Free SSL vs Paid SSL Certificate: What is the Difference?
As cyberattacks are on rise and thousands of Internet users and organizations are targeted by attack vectors, safety and security of data is a major cause of concern. The secure socket layer (SSL) certificates are widely used by websites for data security. Installation of SSL certificate enables encryption and allows users to have a secure experience of visiting websites. It is like a seal of legitimacy.
Today we look more in detail about what is the difference between free SSL and paid SSL certificates, their key differences and which is more secure to use.
Free SSL Certificate
SSL certificates used to encrypt data transmission between server and web browser. Encryption ensures users visiting websites that their data is protected from cyber vectors. Many online e-commerce websites use SSL certificates as the nature of data stored or transmitted via such websites is highly sensitive in nature. Certificates could fall into two categories:
- Free
- Paid
Both provide data protection via encryption but free certificates have limited features as compared to their paid counterparts.
SSL certificates are of three types:
- Domain validation (DV),
- Organization validation (OV), and
- Extended validation (EV)
Free certificates fall in Domain validation (DV) type and are best suited for small, and personal websites such as blogs.
Paid SSL Certificate
Paid certificates entail cost. It is issued and signed by a trustworthy certificate authority (CA). They are either directly issued by a designated trustworthy certificate authority website or you can purchase them from third party entities called ‘Resellers.’ Such as CheapSSLWEB, Certera, etc.
Paid SSL certificates support domain validation (DV), Organization validation (OV), and Extended validation (EV) certificates. Organization validation (OV), and Extended validation (EV) certificates are especially meant for big corporations, banks, financial institutions, e-commerce giants e.g. Amazon, PayPal who often need higher level of protection.
Organization Validation (OV) and Extended Validation (EV) certificates provide capability to authenticate the owner of the website.
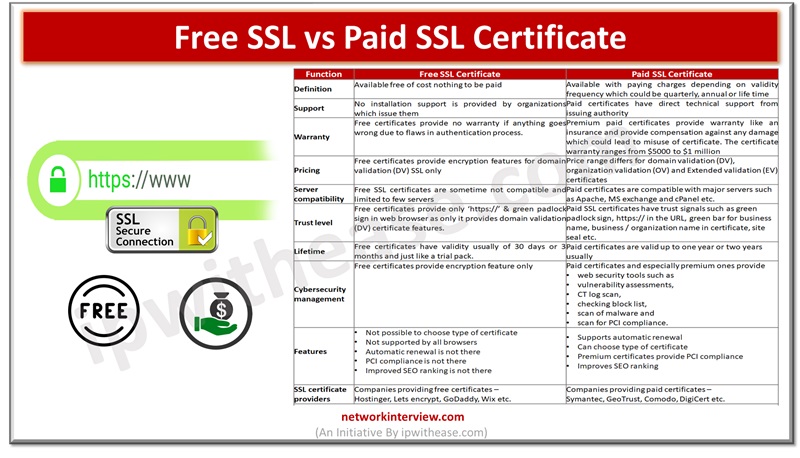
Comparison: Free vs Paid SSL Certificate
| Function | Free SSL Certificate | Paid SSL Certificate |
| Definition | Available free of cost nothing to be paid | Available with paying charges depending on validity frequency which could be quarterly, annual or life time |
| Support | No installation support is provided by organizations which issue them | Paid certificates have direct technical support from issuing authority |
| Warranty | Free certificates provide no warranty if anything goes wrong due to flaws in authentication process. | Premium paid certificates provide warranty like an insurance and provide compensation against any damage which could lead to misuse of certificate. The certificate warranty ranges from $5000 to $1 million |
| Pricing | Free certificates provide encryption features for domain validation (DV) SSL only | Price range differs for domain validation (DV), organization validation (OV) and Extended validation (EV) certificates |
| Server compatibility | Free SSL certificates are sometime not compatible and limited to few servers | Paid certificates are compatible with major servers such as Apache, MS exchange and cPanel etc. |
| Trust level | Free certificates provide only ‘https://’ & green padlock sign in web browser as only it provides domain validation (DV) certificate features. | Paid SSL certificates have trust signals such as green padlock sign, https:// in the URL, green bar for business name, business / organization name in certificate, site seal etc. |
| Lifetime | Free certificates have validity usually of 30 days or 3 months and just like a trial pack. | Paid certificates are valid up to one year or two years usually |
| Cybersecurity management | Free certificates provide encryption feature only | Paid certificates and especially premium ones provide – •web security tools such as •vulnerability assessments, •CT log scan, •checking block list, •scan of malware and •scan for PCI compliance. |
| Features | •Not possible to choose type of certificate •Not supported by all browsers •Automatic renewal is not there •PCI compliance is not there •Improved SEO ranking is not there | •Supports automatic renewal •Can choose type of certificate •Premium certificates provide PCI compliance •Improves SEO ranking |
| SSL certificate providers | Companies providing free certificates – Hostinger, Lets encrypt, GoDaddy, Wix etc. | Companies providing paid certificates – Symantec, GeoTrust, Comodo, DigiCert etc. |
Download: Free SSL vs Paid SSL Comparison Table
Continue Reading:
SSL Inspection in Checkpoint Firewall
SSL VPN Configuration in Palo Alto
Tag:Security



