless network. It may include technologies such as mesh networking, wi-fi or many proprietary equipment’s.
Continue Reading:
Tag:Security



