Introduction to Hyper-Threading
What is Hyper-Threading?
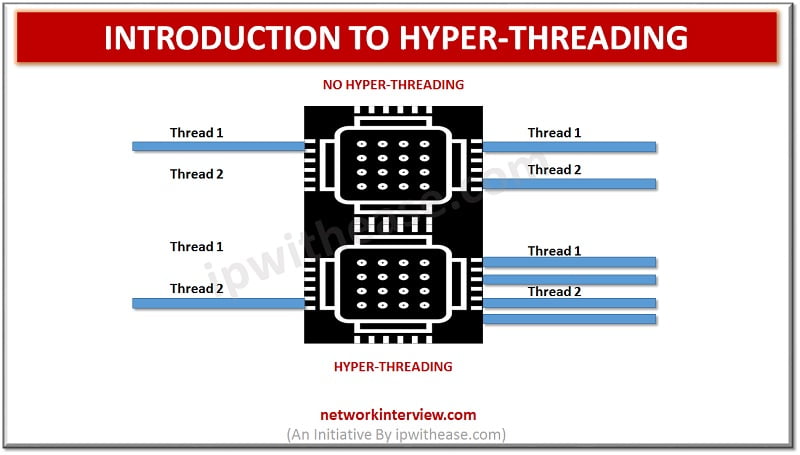
Hyper-Threading (HT) concept was introduced by Intel on desktop CPUs with the Pentium 4 HT. Pentium 4 is a single CPU core and cannot perform multi-tasking and in order to address this situation, Hyper threading allows the two logical CPU cores to share physical execution resources. HT enables multiple threads which are sequences of instruction to be run by each core to make the CPU run more efficiently. CPU can execute more task in the same amount of time –
- 1 to 4 Physical processors up to 4 Threads
- 1 to 4 Hyper-Thread enabled processors = 8 Logical Processors = 8 Threads
Uses of Hyper-threading
When the hyper-threading is enabled, each logical core of processor can act independently and can be interrupted, halted and operated separately from the other virtual processor sharing the same core. In this process, when one logical core is idle, the second core can take over the resources of other logical core. Hyper threading allows the processor to work on more instruction threads in a given time. Hyper threading is a hardware-based virtualization at the processor hardware level. Applications that take benefit of hyper-threading are heavy-duty audio/video transcoding apps and scientific applications built for maximum multi-threaded performance. By using hyper-threading performance can be boost up to 30%.
Related – What is Hyper Converged Infrastructure?
How Hyper-Threading works
HT Technology is applied where multiple tasks are scheduled so that there will be no idle time on your processor. Video editing, 3D rendering are examples of hyper-threading. Hyper Threading does not increase the cores of processors; it will only help to handle the task efficiently. Hyper Threading technology enables each core to run two threads at same time parallelly.
Hyper-Threading Performance
Hyper Threading increases the performance of CPU cores by enabling hyper-threading feature. Multiple threads are sequences of the instructions to be run by each core to make the CPU operate more efficiently. CPU can execute more tasks in the same amount of time. Hyper threading only helps to handle the instructions. With Hyper Threading, the OS will recognize each physical core as 2 virtual or logical cores. Eventually, Hyper threading virtually doubles the number of cores that are on the CPU. Dual-core processors acts like a virtual quad-core processor.
Hyper-Threading Technology Benefits
Hyper Threading Technology improves the utilization of CPU resources so that a second thread can be processed in the same processor. Hyper Threading provides two logical processors in a single processor package. Hyper Threading Technology offers:
- Improved overall system performance.
- Increased number of users.
- Improved throughput because tasks run on different threads.
- Improved reaction and response time.
- Increased number of instructions that can be executed at a same time.
- Compatibility with existing IA-32 software.
Disadvantages of using Hyper threading
HT is responsible for generating extra heat. Cores are made to perform additional calculations per cycle, which results in more leakage, consequently more heat, which negatively impacts overclocking.
Utilization of Processor Resources
Hyper Threading Technology improves performance of multi-threaded applications by increasing the utilization of the on-chip resources available in the micro architecture. The micro architecture provides optimal performance when executing a single instruction stream. A typical thread of code with a typical mix of Intel IA-32-based instructions, however, utilizes only about 35 percent of the micro architecture execution resources. HT Technology makes these underutilized resources available to a second thread of code, enhanced throughput and overall system performance. HT Technology provides a second logical processor in a single package for higher system performance. Systems containing multiple Hyper Threading Technology supported processors can expect further performance improvement.
Conclusion
Hyper Threading is a technology that allows processors to work more efficiently. This technology enables the processor to execute two series or threads of instructions at the same time thereby improving performance and system responsiveness.



